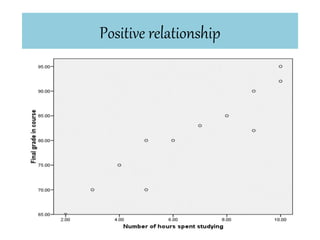
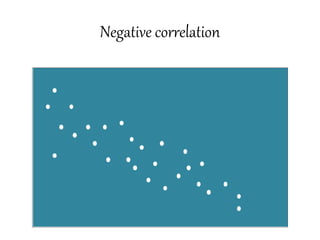
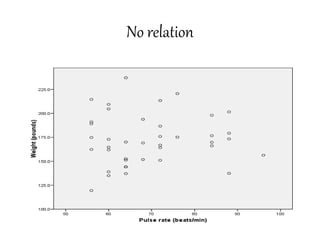
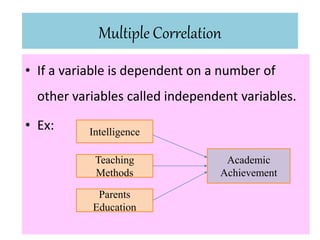
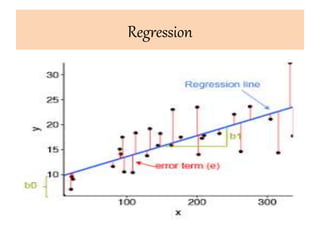
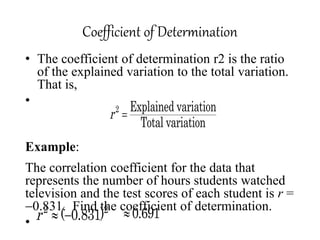
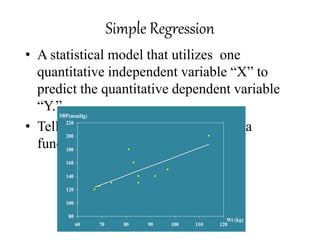
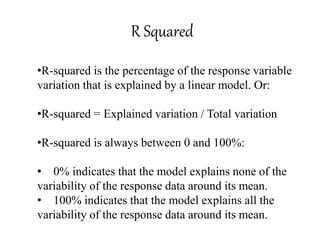
This document discusses correlation coefficient and regression analysis. It defines correlation coefficient as representing the relationship between two variables with a straight line and ranging from -1 to 1. Regression analysis predicts changes in a dependent variable from changes in independent variables. The coefficient of determination measures the proportion of variance explained by the regression model. Multiple regression uses two or more explanatory variables to predict an outcome.