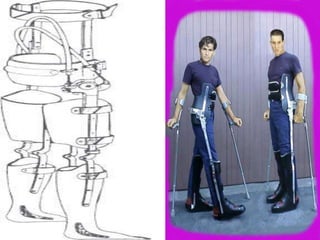
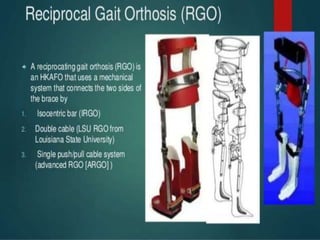
Custom-made orthoses can provide stability and support for standing and ambulation with assistive devices like crutches. A trial period with adjustable temporary orthoses is advisable. Craig-Scott knee-ankle-foot orthoses (KAFOs) enable standing with back support and do not restrict hip motion. Walkabout orthoses link the knees to allow greater mobility. Reciprocating gait orthoses use cables or rods to link the hips and allow a four-point walking pattern. Externally powered orthoses combine pneumatic or electrical stimulation to help with ambulation but have high metabolic costs.