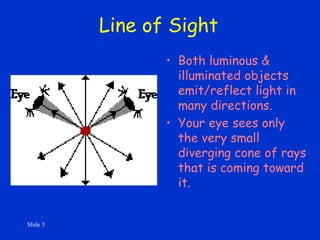
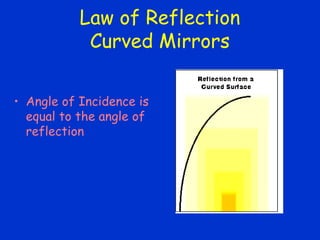
This document discusses the reflection of light, including key definitions and concepts. It explains that luminous objects generate their own light, while illuminated objects reflect light. It also defines line of sight as the line from an object to the eyes, along which light travels. The document then discusses the law of reflection, which states that the angle of incidence equals the angle of reflection. It provides examples of reflection from plane and curved mirrors, and discusses the formation of real and virtual images.