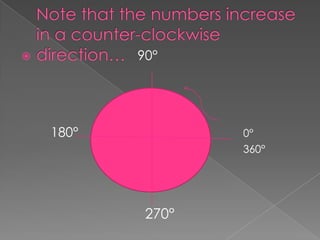
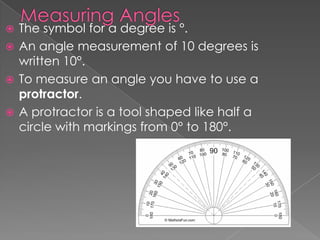
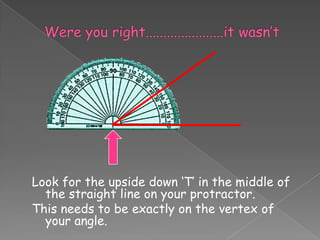
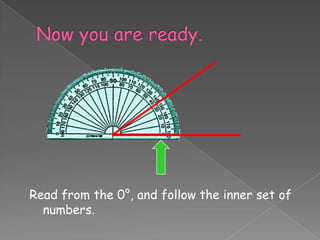
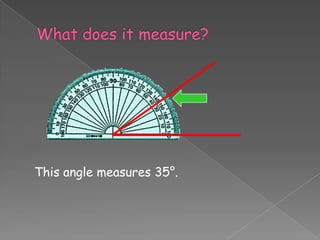
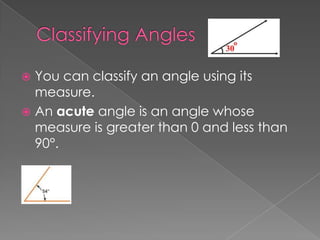
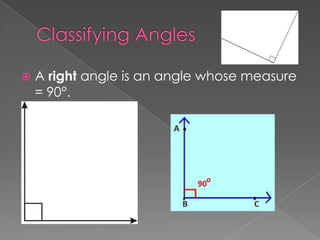
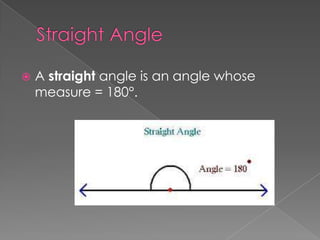
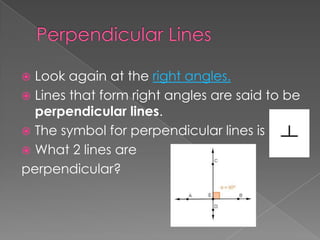
The document discusses angles and how to measure them using a protractor. It provides examples of angles in everyday life and notes that the ancient Babylonians were the first to divide a circle into 360 equal parts called degrees. It explains how to properly use a protractor to measure angles, including making sure the protractor is lined up with the vertex of the angle and reading the measurement. The document also classifies different types of angles such as acute, right, obtuse, and straight angles.