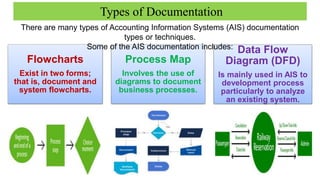
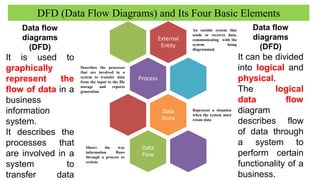
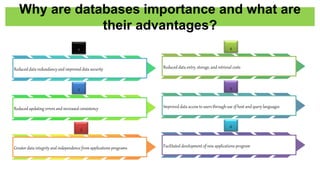
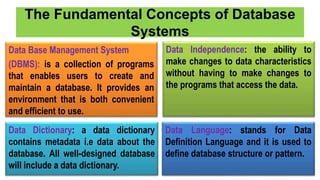
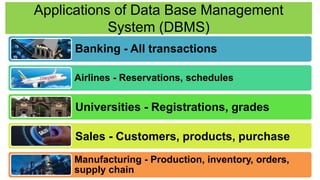
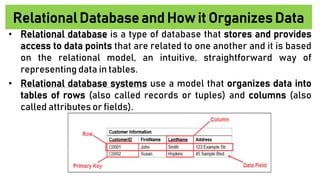
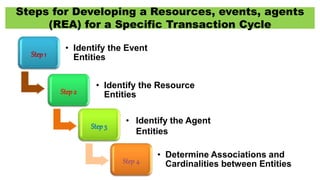
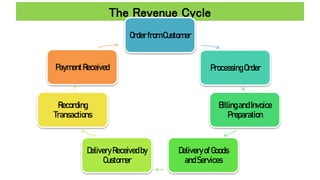
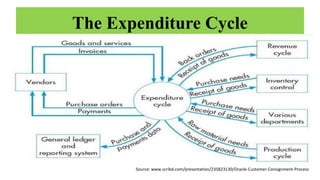
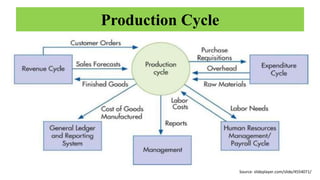
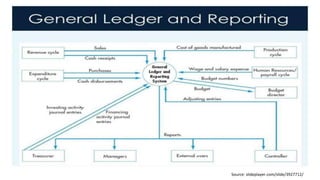
The document discusses accounting information systems (AIS), focusing on flowcharts, data flow diagrams (DFDs), and the importance of database management systems (DBMS). It outlines different documentation types and the significance of data independence, along with steps for designing a database system. Additionally, it covers applications of DBMS in various sectors and the purpose of AIS output, including financial statements and payroll stubs.