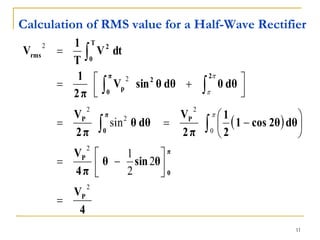
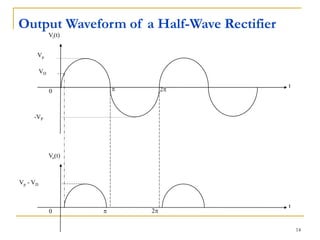
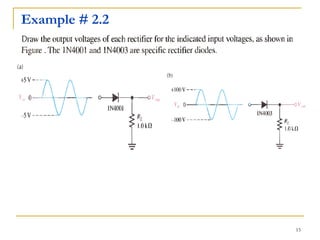
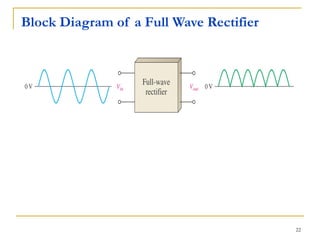
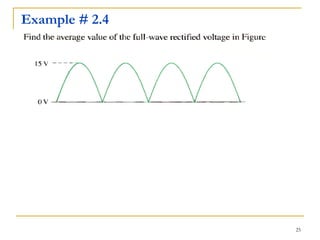
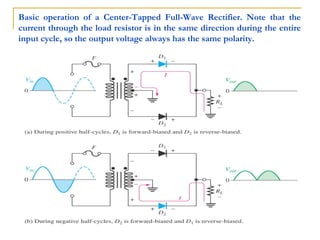
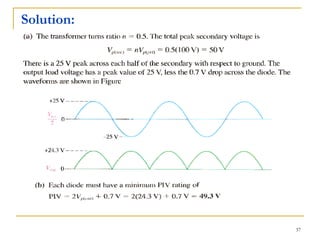
The document discusses various diode applications in power supplies including half-wave and full-wave rectifiers. It provides block diagrams and equations for calculating average output voltage, RMS voltage, and peak inverse voltage. Different rectifier circuits are covered such as center-tapped and bridge full-wave rectifiers. The role of filters in reducing ripple is explained along with the effects of capacitor size and load resistance on ripple factor. Formulas are given for calculating ripple voltage and ripple factor for half-wave and full-wave rectified outputs with capacitor input filters.