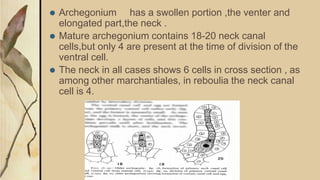
Reboulia hemisphaerica is a perennial liverwort found worldwide except Antarctica, with a notable depleting presence in the Himalayas and Central India. The plant exhibits a unique morphology, including dichotomously branched thalli characterized by pale green colors and purple margins, and reproduces via both vegetative and sexual methods. The species produces a significant number of spores post-fertilization, contributing to its lifecycle in various moist habitats.