This document summarizes Spark as a service on YARN clusters and discusses key features:
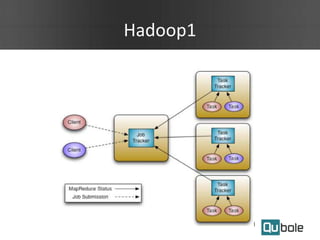
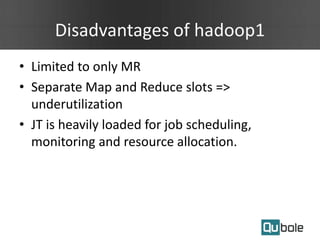
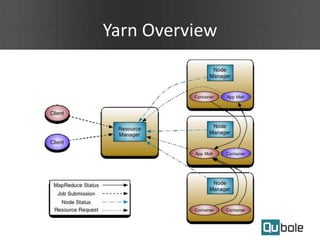
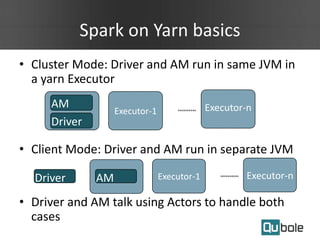
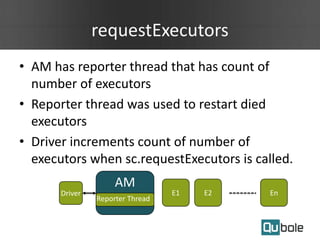
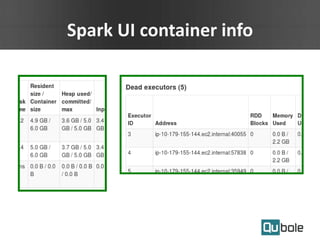
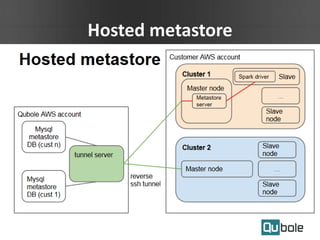
- Spark on YARN allows running multiple workflows like Spark and Hadoop on the same cluster and improves resource utilization. The application master can dynamically request more containers as needed.
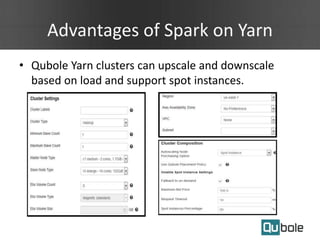
- Qubole YARN clusters support autoscaling to upscale and downscale based on load and use spot instances for cost savings.
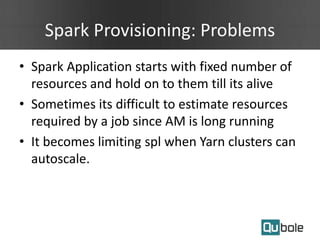
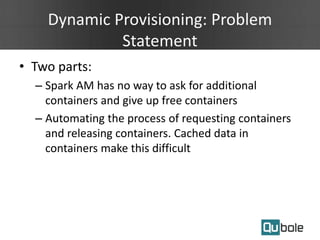
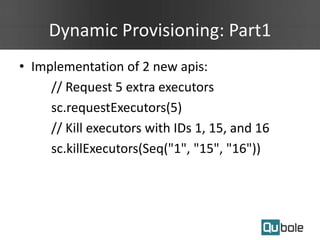
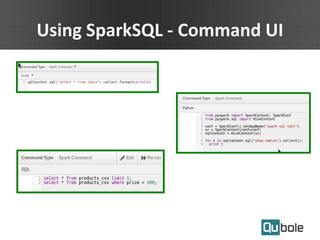
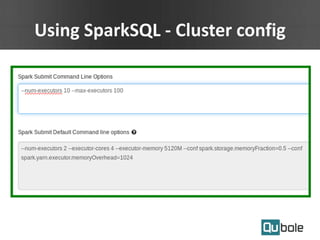
- Spark applications were limited by initial resource allocation. Dynamic provisioning allows applications to request more executors or release unused executors to improve performance and cluster utilization.