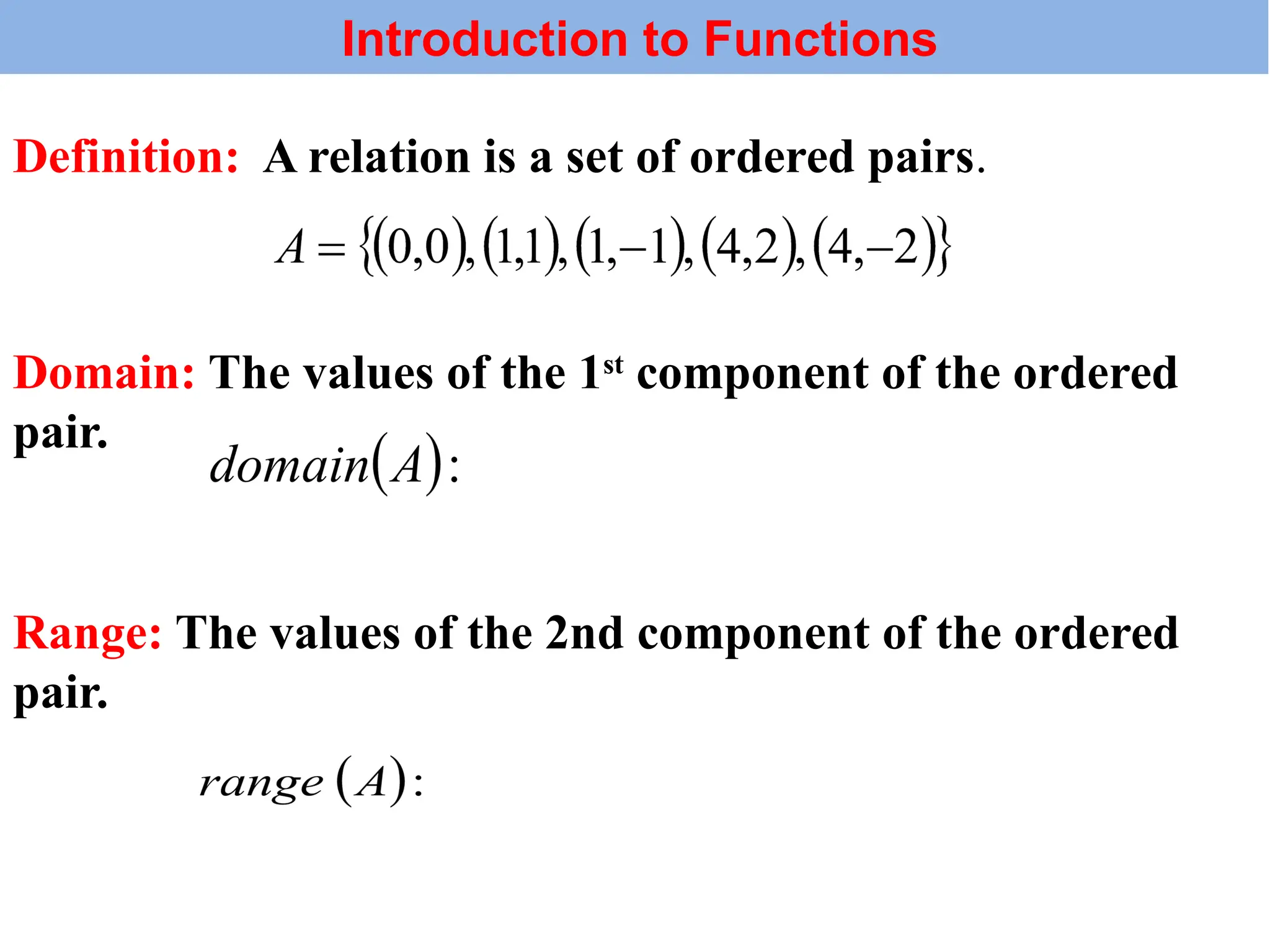
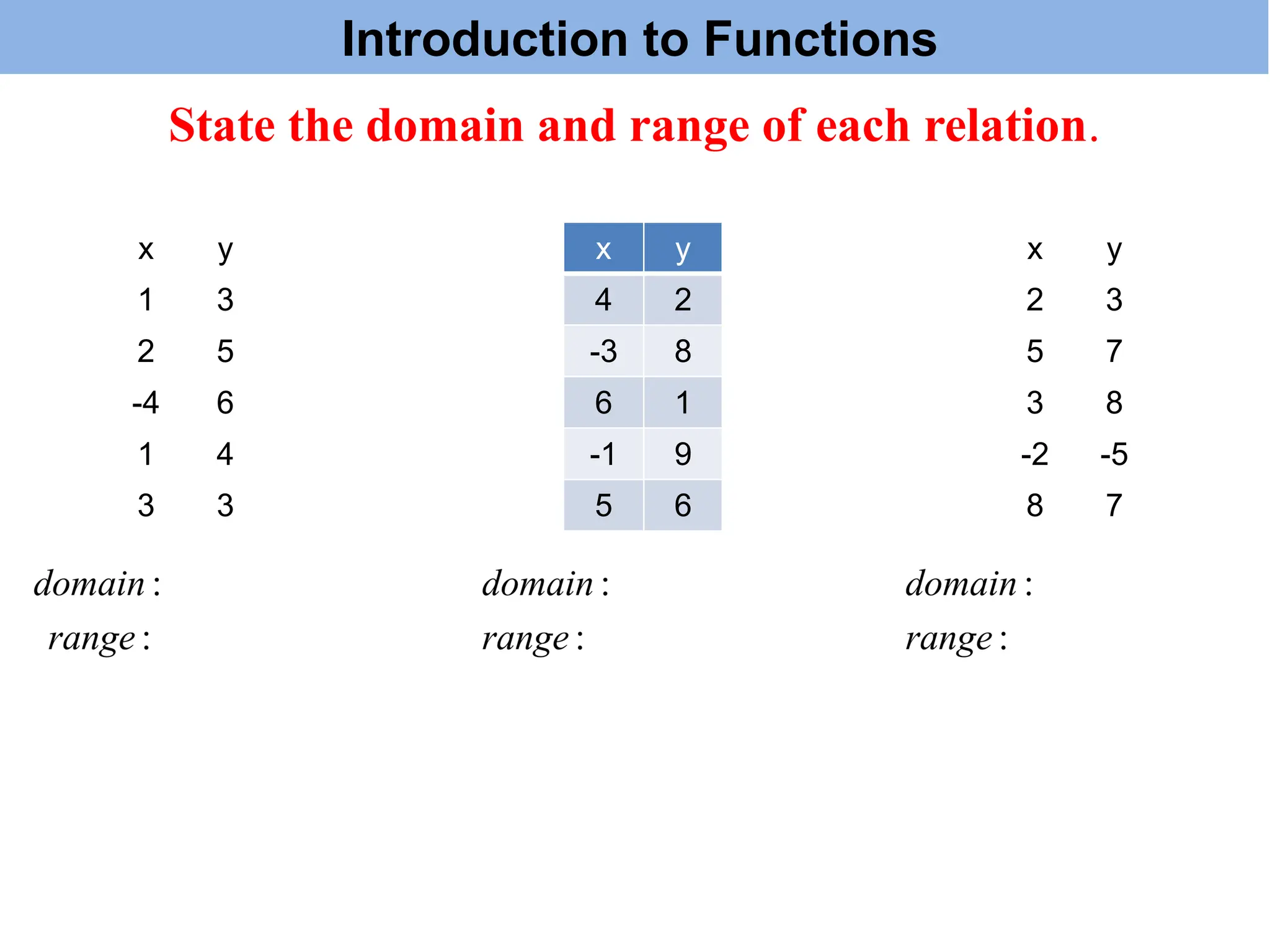
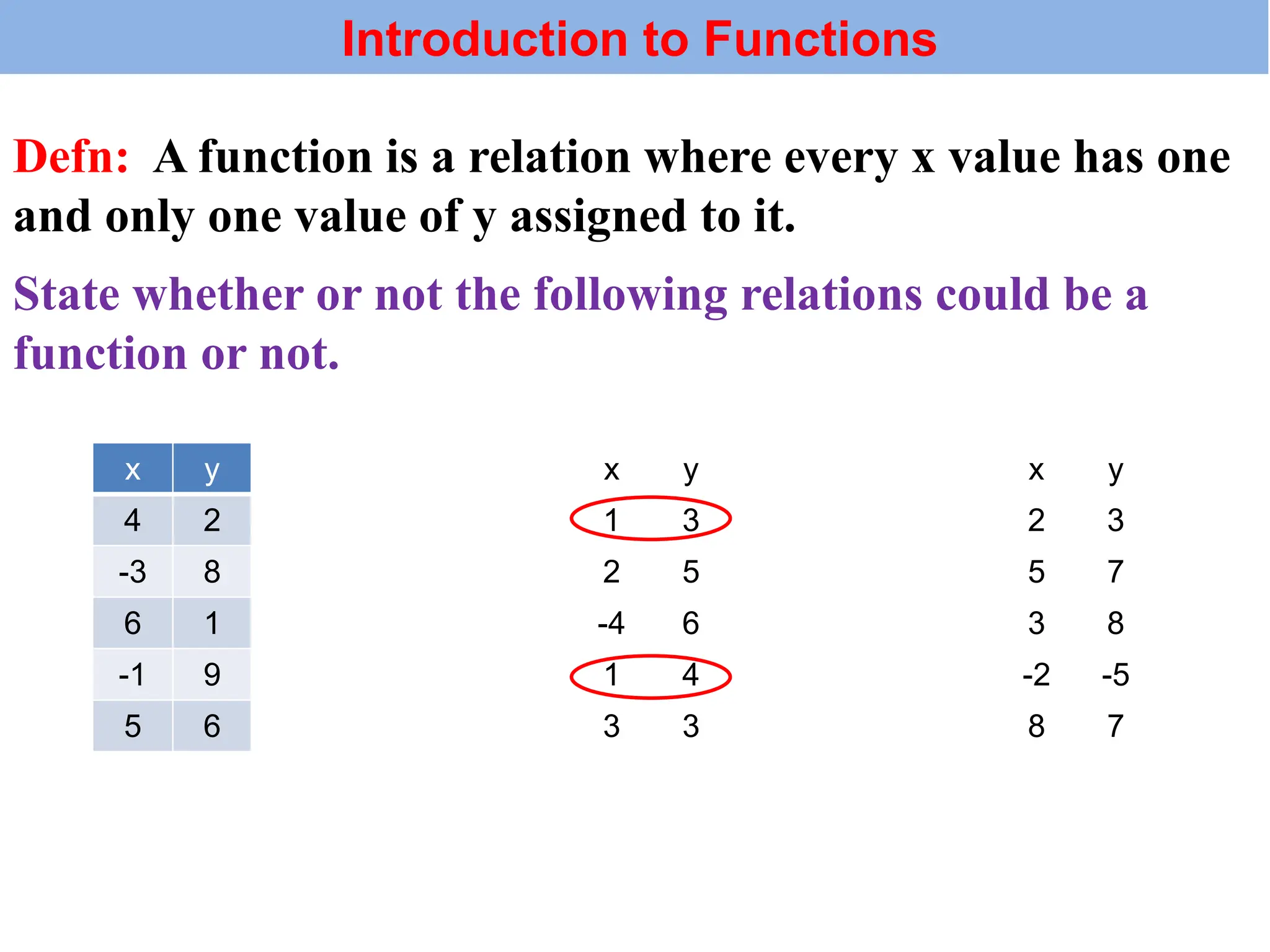
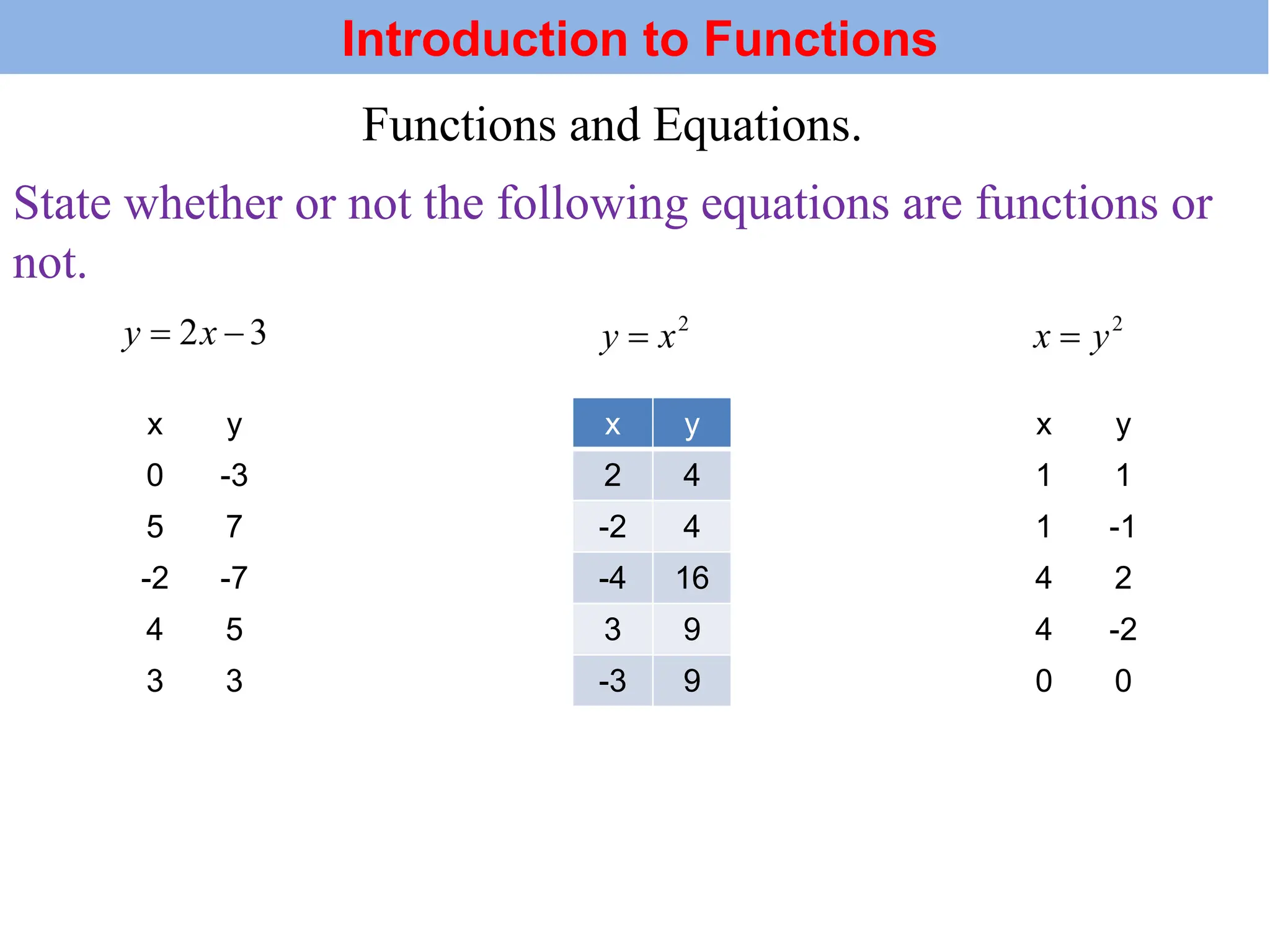
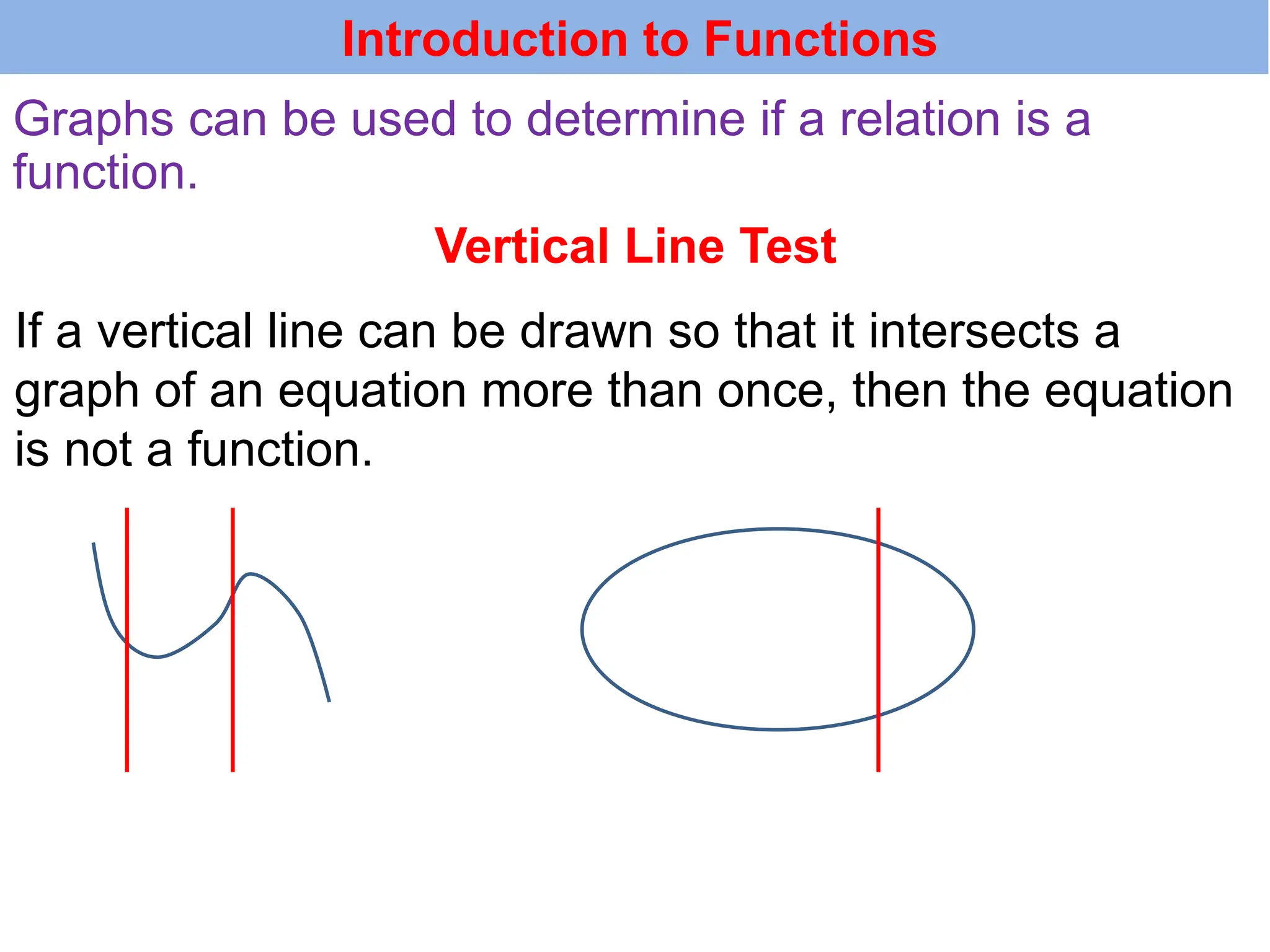
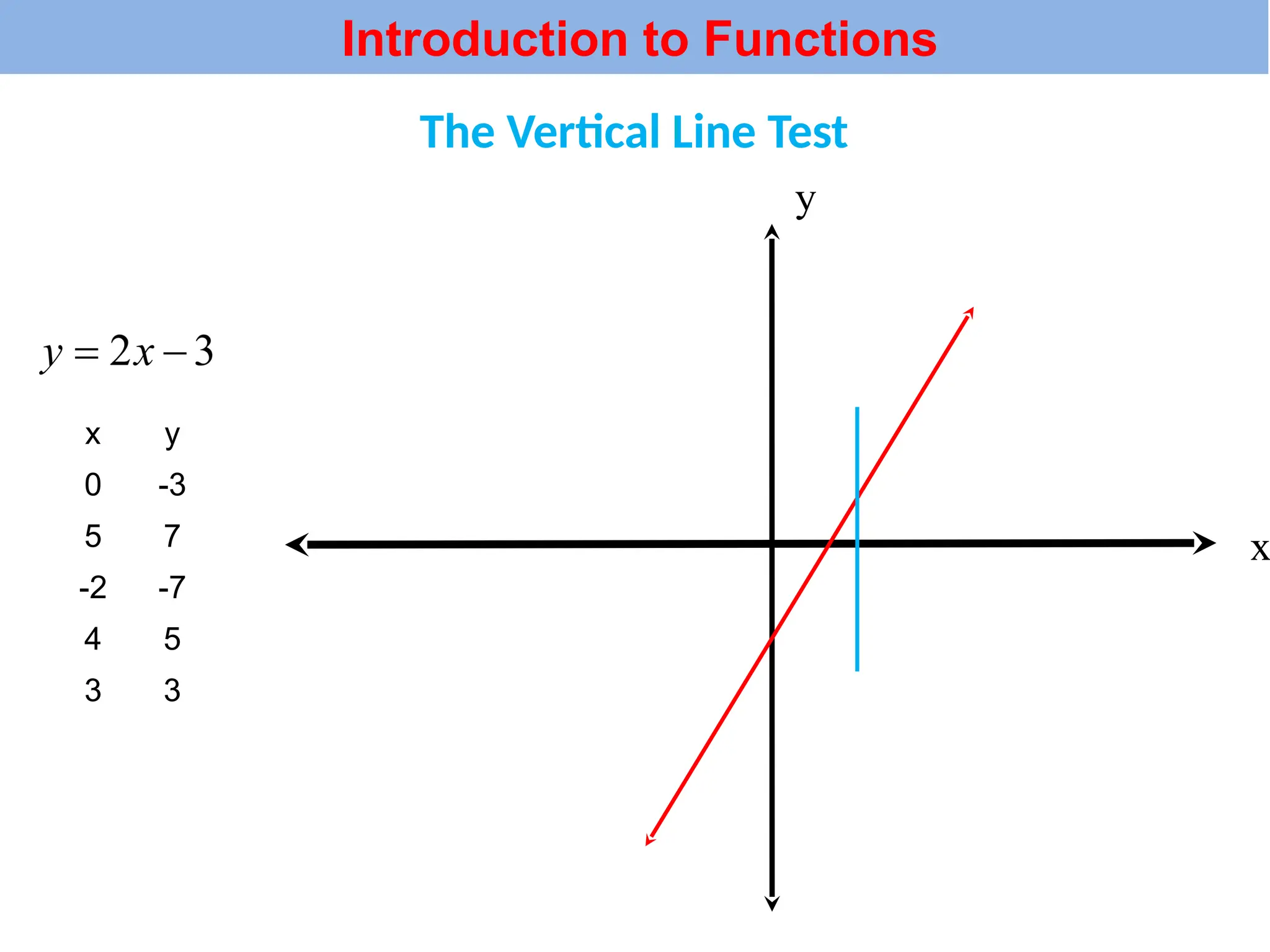
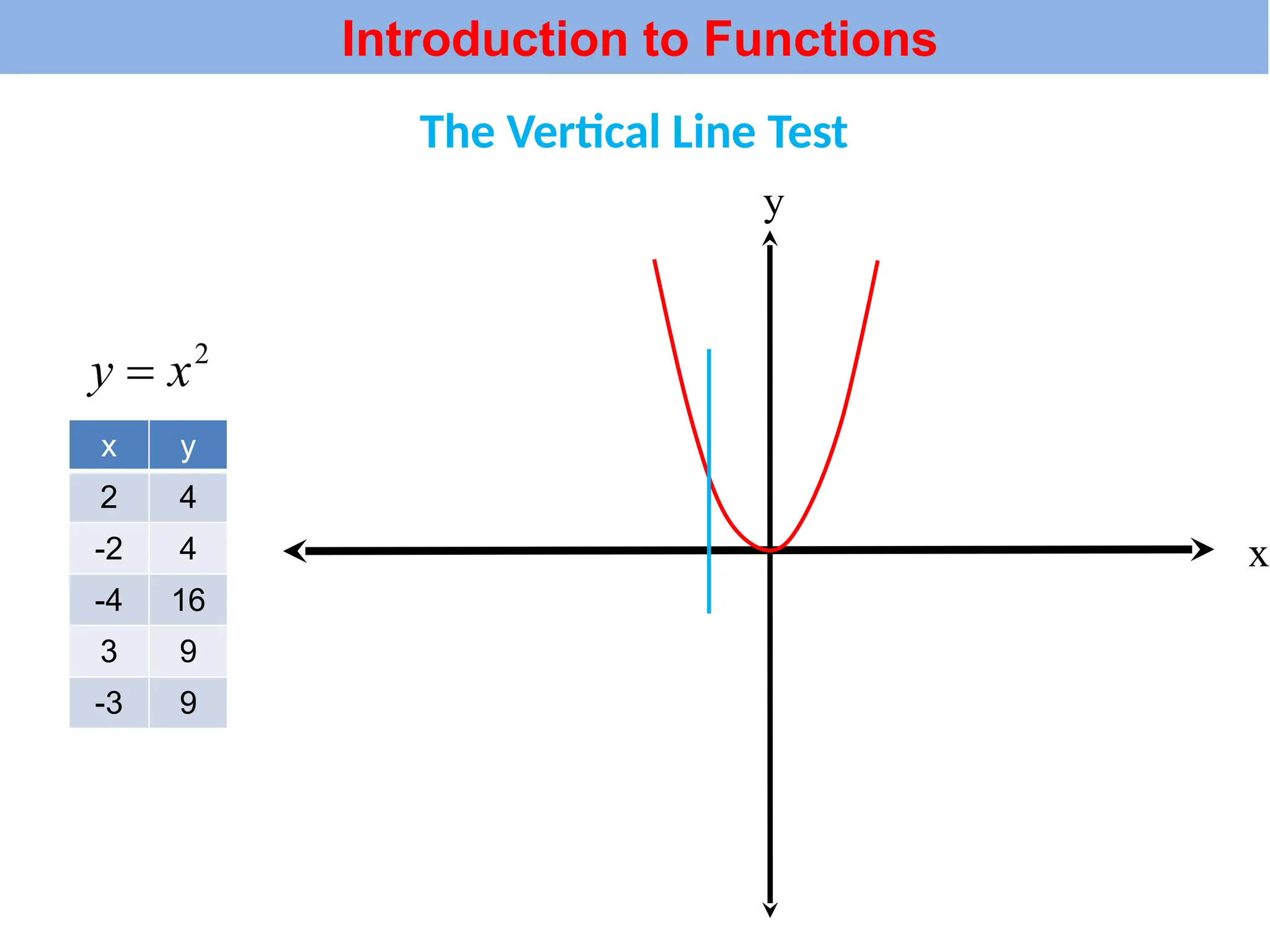
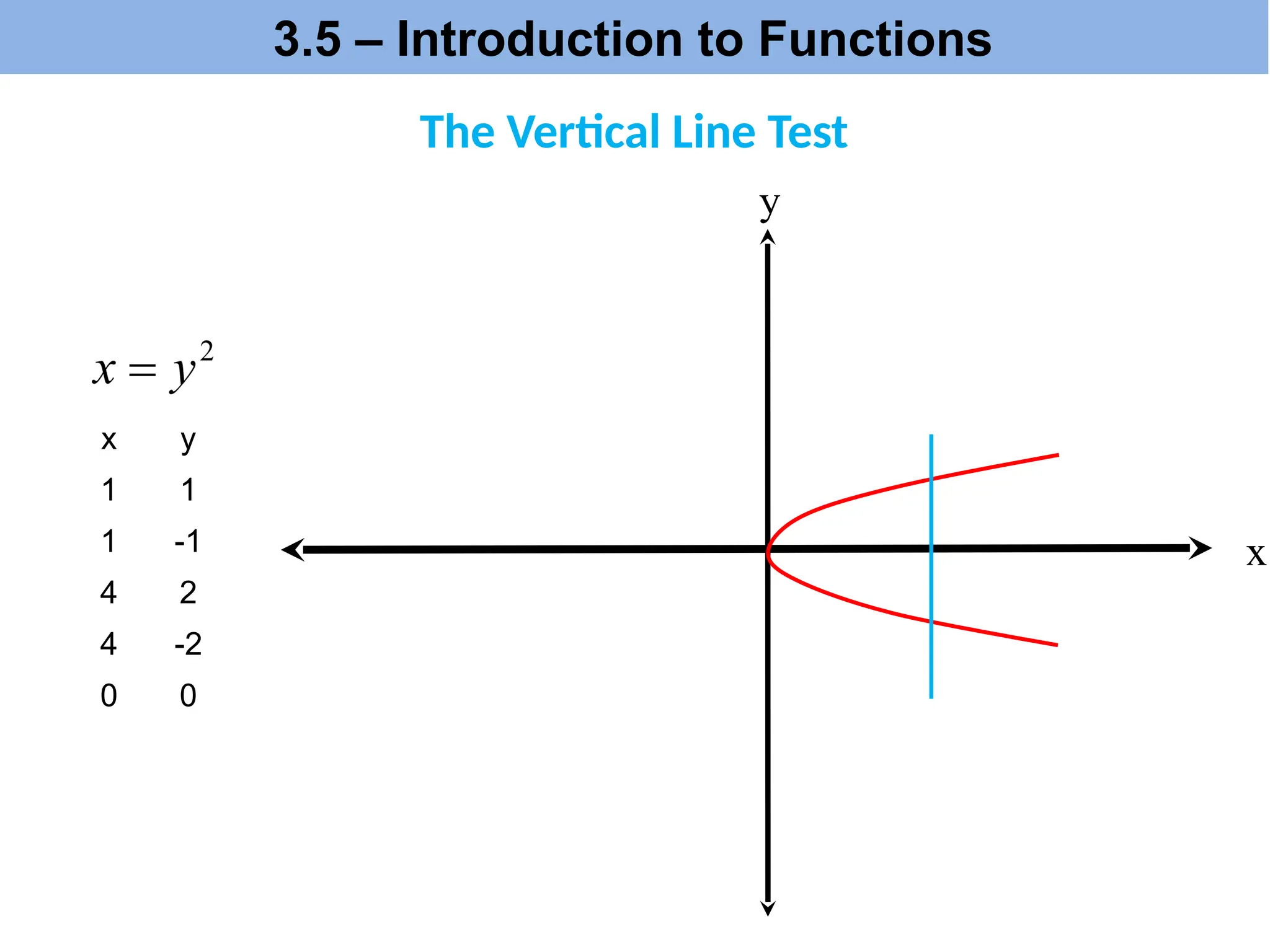
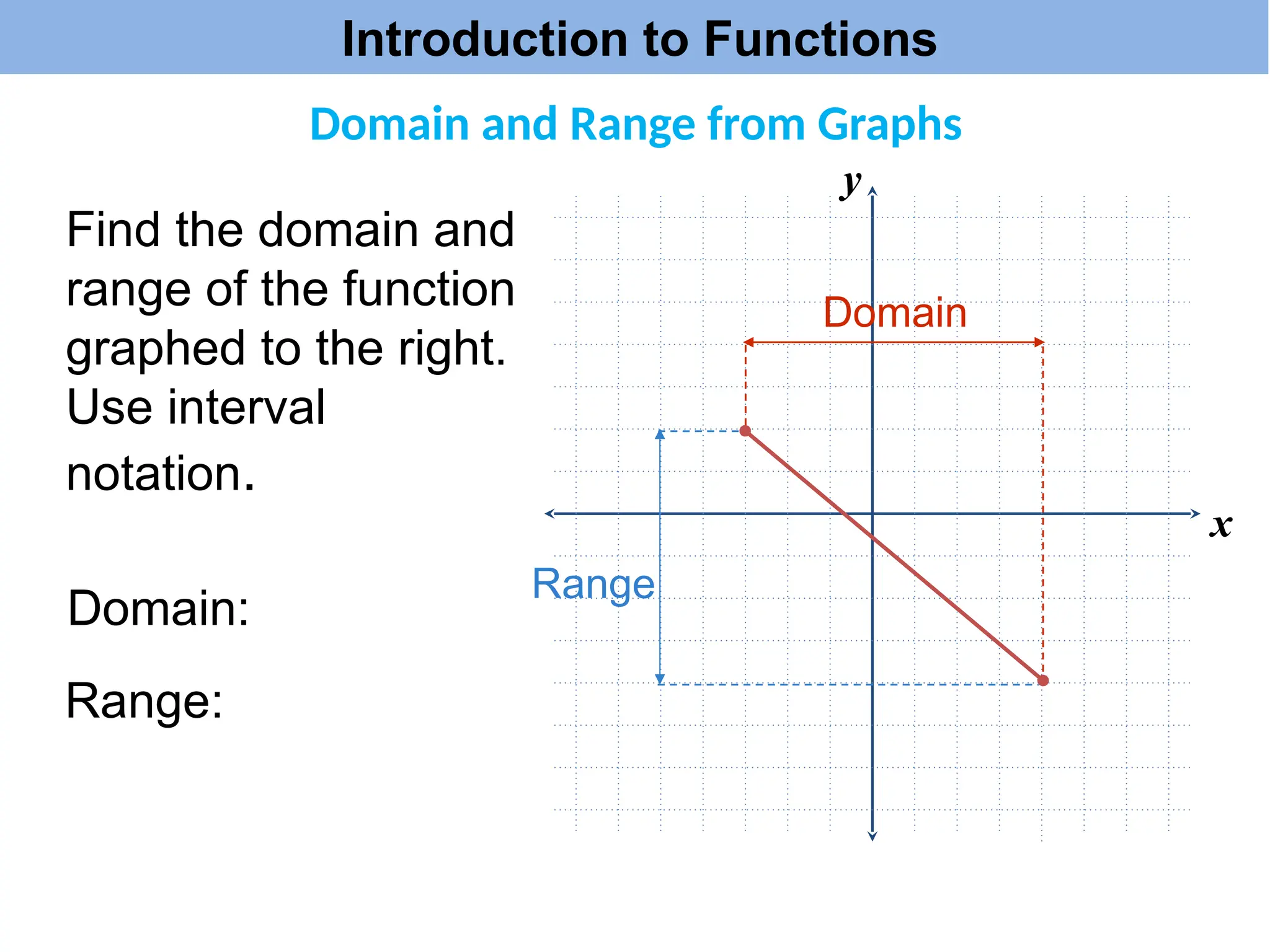
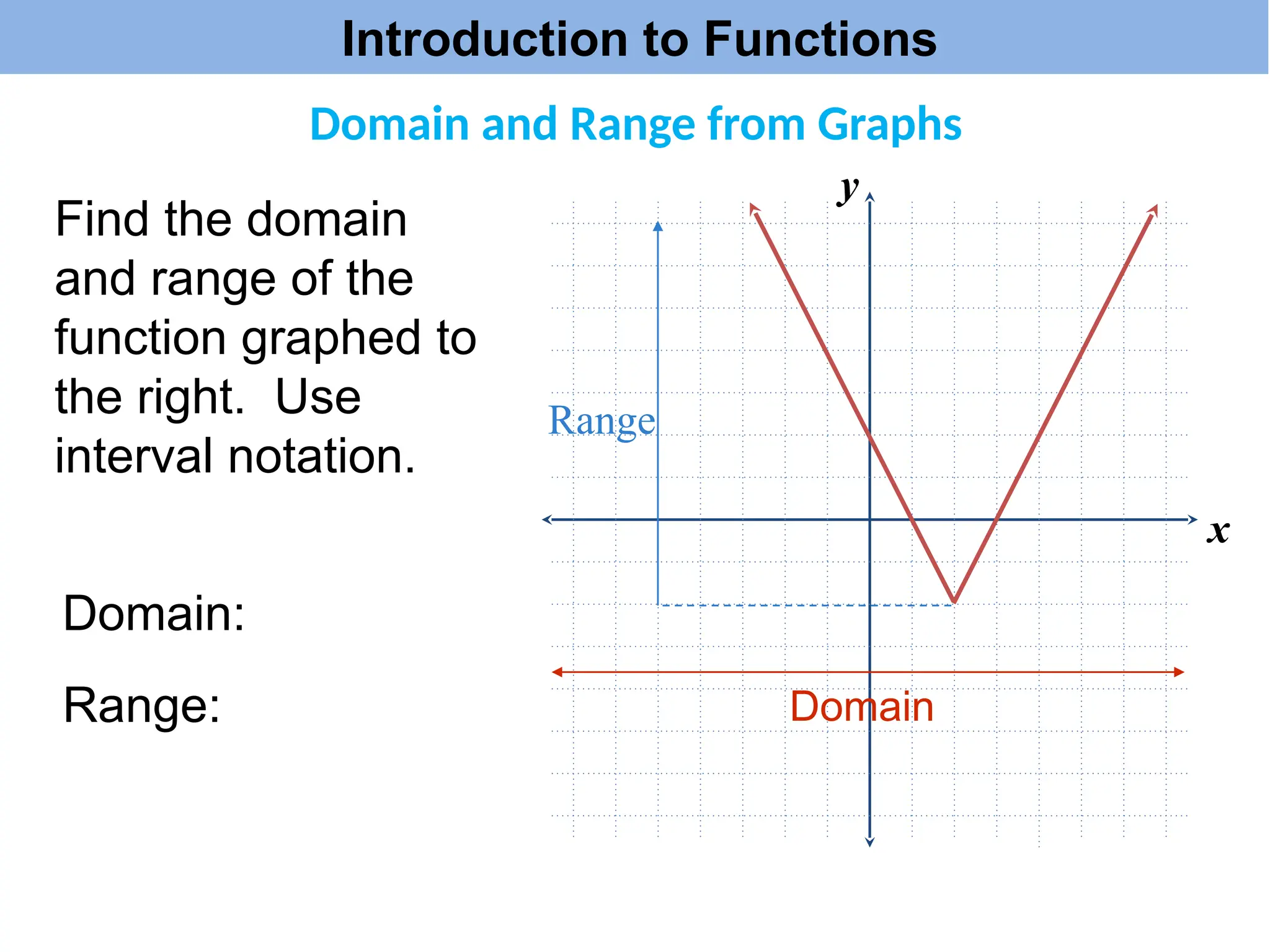
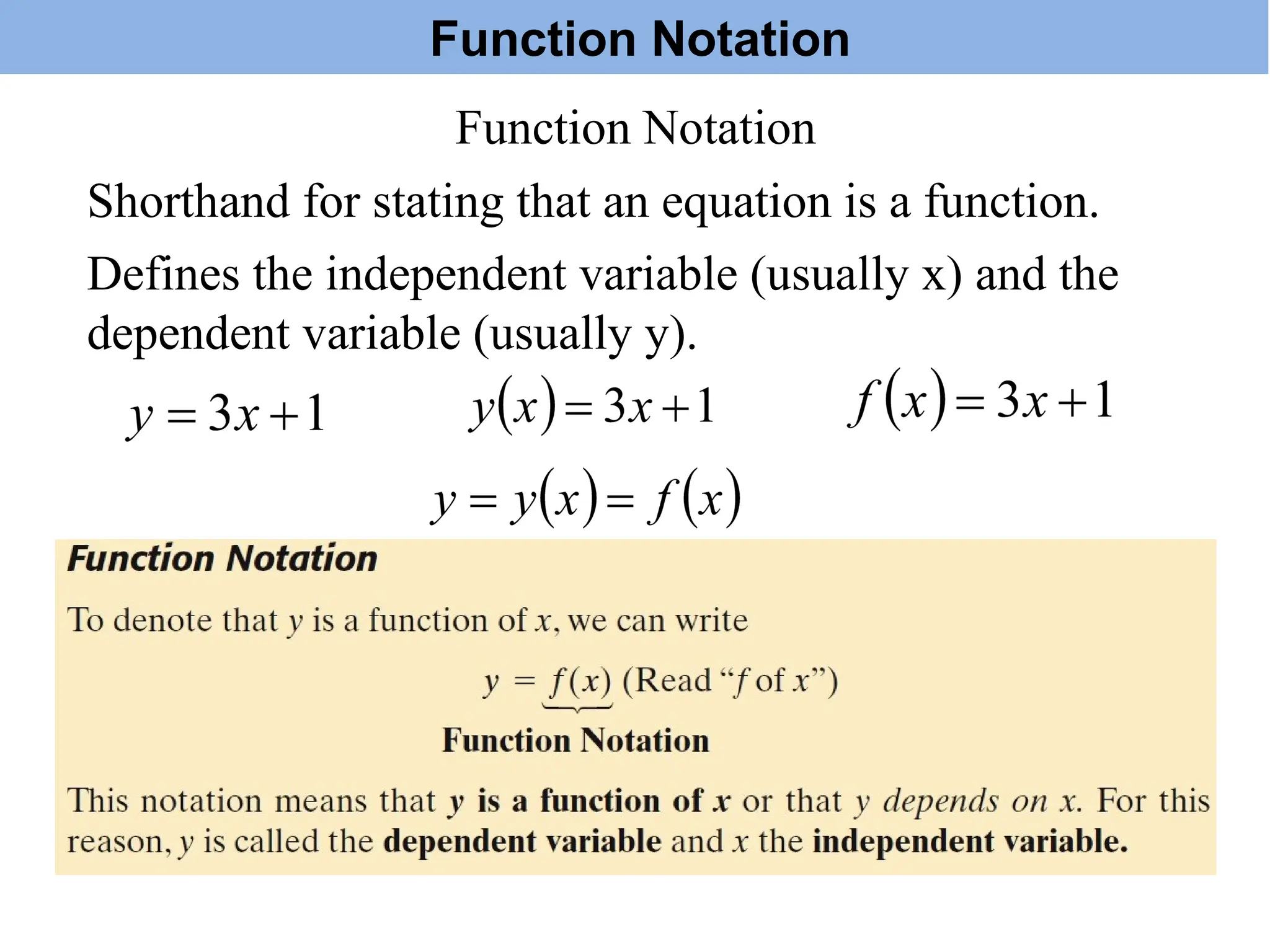
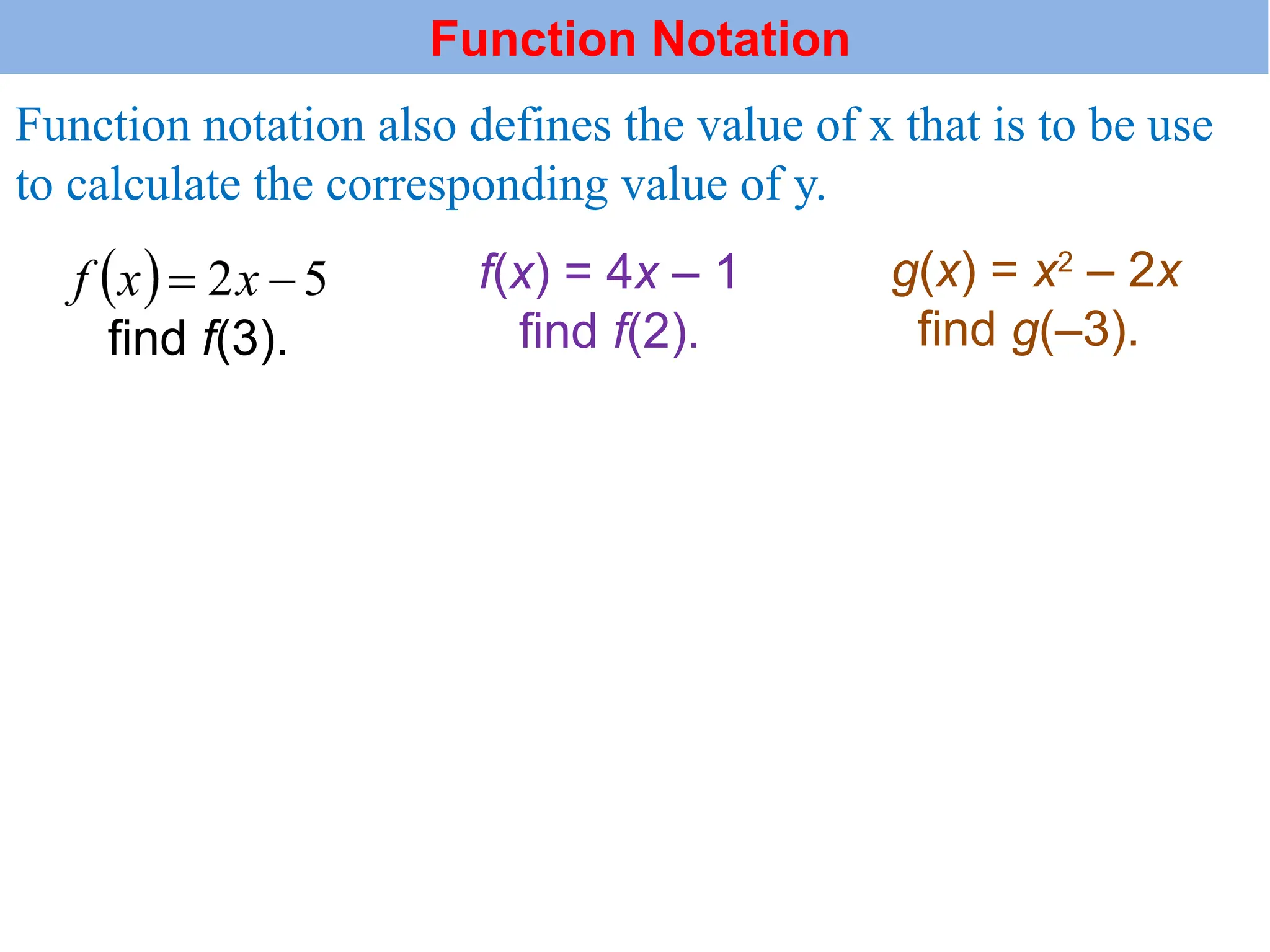
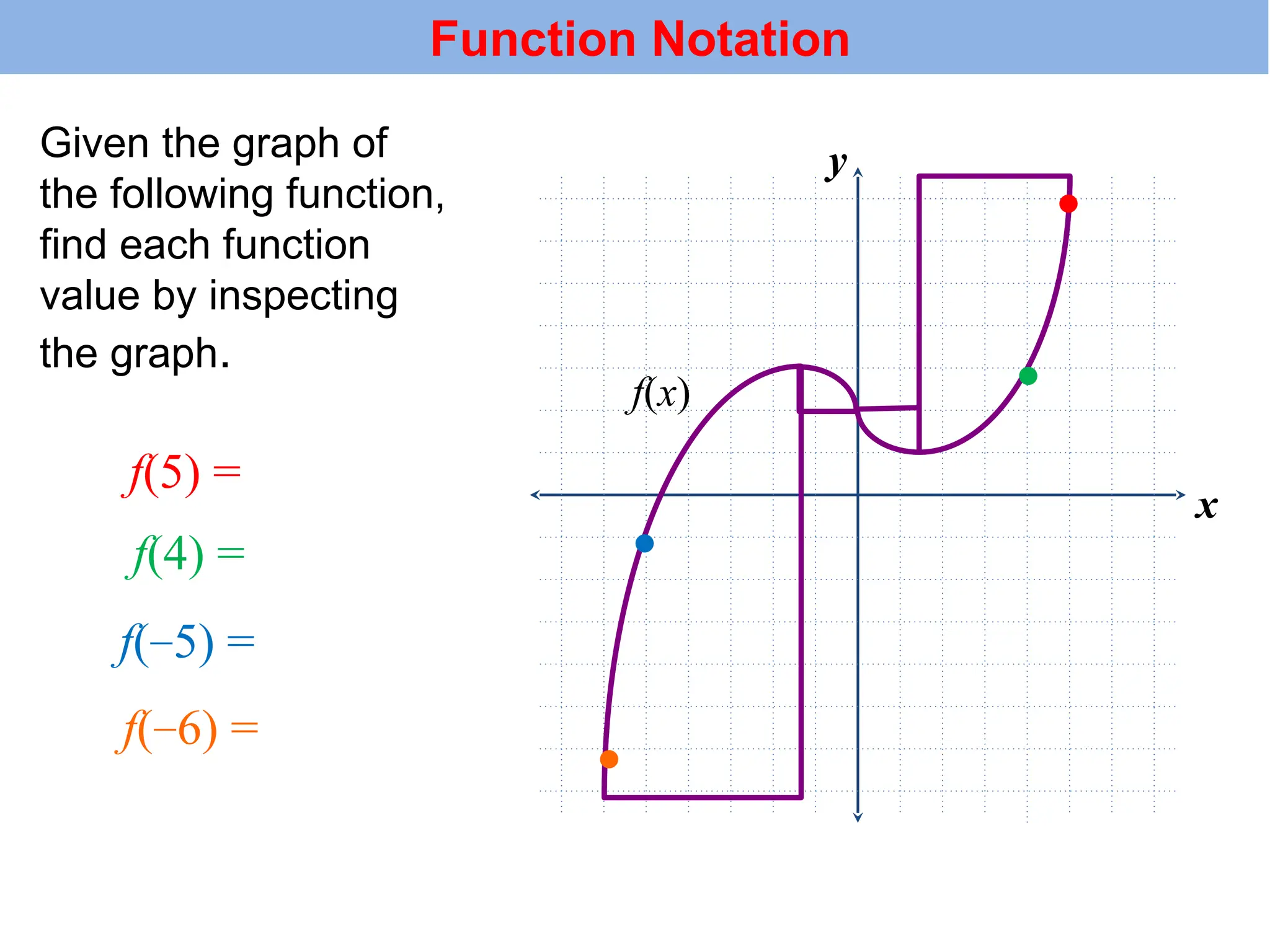
The document introduces the concepts of relations and functions, defining relations as sets of ordered pairs with specified domains and ranges. It discusses the vertical line test for identifying functions and provides examples for practice. Function notation is also explained, emphasizing its use in calculating function values based on independent variables.