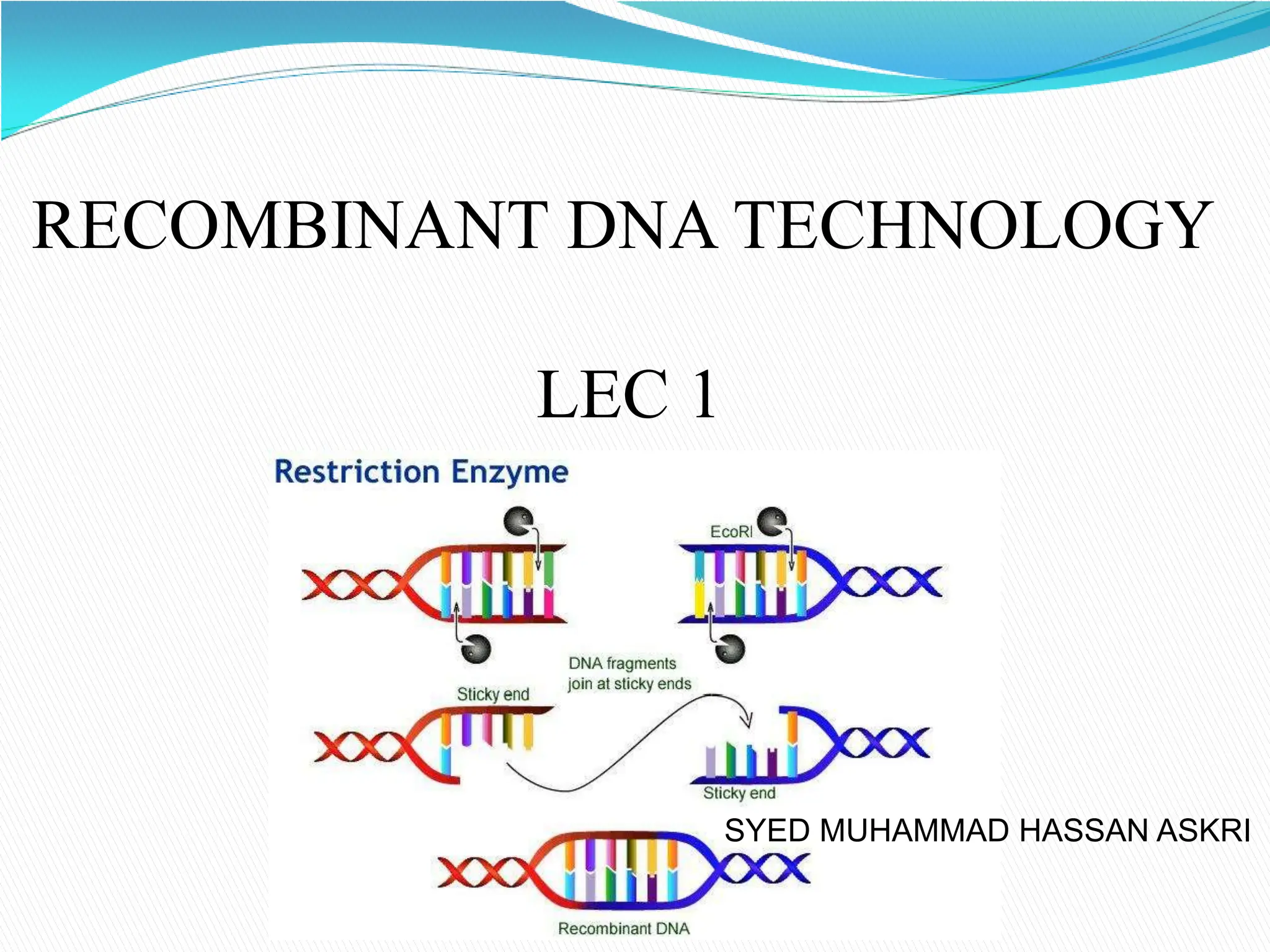
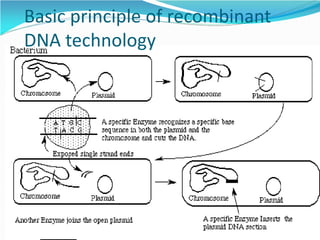
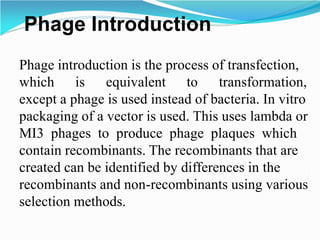
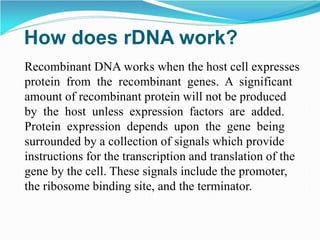
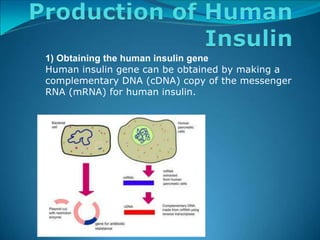
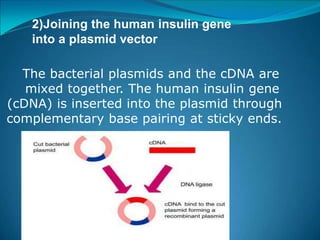
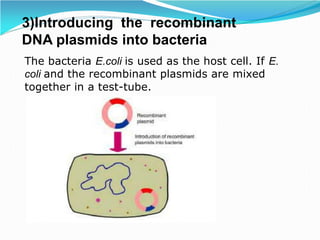
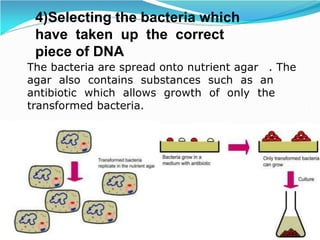
Recombinant DNA technology involves procedures to recombine DNA segments, allowing the creation of recombinant DNA molecules that can replicate within host cells. Key methods include transformation, microinjection, and phage introduction, with applications in producing human proteins like insulin and developing vaccines. Despite its advancements, safety concerns persist regarding the potential creation of pathogenic recombinant bacteria, leading to the establishment of regulatory bodies and safety protocols.