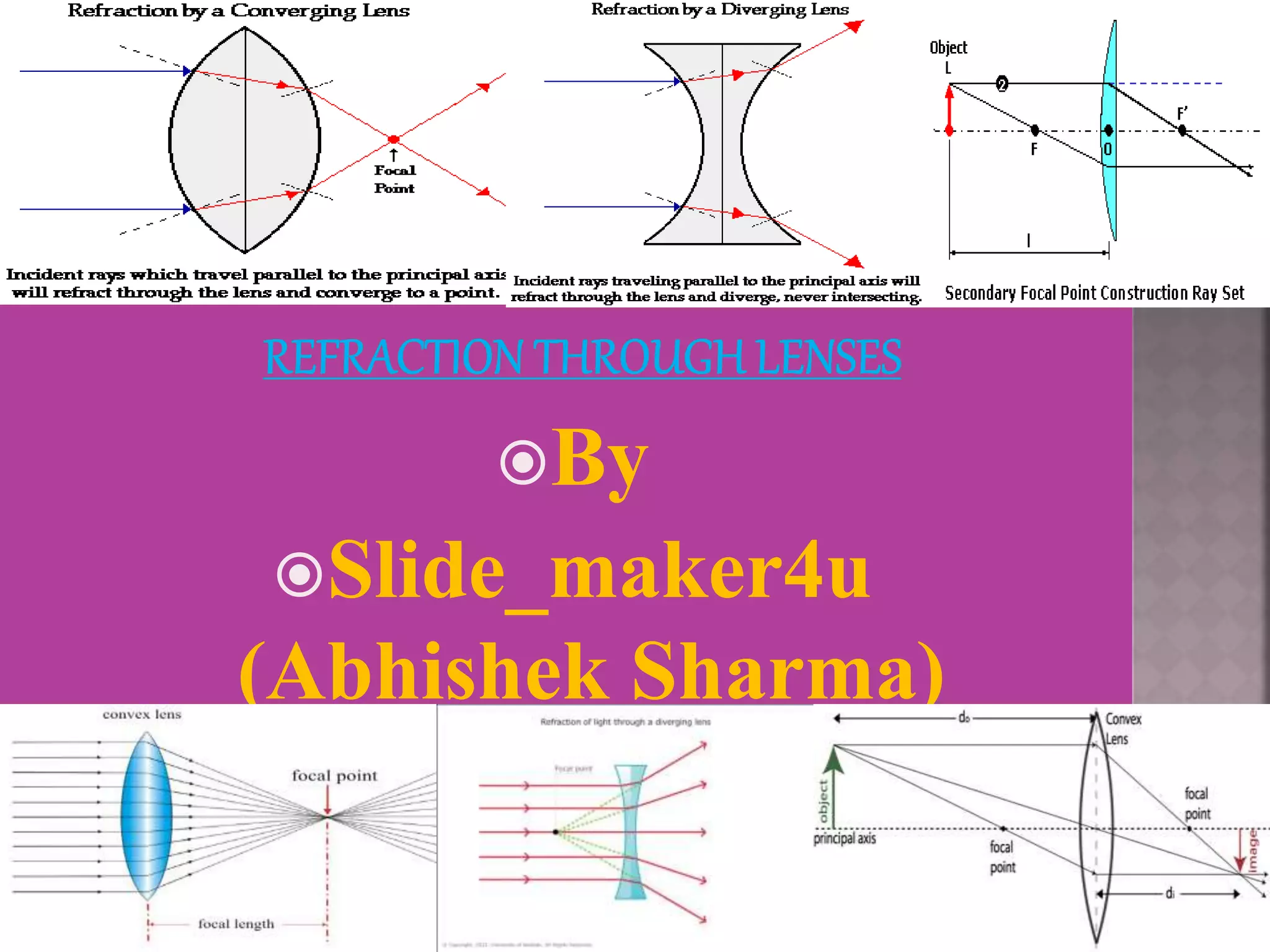
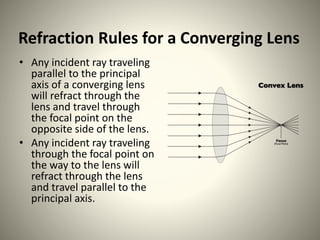
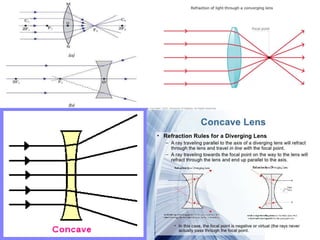
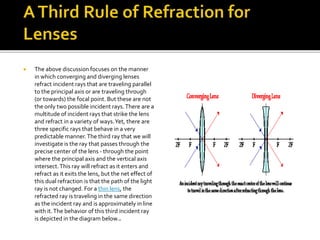
The document discusses refraction rules for converging and diverging lenses. It states that for a converging lens, any ray parallel to the principal axis will pass through the focal point on the opposite side, and any ray through the focal point will exit parallel to the principal axis. For a diverging lens, any ray parallel to the principal axis will pass through the focal point, and any ray toward the focal point will exit parallel to the principal axis. Additionally, any ray passing through the center of either lens will continue in the same direction.