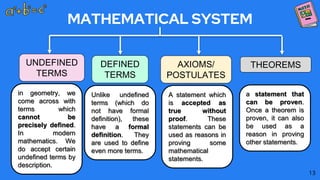
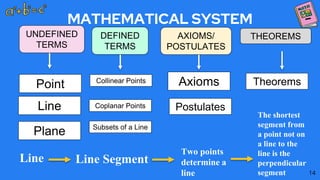
The document discusses the key components of a mathematical system:
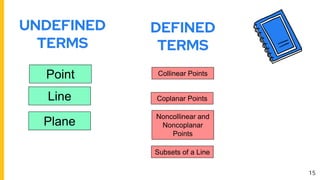
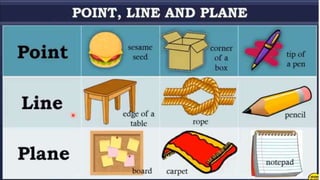
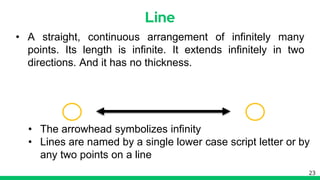
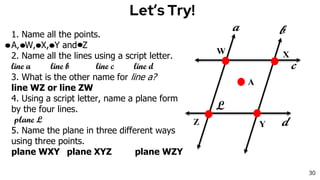
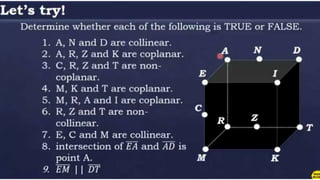
1. Undefined terms are concepts that cannot be precisely defined, such as points, lines, and planes in geometry.
2. Defined terms have a formal definition using undefined terms or other defined terms, such as line segments, rays, and collinear/coplanar points.
3. Axioms or postulates are statements assumed to be true without proof, which can be used to prove theorems.
4. Theorems are statements that have been formally proven using axioms, postulates and previously proven theorems. The four components are related such that defined terms are defined using undefined terms, axioms are