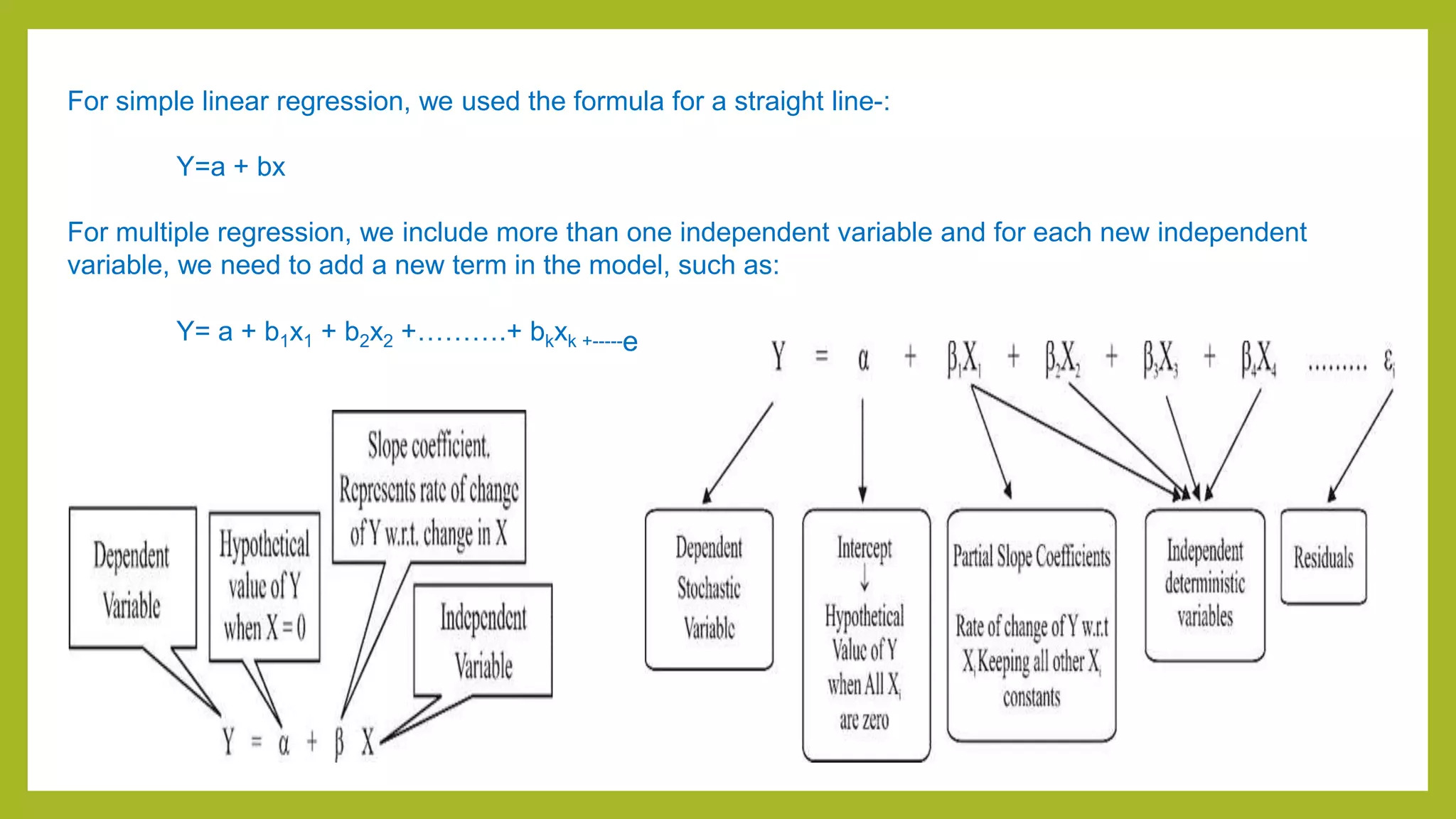
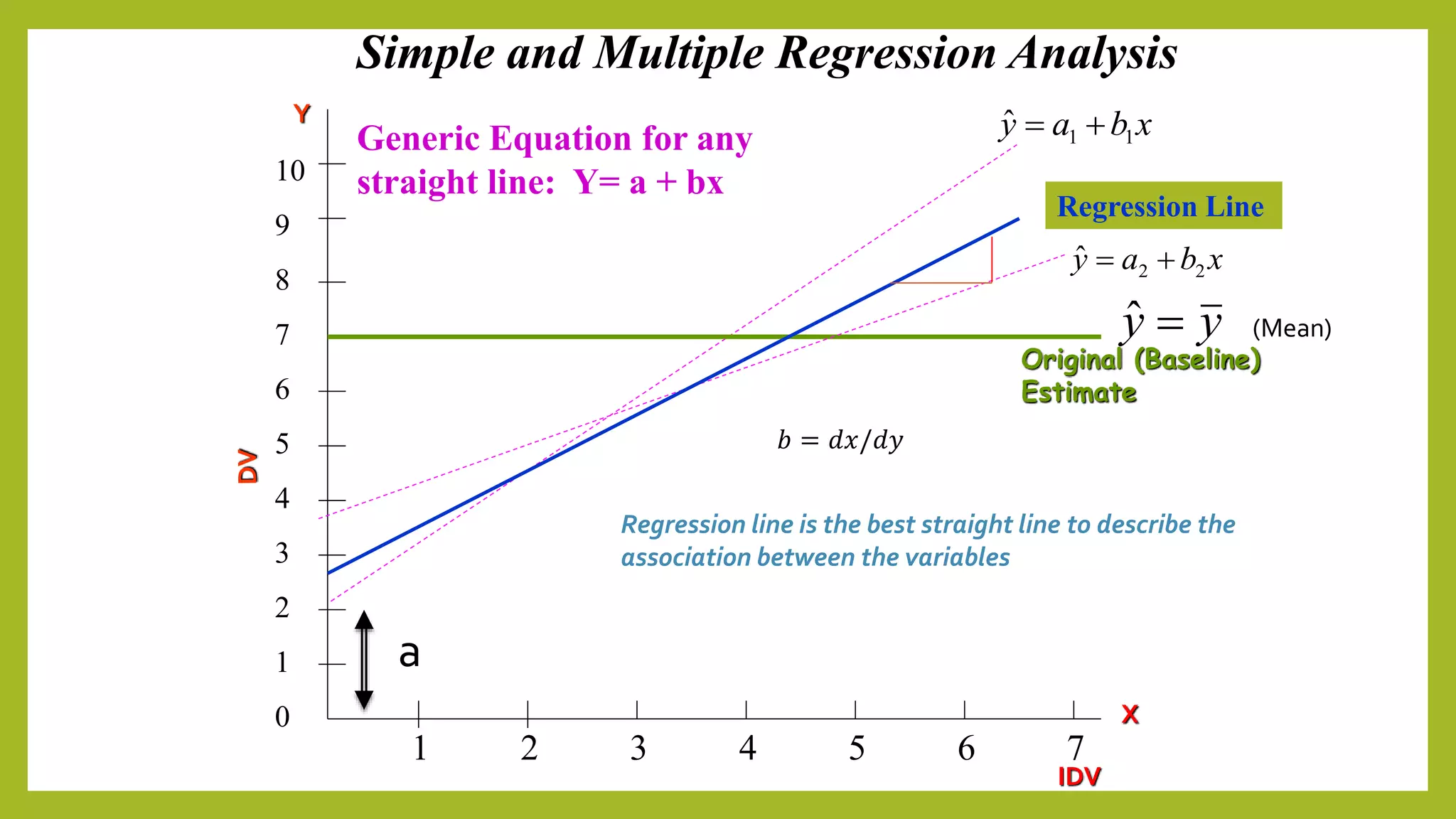
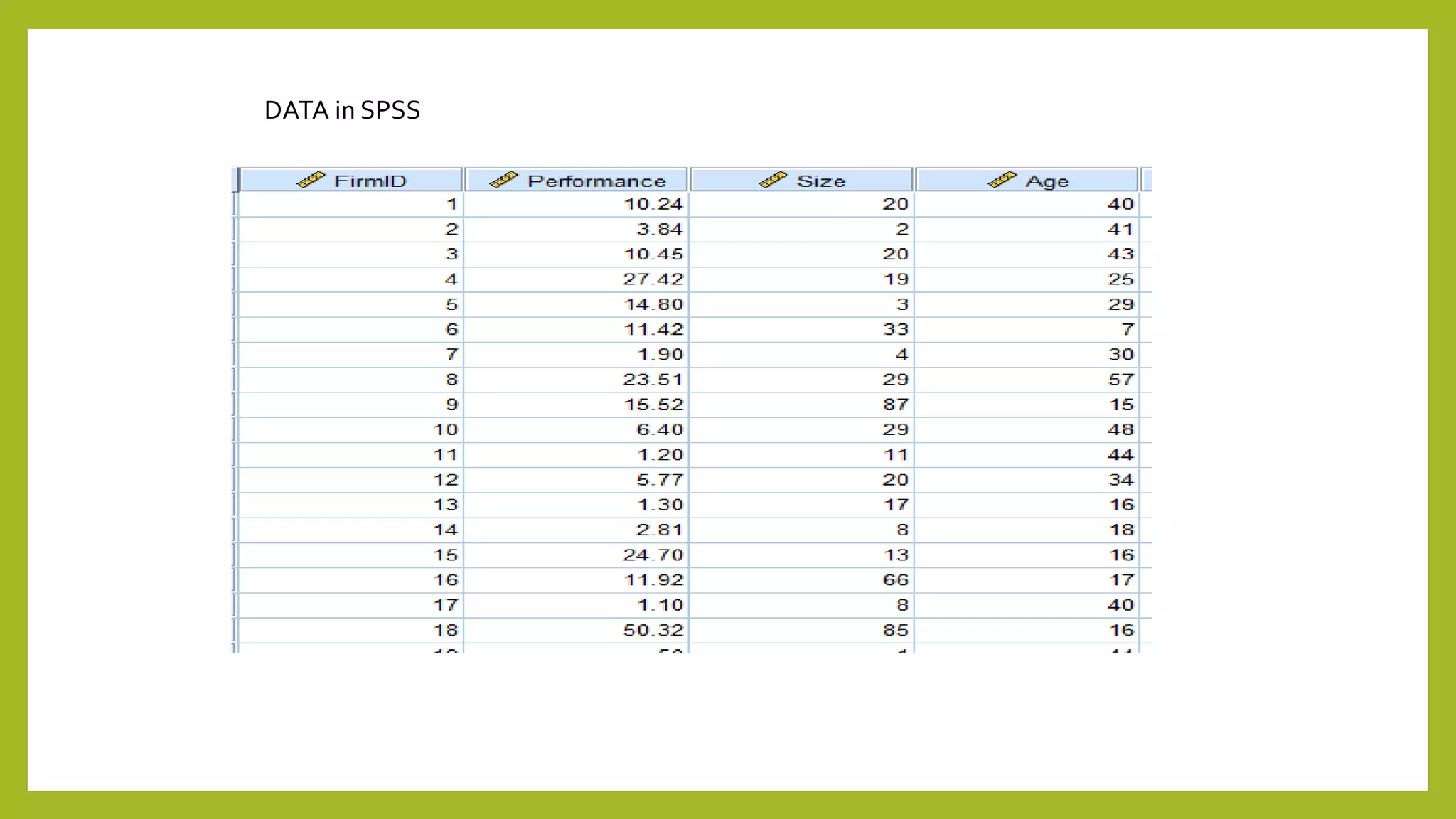
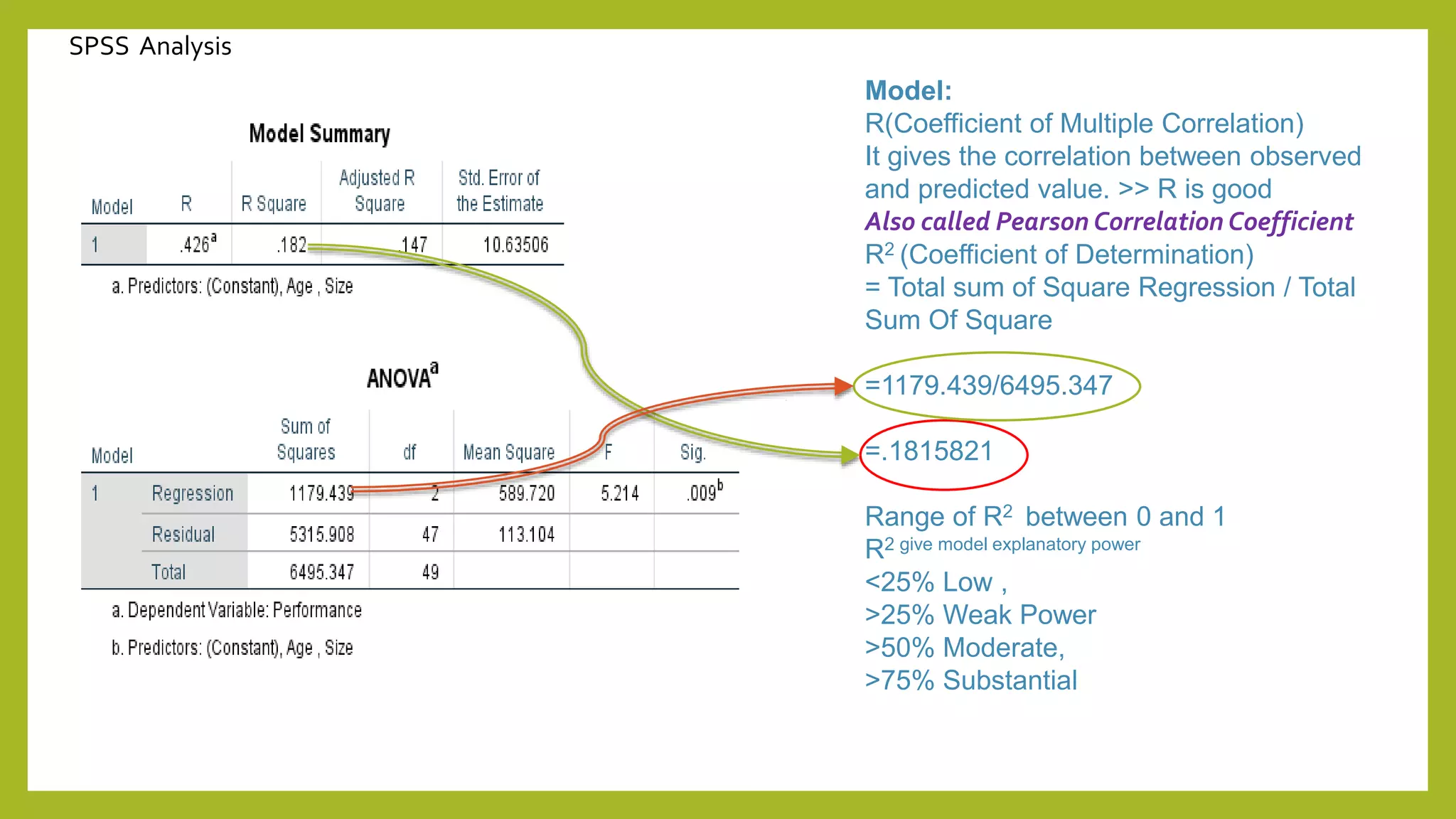
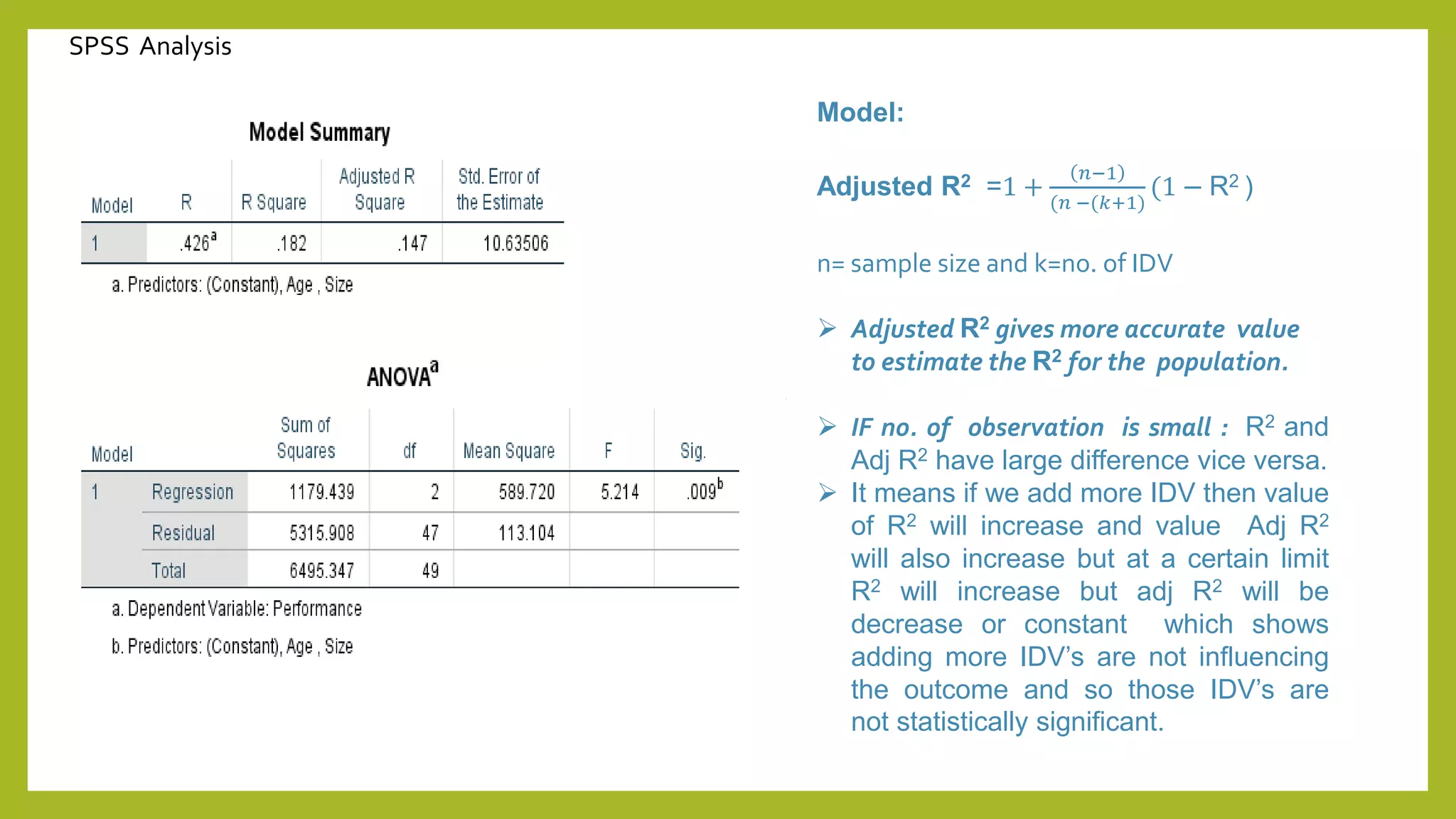
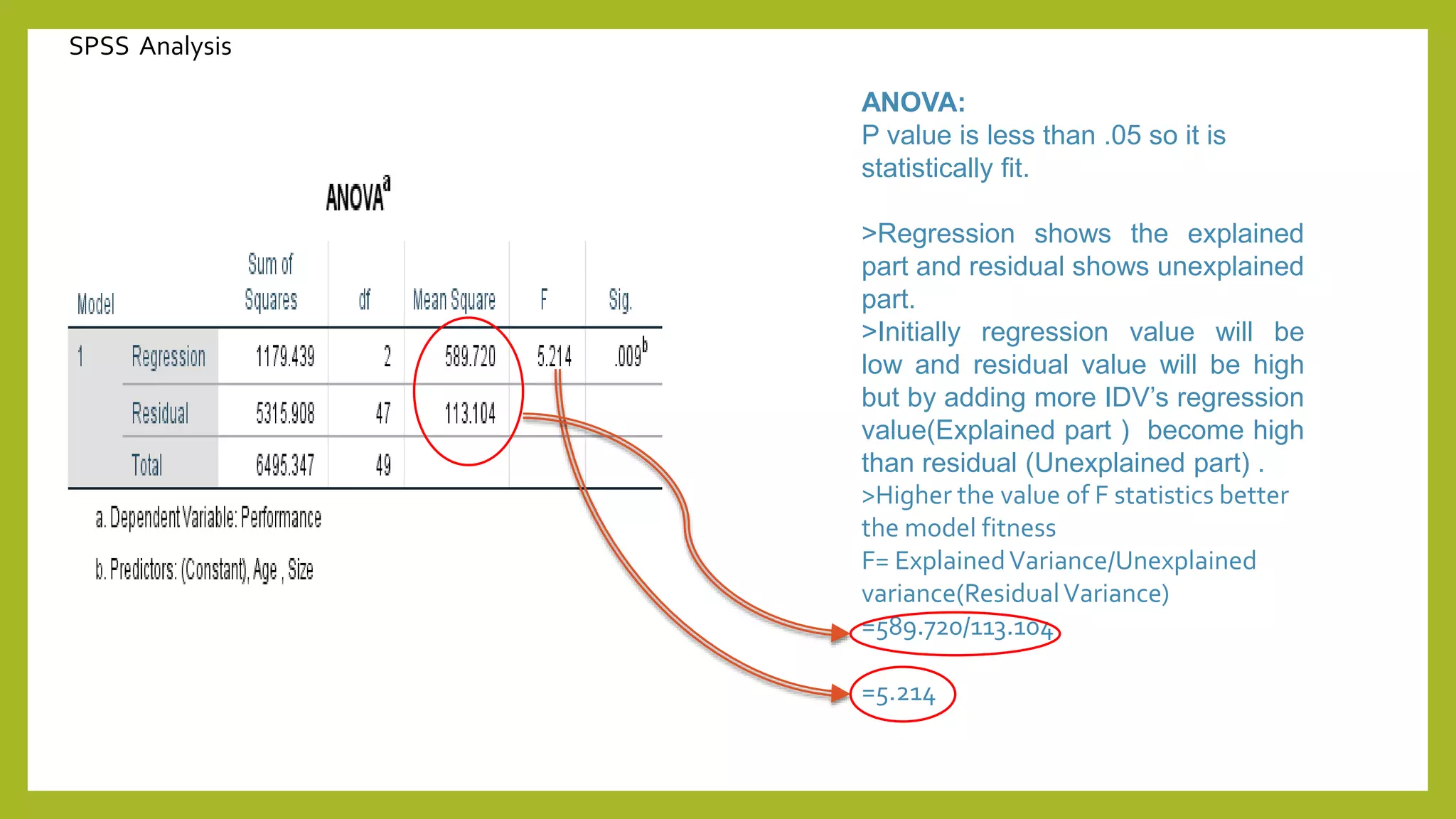
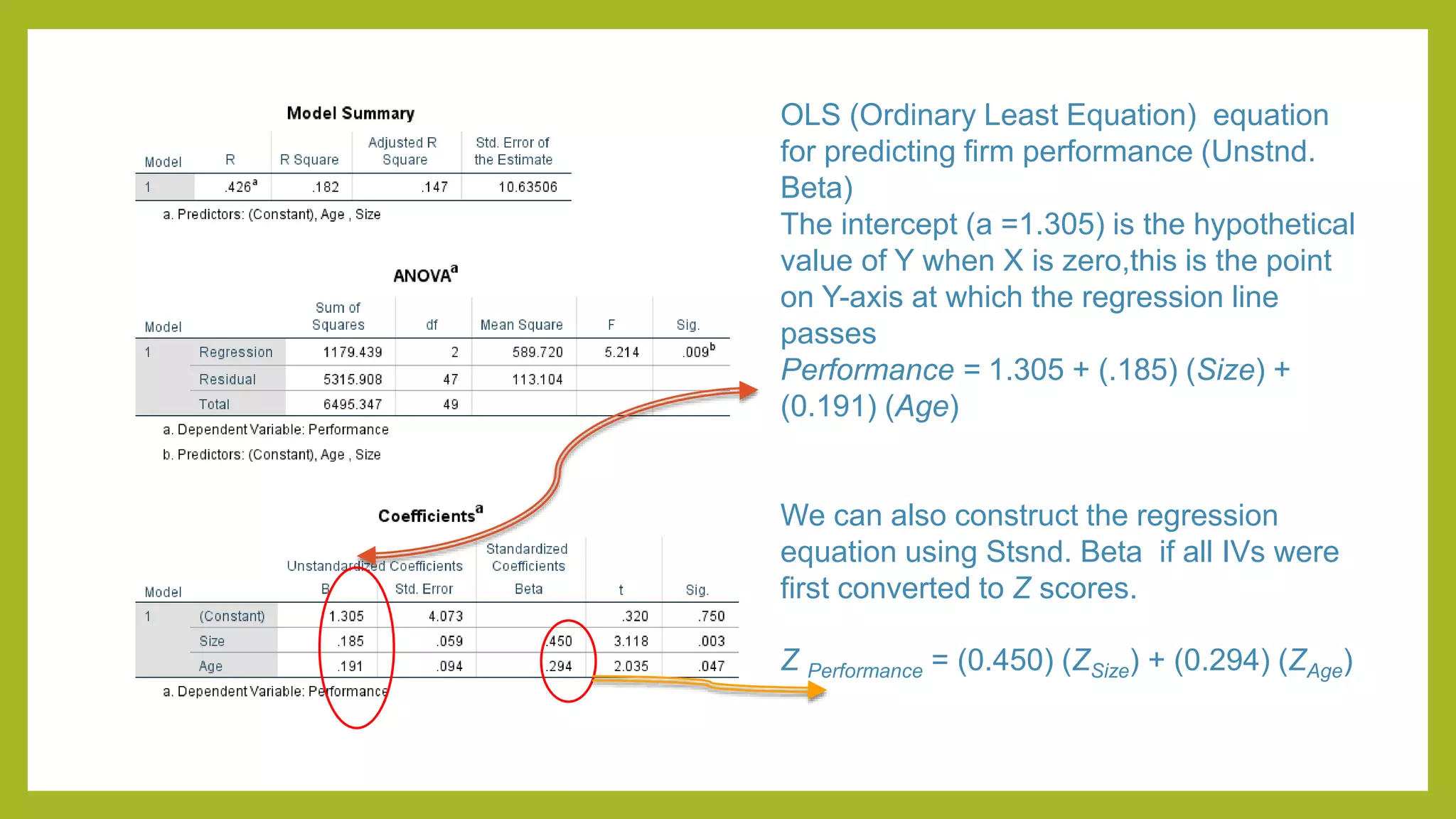
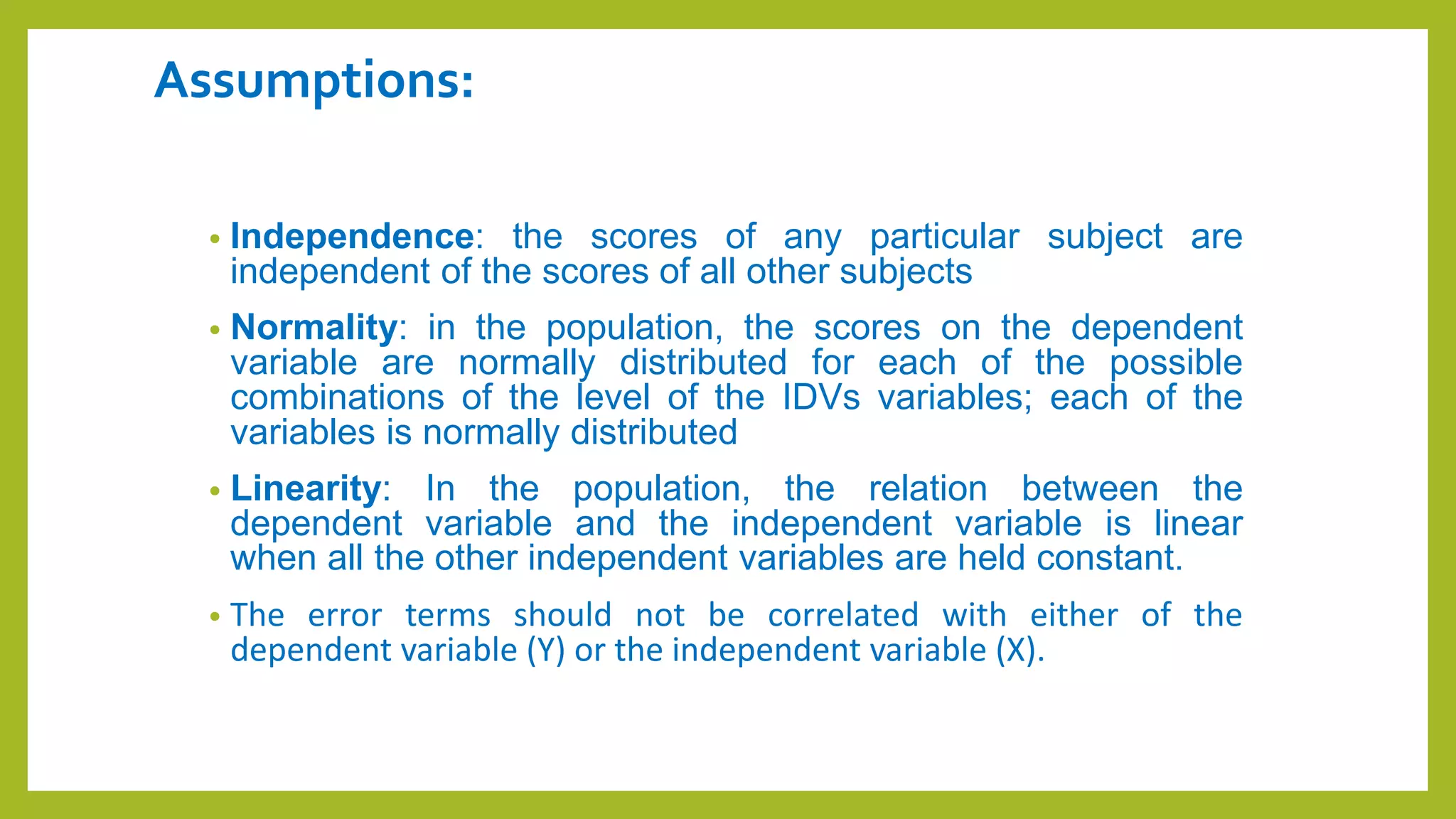
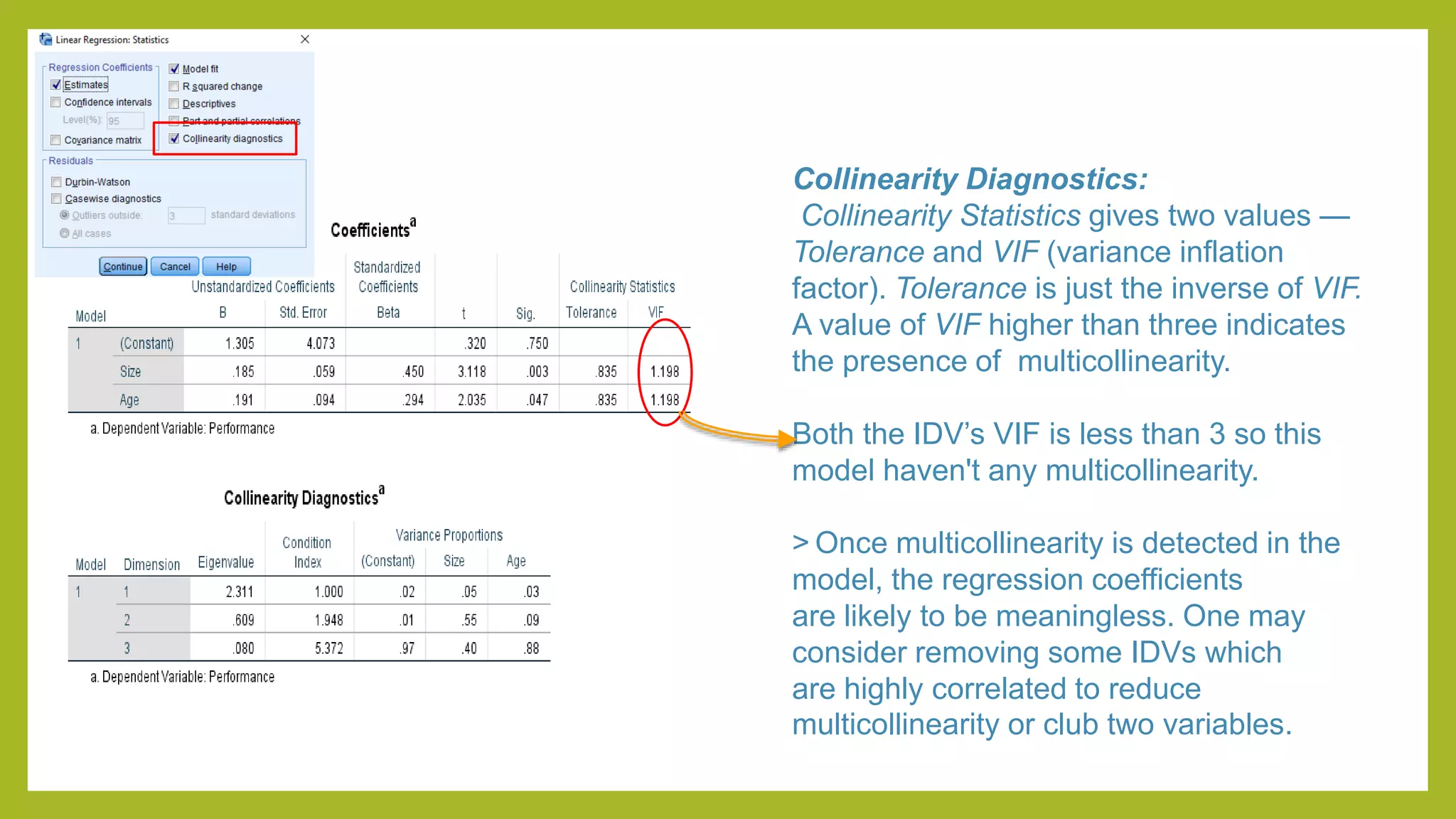
This document discusses simple and multiple regression analysis. Simple regression considers the relationship between one explanatory variable and one response variable, while multiple regression considers the relationship between one dependent variable and multiple independent variables. The document provides the formulas for simple and multiple linear regression. It also presents an example using SPSS to analyze the relationship between firm size, age, and performance. The SPSS output includes measures of model fit like R, R-squared, adjusted R-squared, ANOVA, regression coefficients, and diagnostics for assumptions. Hypothesis testing is conducted on the regression coefficients.

![Simple regression considers the relation
between a single explanatory variable and
response variable
Multiple regression :Regression analysis is used to assess
the relationship between one dependent variable (DV) and
several independent variables (IVs) .
Regression analysis assumes a linear relationship. It focuses
on association, not causation.
Purposes of Regression:
• Prediction
• Explanation-Magnitude ,sign and statistical Significance
Research Design:
(i) Sample size [5:1]
(ii)Variables- Metric
X1
X2
X3
ŷ](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/regressionanalysisantimdevmishra-210614083742/75/Regression-analysis-on-SPSS-2-2048.jpg)