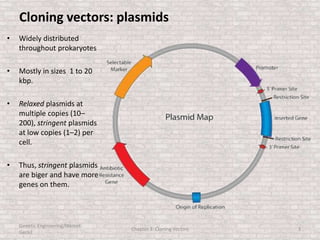
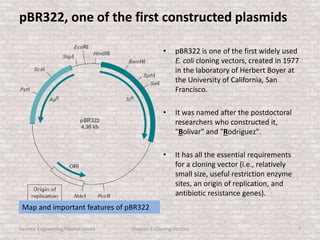
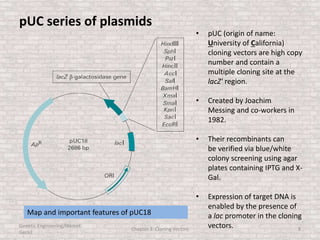
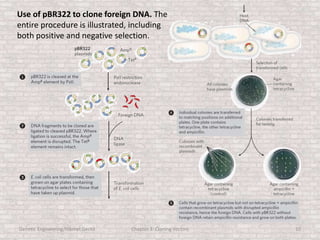
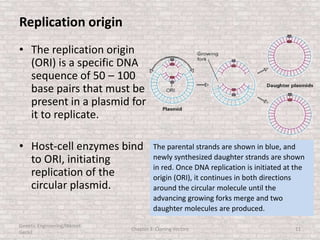
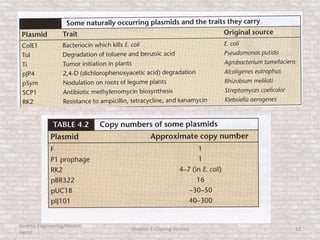
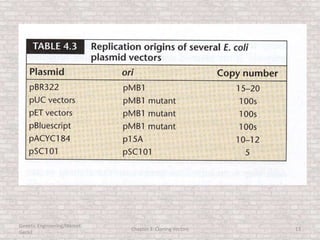
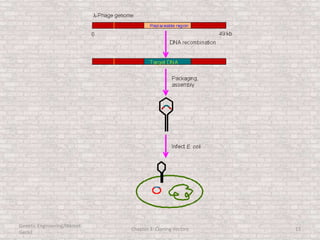
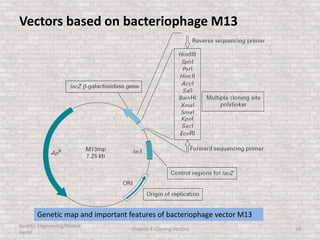
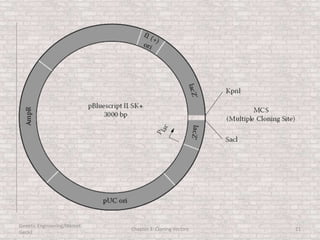
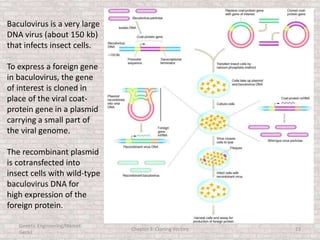
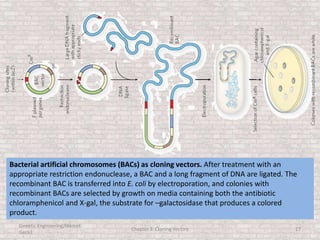
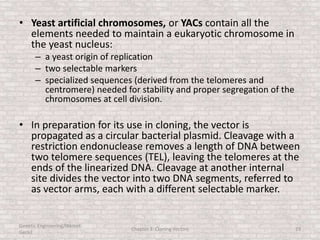
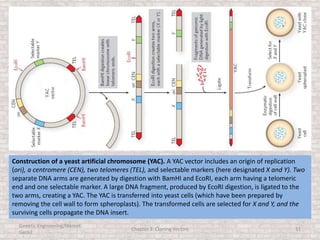
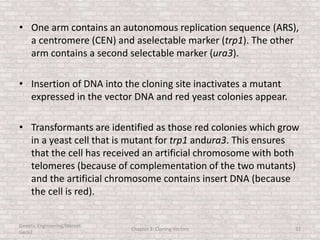
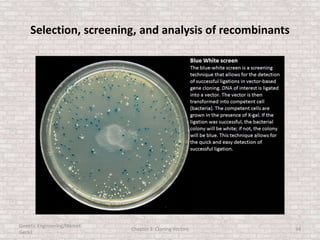
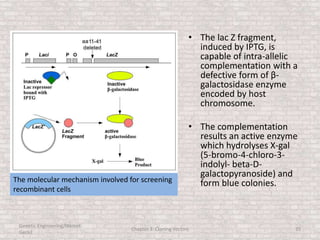
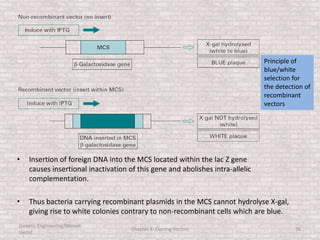
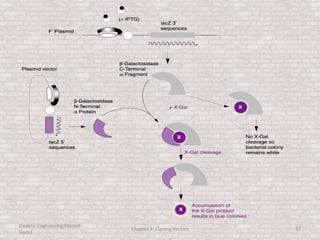
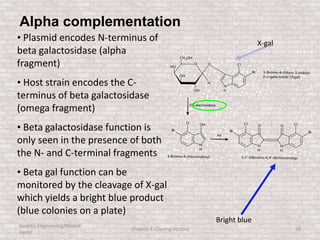
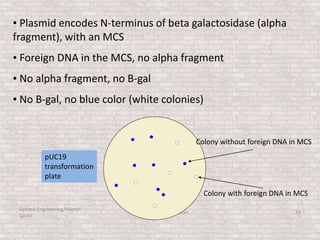
This document discusses various types of cloning vectors used in genetic engineering experiments. It begins by describing the basic features a vector must possess, including the ability to self-replicate and contain selectable markers. It then focuses on plasmids, noting that E. coli is commonly used as a host and that vectors like pBR322 were early workhorses. Later sections cover lambda phage vectors, cosmids, YACs, and BACs, which can accommodate larger DNA fragments. The document provides detailed information on widely used vectors like pUC, M13, and their features to replicate, package DNA, and enable cloning experiments.