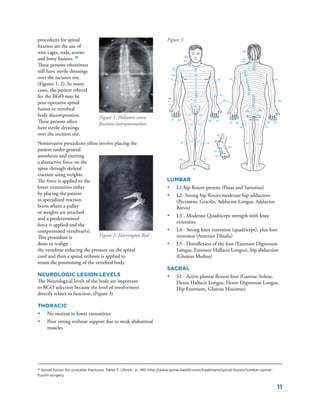
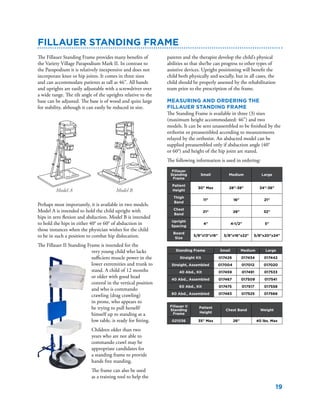
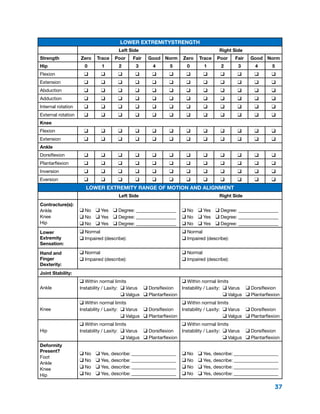
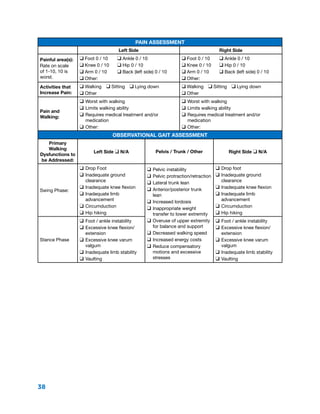
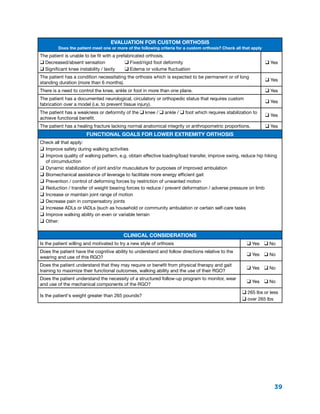
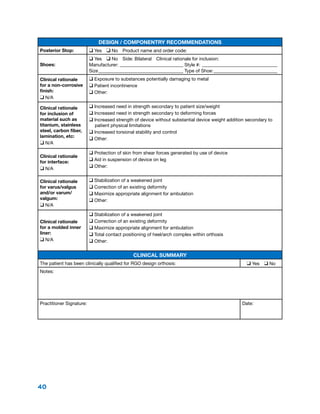
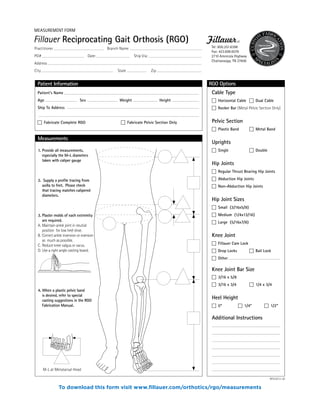
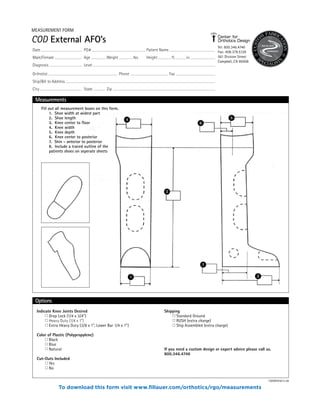
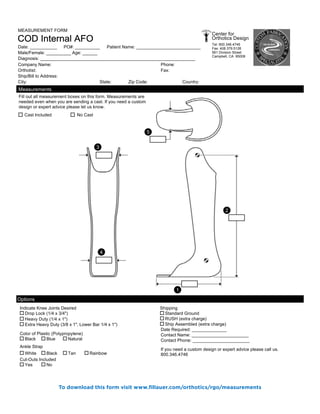
The document summarizes the history and purpose of the Reciprocating Gait Orthosis (RGO). It was first introduced in 1967 to allow paraplegic individuals to stand and walk without immobilizing the hips. The RGO links the legs and torso so that hip flexion in one leg causes extension in the other, maintaining an upright torso position. This reciprocal motion and dynamic torso support enables a more natural gait with less energy expenditure than other hip-knee-ankle-foot orthoses. The RGO has continued to be improved since its introduction to provide paraplegic individuals with greater mobility and independence.