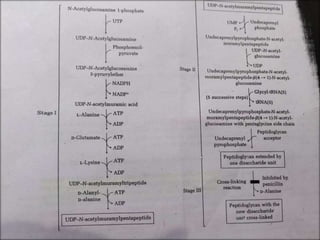
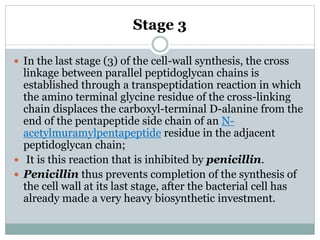
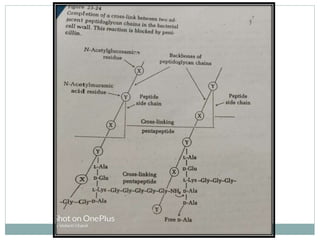
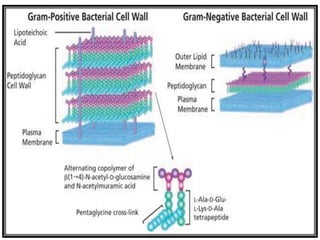
1. The cell wall peptidoglycan of bacteria is synthesized in three major stages, with stage 3 involving a transpeptidation reaction that cross-links parallel peptidoglycan chains and is inhibited by penicillin.
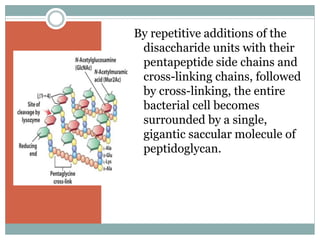
2. By repetitive additions of disaccharide units with pentapeptide side chains and cross-linking chains, the bacterial cell becomes surrounded by a single gigantic peptidoglycan molecule.
3. Peptidoglycan synthesis is regulated at multiple levels to ensure shape-maintaining growth and cell division.