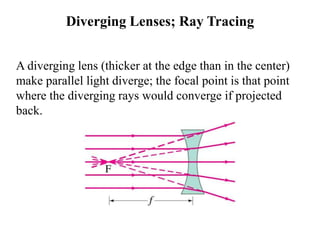
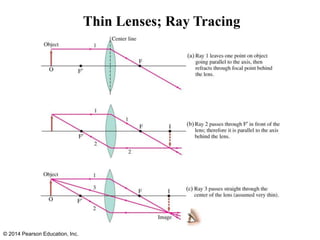
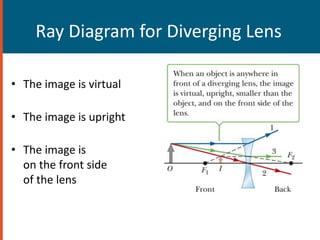
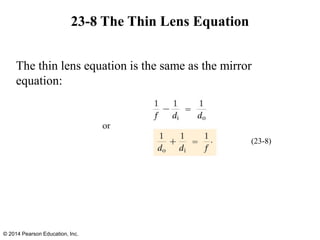
Thin lenses can be converging or diverging. Converging lenses bring parallel rays to a focus, while diverging lenses cause parallel rays to diverge. The thin lens equation relates the focal length of a lens to the object and image distances, and is used to solve for unknown values. The magnification of a lens is the ratio of the image height to the object height.