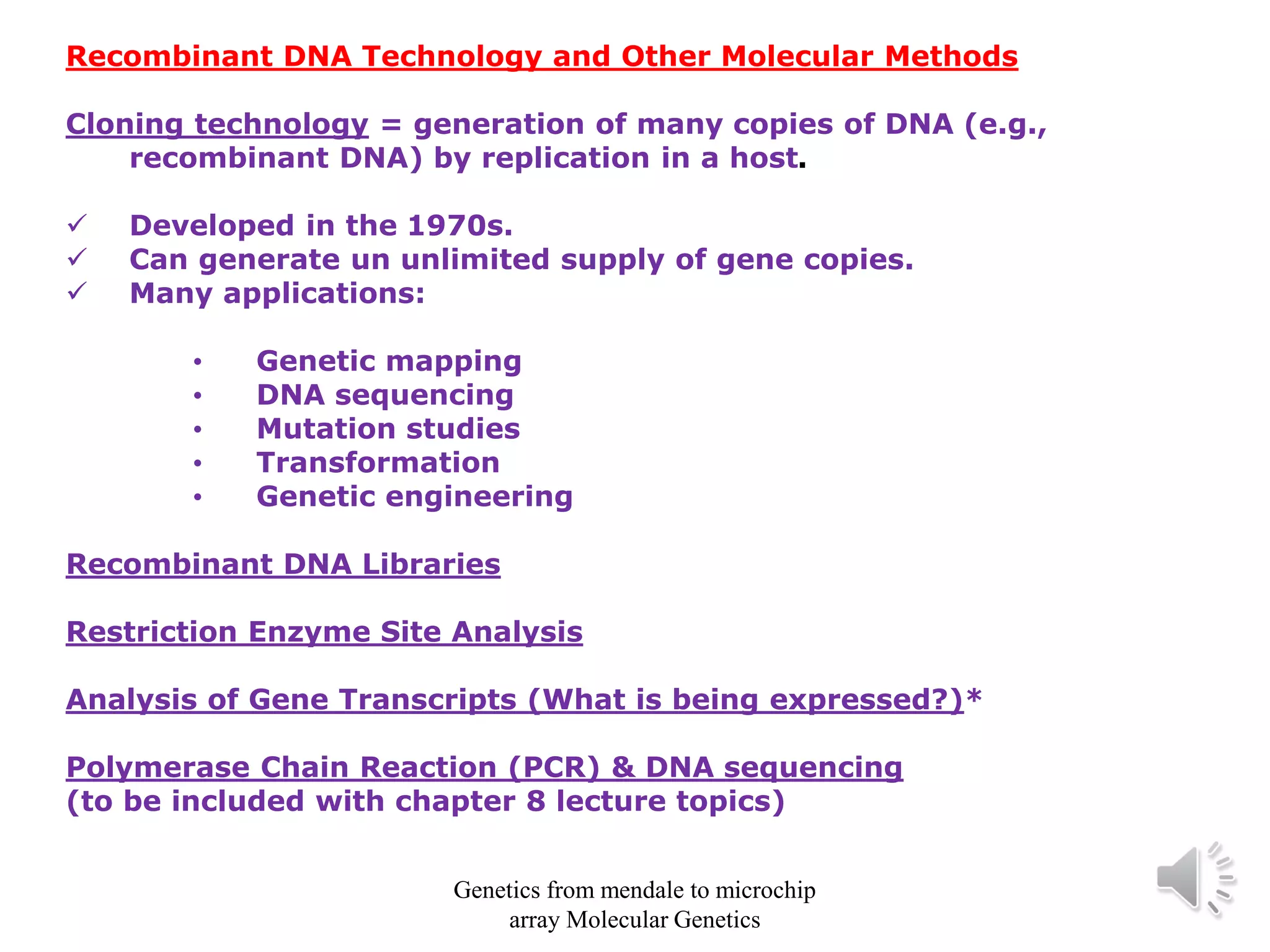
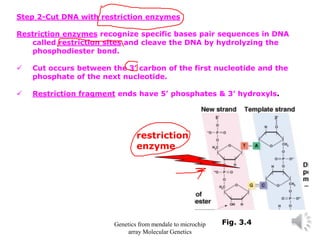
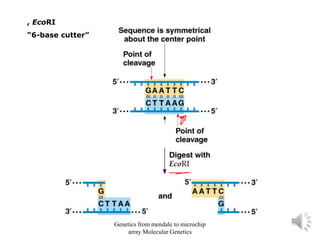
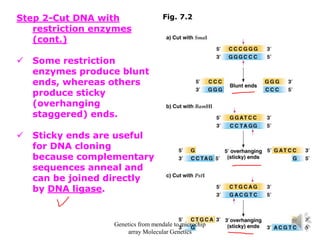
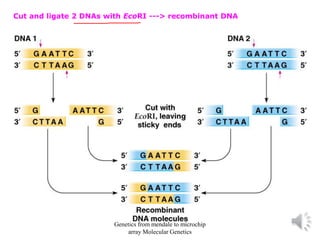
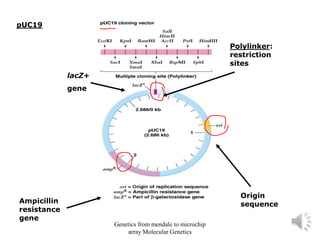
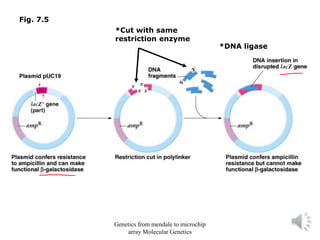
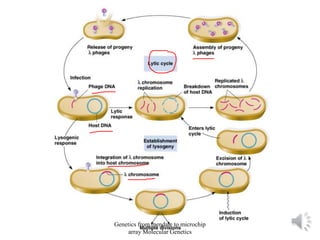
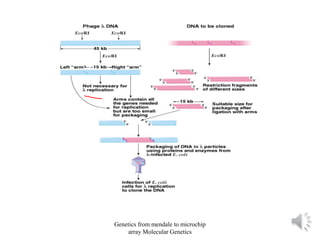
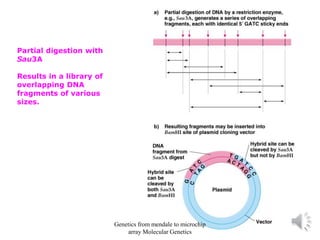
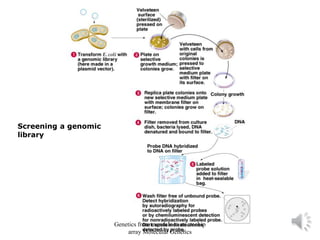
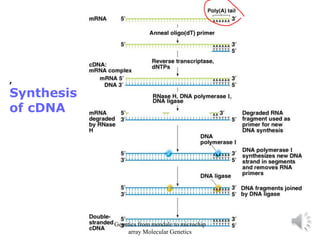
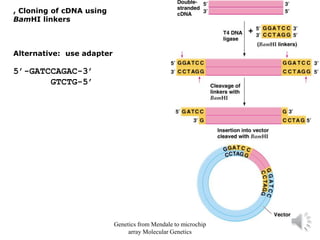
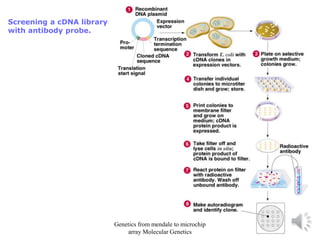
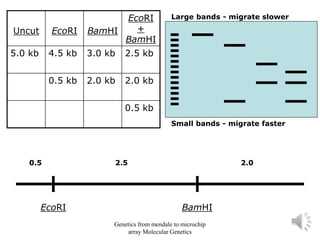
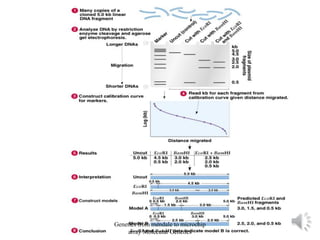
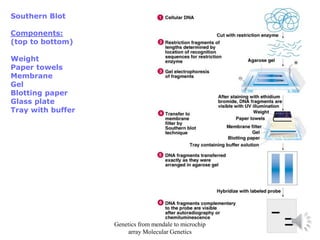
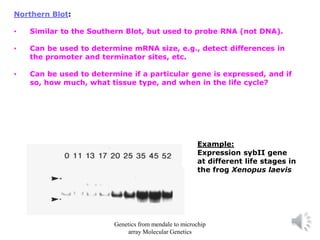
Recombinant DNA technology allows for the cloning and manipulation of DNA. DNA is first isolated from an organism and cut with restriction enzymes. The cut DNA fragments are then inserted into cloning vectors like plasmids or phage lambda. These recombinant DNA molecules are introduced into host cells, where they can be replicated in large quantities. Libraries of cloned DNA fragments can be generated that represent entire genomes or individual chromosomes, enabling applications such as genetic mapping, DNA sequencing, and genetic engineering.