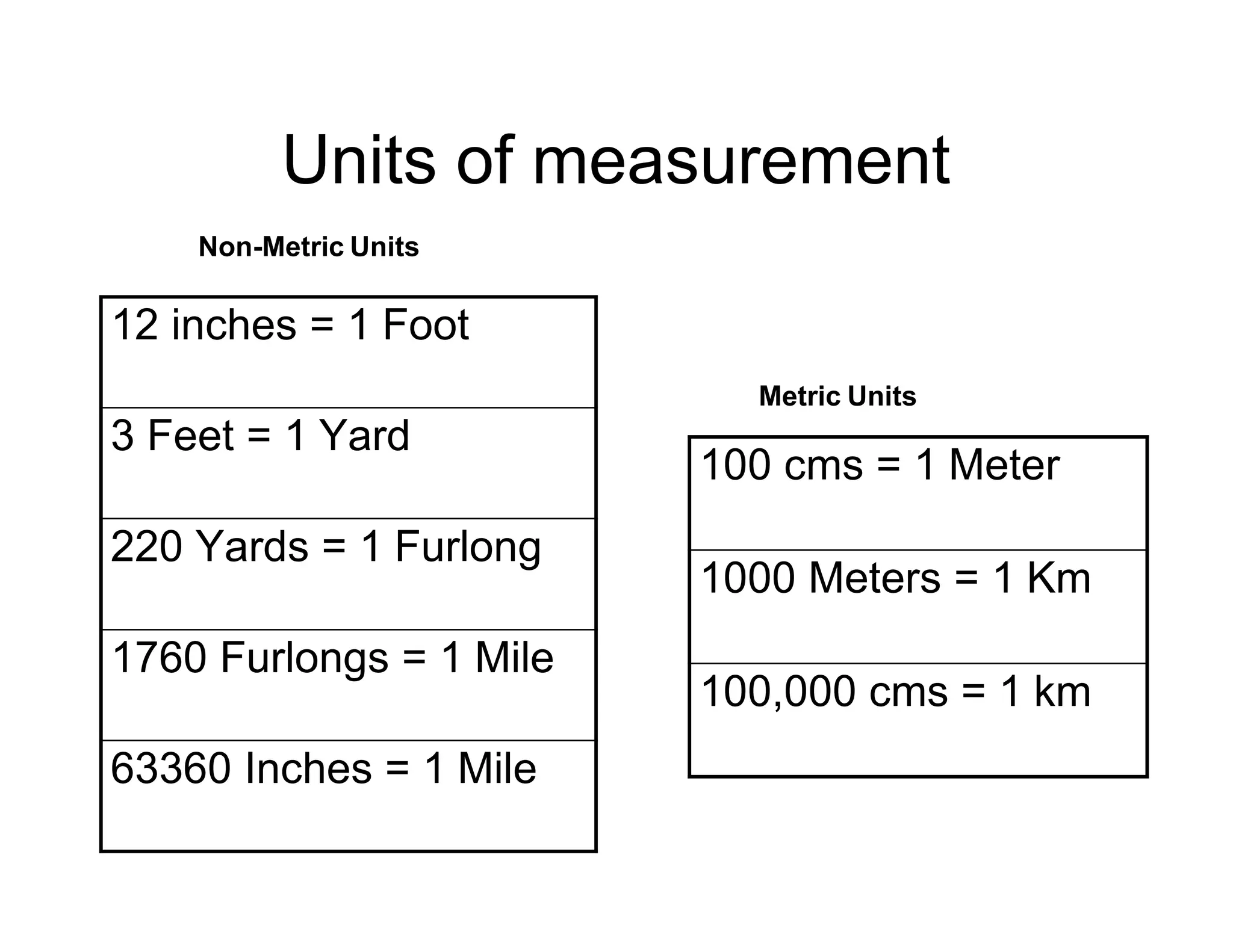
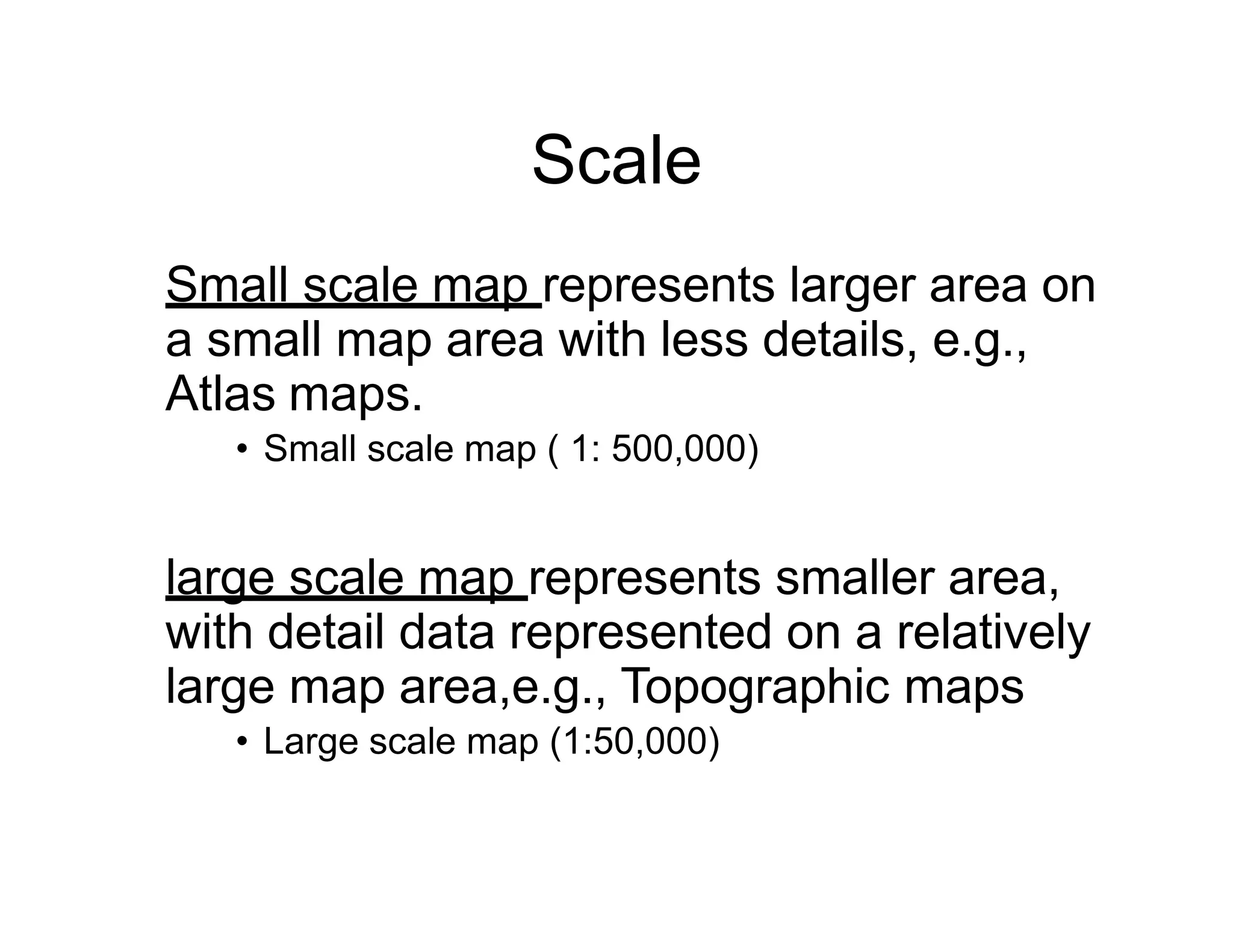
Cartography is the science and art of map making. Maps are representations of areas of the earth on a flat surface and include titles, scales, legends, and source statements. Scale expresses the ratio between distances on a map and in real life using statements of scale, representative fractions, and linear scales. There are different units of measurement for distances and scales can be small, showing larger areas with less detail, or large, showing smaller areas with more detail. Maps are also classified based on their communicative objectives like reference maps or thematic maps, and by their subject matter and function like cadastral, topographic, soil, weather, and population maps.