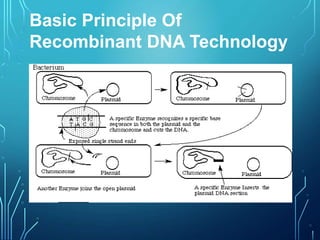
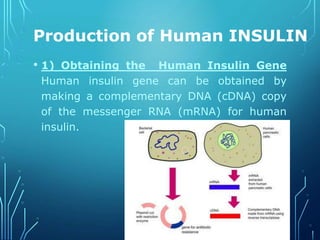
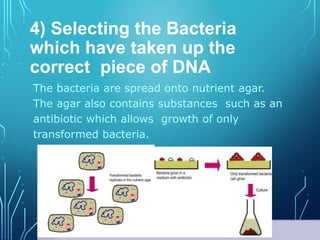
Recombinant DNA technology involves procedures to recombine DNA segments, enabling cloned molecules to replicate within host cells. Developed by Boyer and Cohen in 1973, it allows for large-scale production of human proteins, such as insulin, using genetically engineered bacteria and explores potential applications in gene therapy for genetic diseases. Safety concerns exist regarding the possible creation of pathogenic recombinant bacteria and the recommendations of containment practices are supported by the Recombinant DNA Advisory Committee.