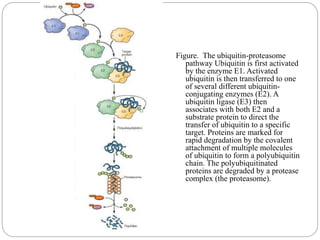
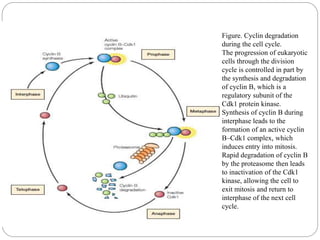
The ubiquitin-proteasome pathway is the major mechanism for regulated protein degradation in eukaryotic cells. Ubiquitin tags proteins for degradation by attaching to lysine residues in a multi-step process involving E1, E2, and E3 enzymes. E3 ligases provide specificity by recognizing target proteins. Polyubiquitinated proteins are degraded by the proteasome. The levels and degradation of cyclin B, which controls cell cycle progression, demonstrates the importance of this pathway in regulating fundamental cellular processes.