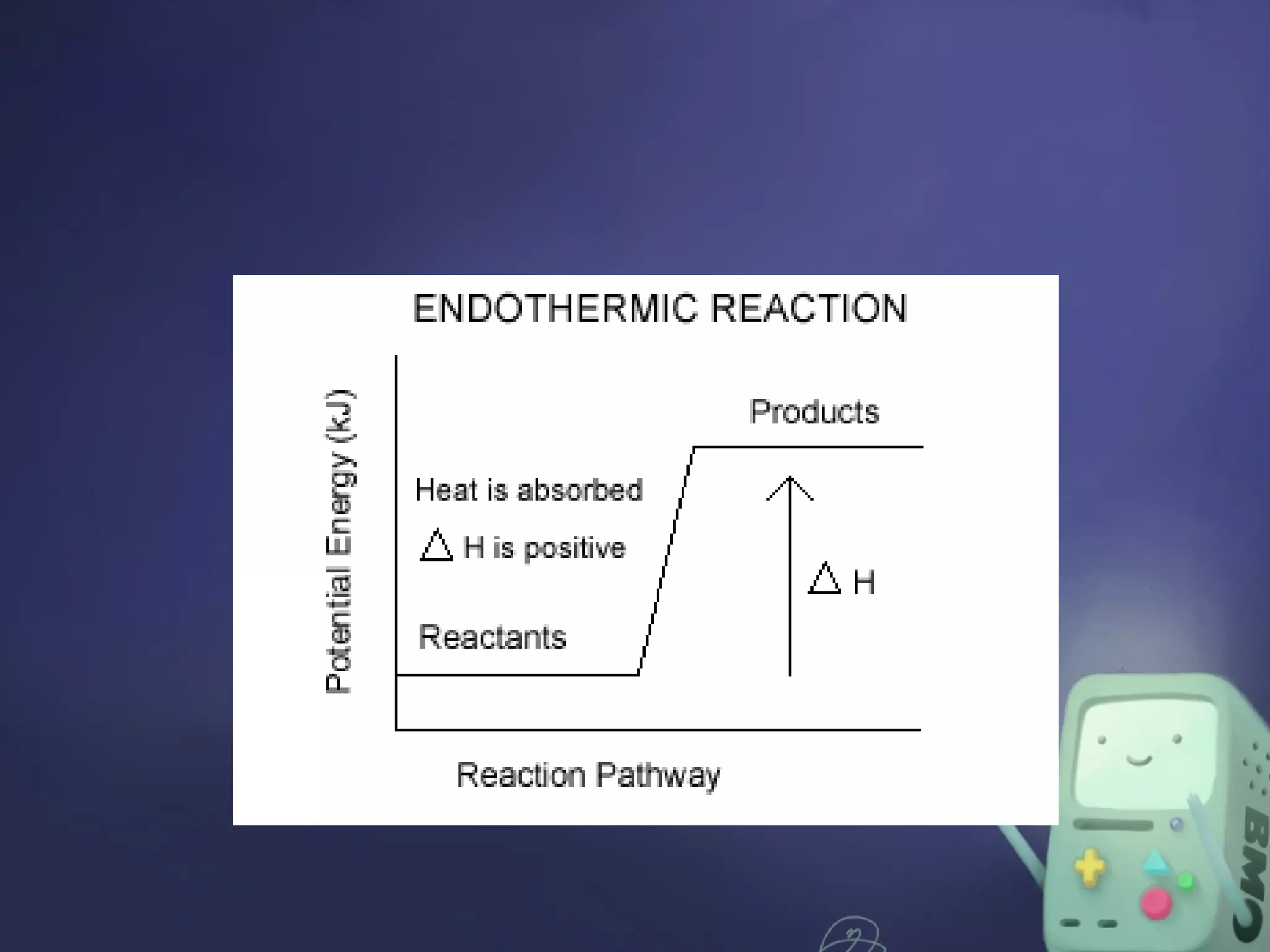
The document discusses energy changes in chemical reactions, particularly in relation to endothermic and exothermic processes, and the concept of activation energy. It outlines factors affecting reaction rates, such as surface area, temperature, concentration, pressure, catalysts, and inhibitors. Additionally, it highlights the role of enzymes as biological catalysts that facilitate essential reactions in living organisms.