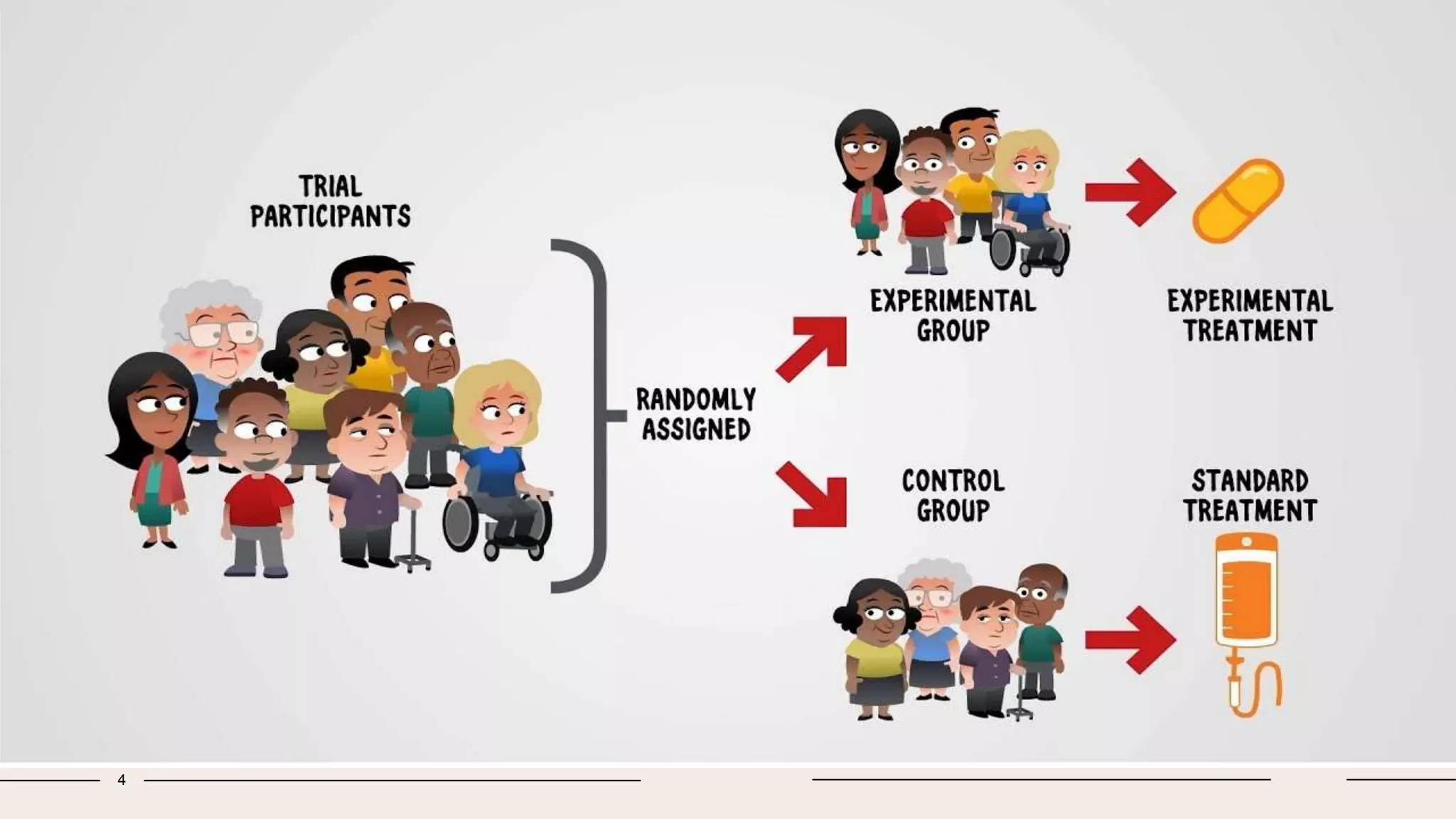
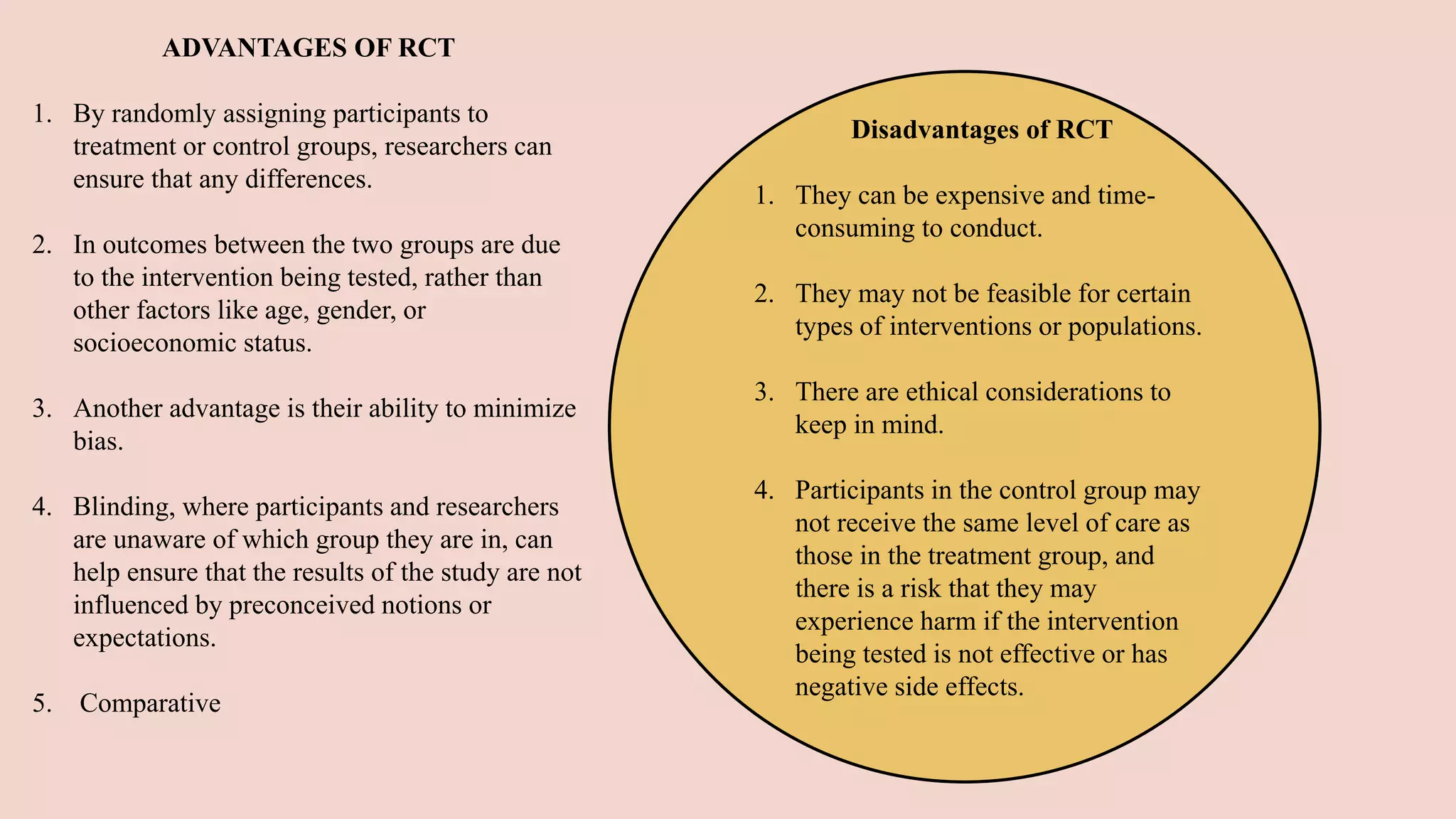
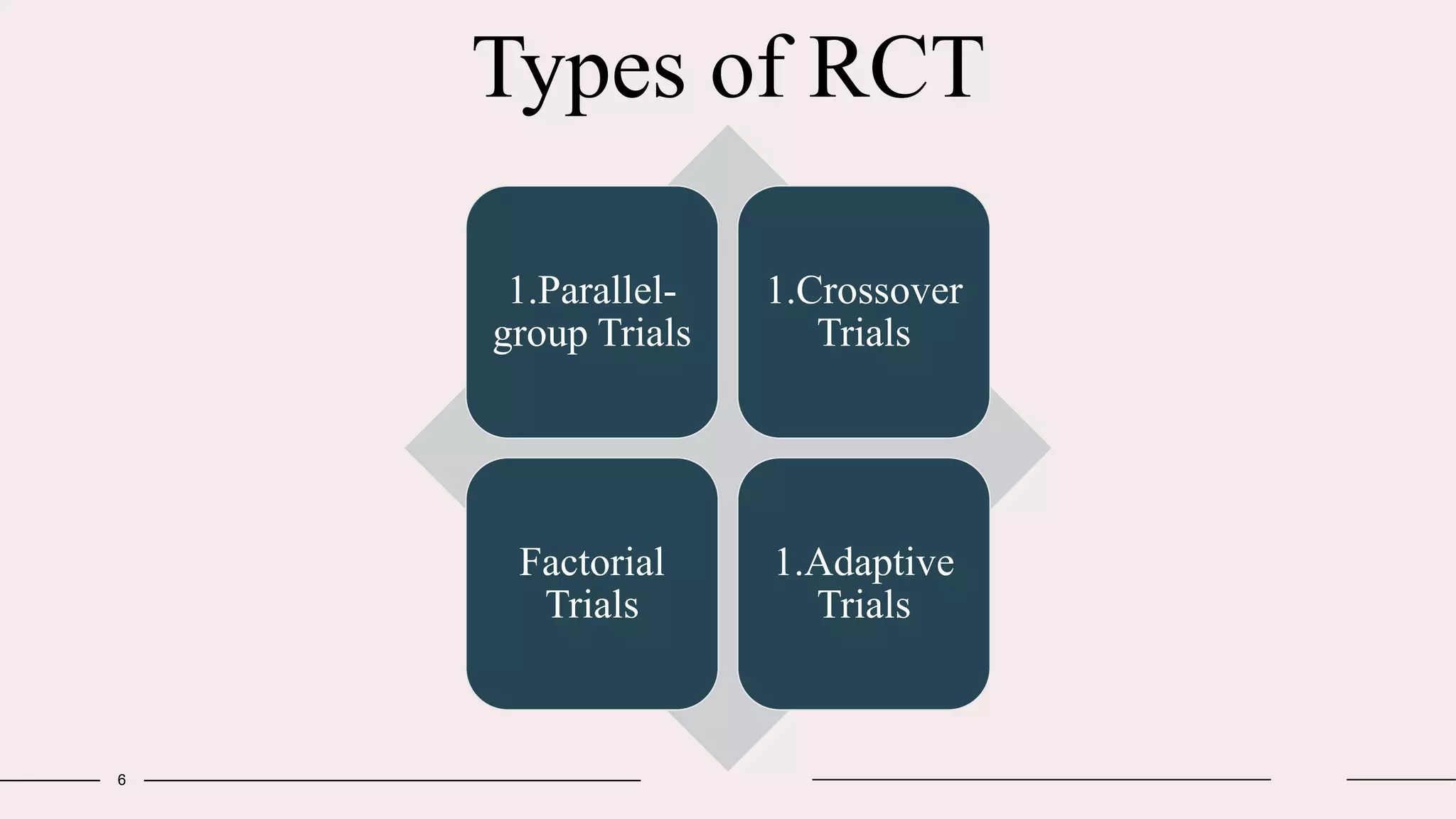
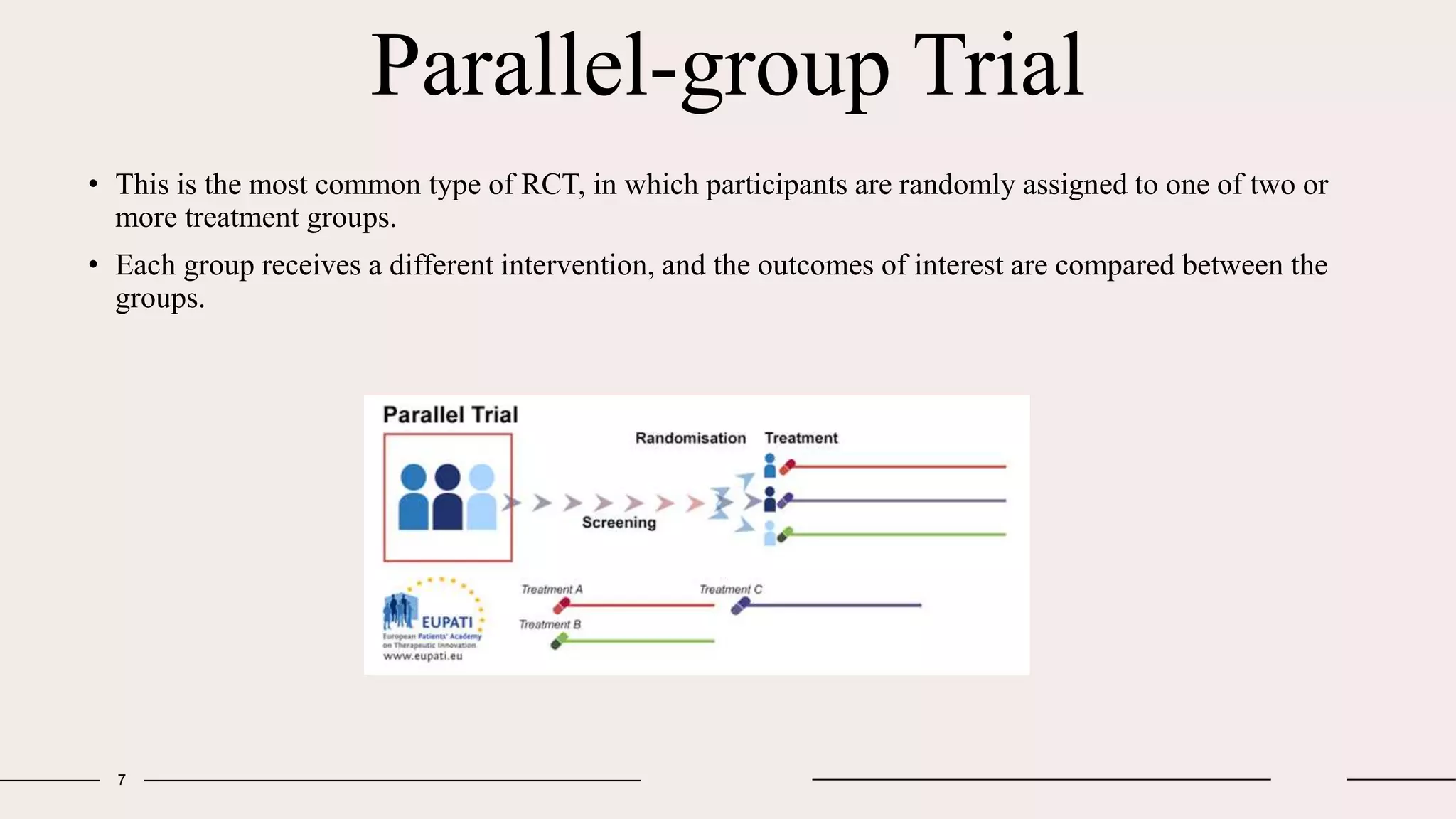
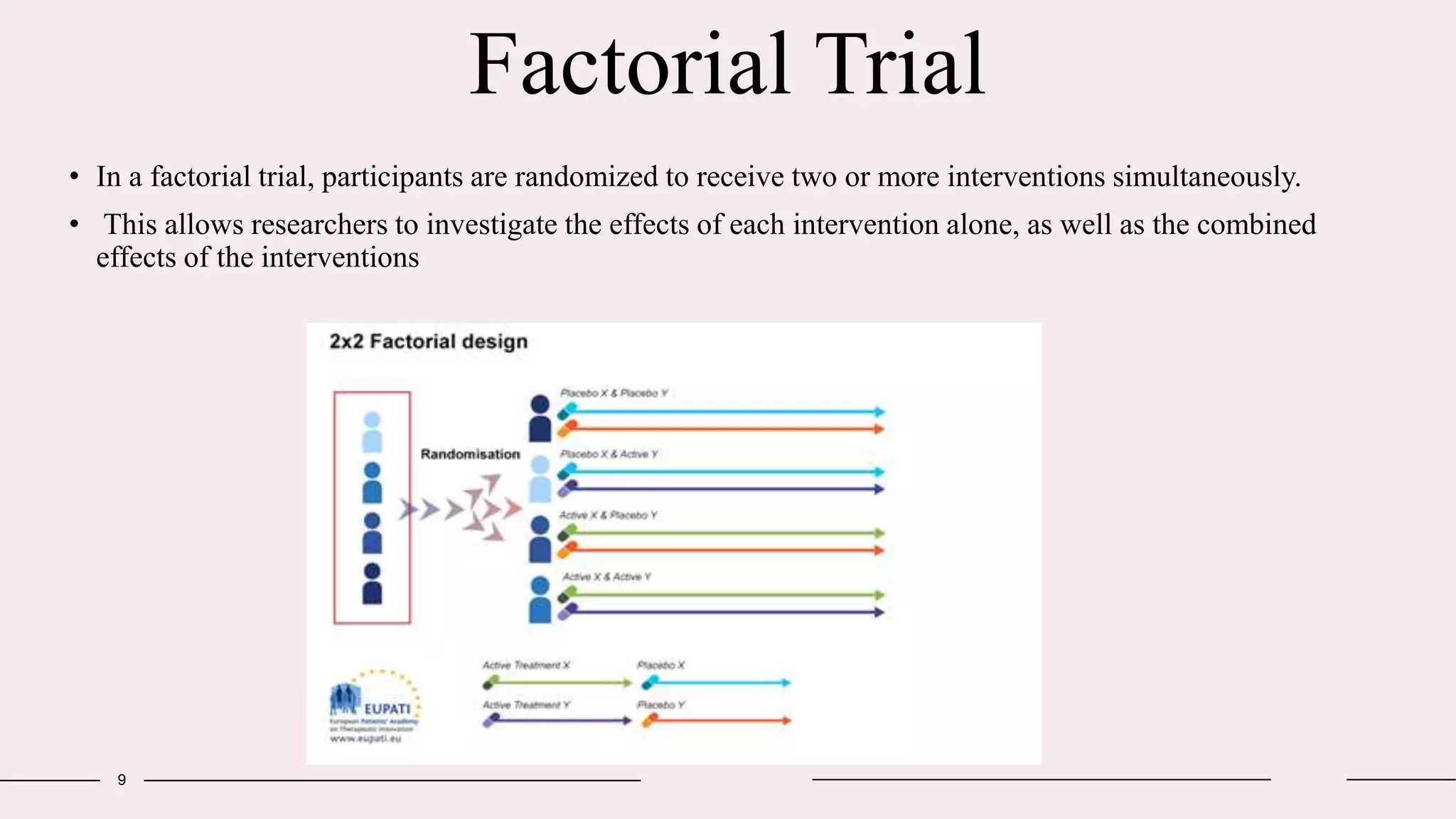
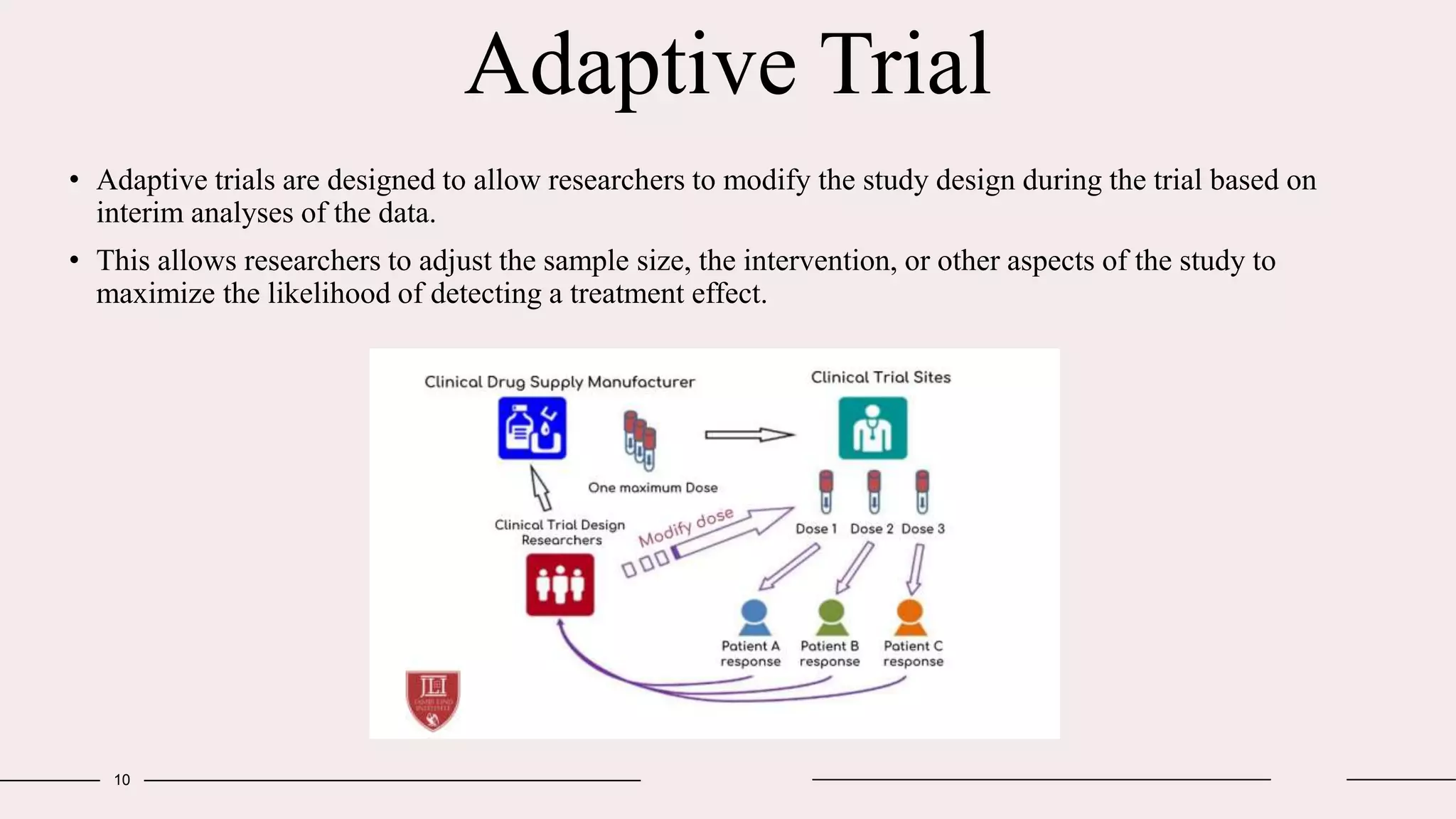
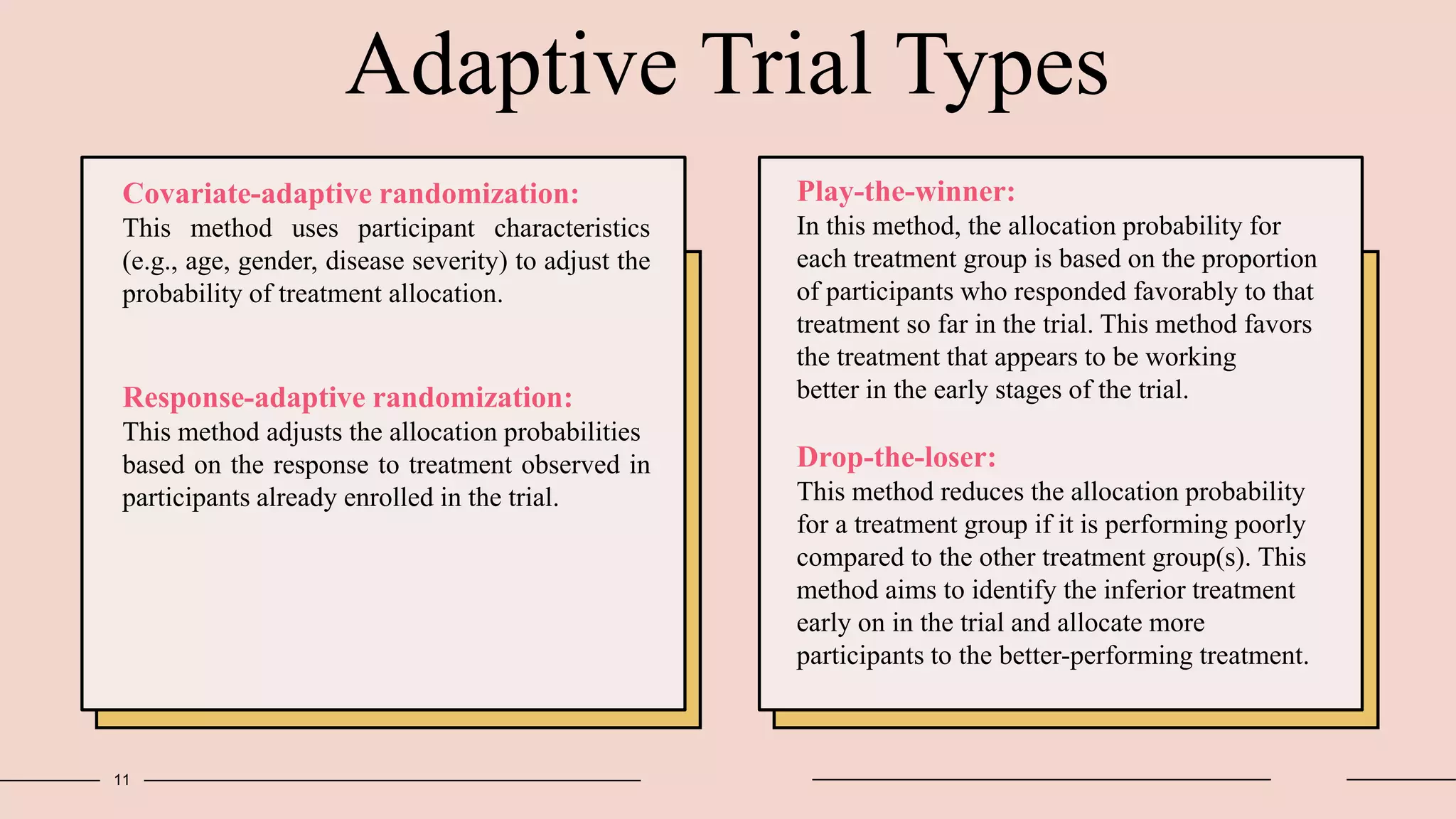
Randomized clinical trials are a type of study design used in medical research to evaluate new treatments. They work by randomly assigning participants to either a treatment group, which receives the new intervention, or a control group, which receives an existing standard treatment or placebo. The outcomes of the participants in each group are then compared. Randomized clinical trials are considered the gold standard for determining causality because randomization reduces bias from confounding factors. There are different types of randomized clinical trials, including parallel-group trials, crossover trials, and factorial trials, which test multiple interventions simultaneously. Adaptive trials allow modification of the trial design based on interim outcome data.