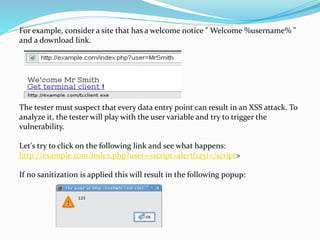
Cross-site scripting (XSS) attacks involve injecting malicious scripts into trusted websites, exploiting flaws in web applications that do not validate user input. There are two main types of XSS: reflected, where the code is executed immediately by the user's browser, and stored, where malicious code is saved on a server and executed when users access that page. Effective testing for XSS vulnerabilities requires both black box and gray box testing methodologies, utilizing various tools to detect and analyze potential exploits.