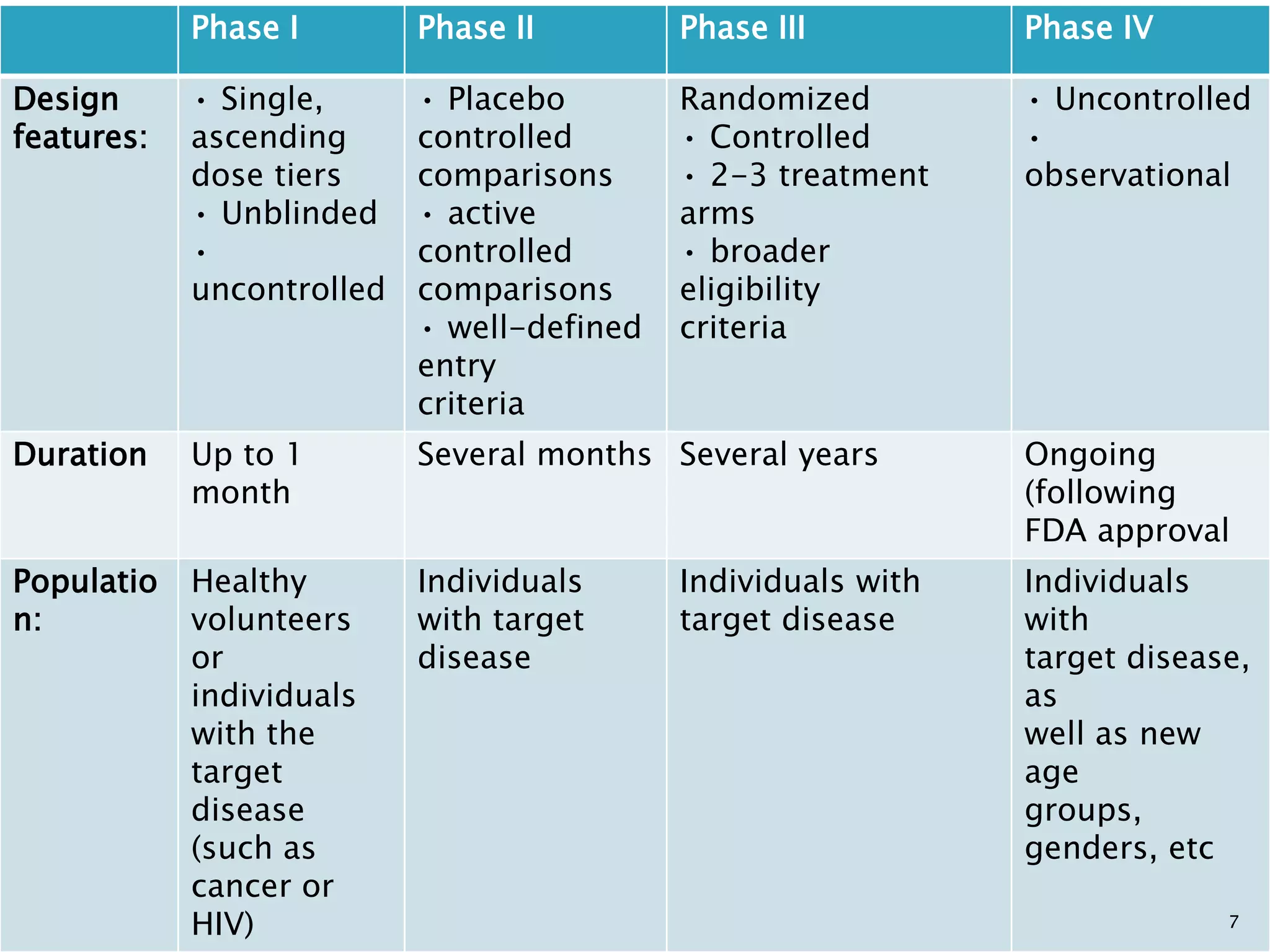
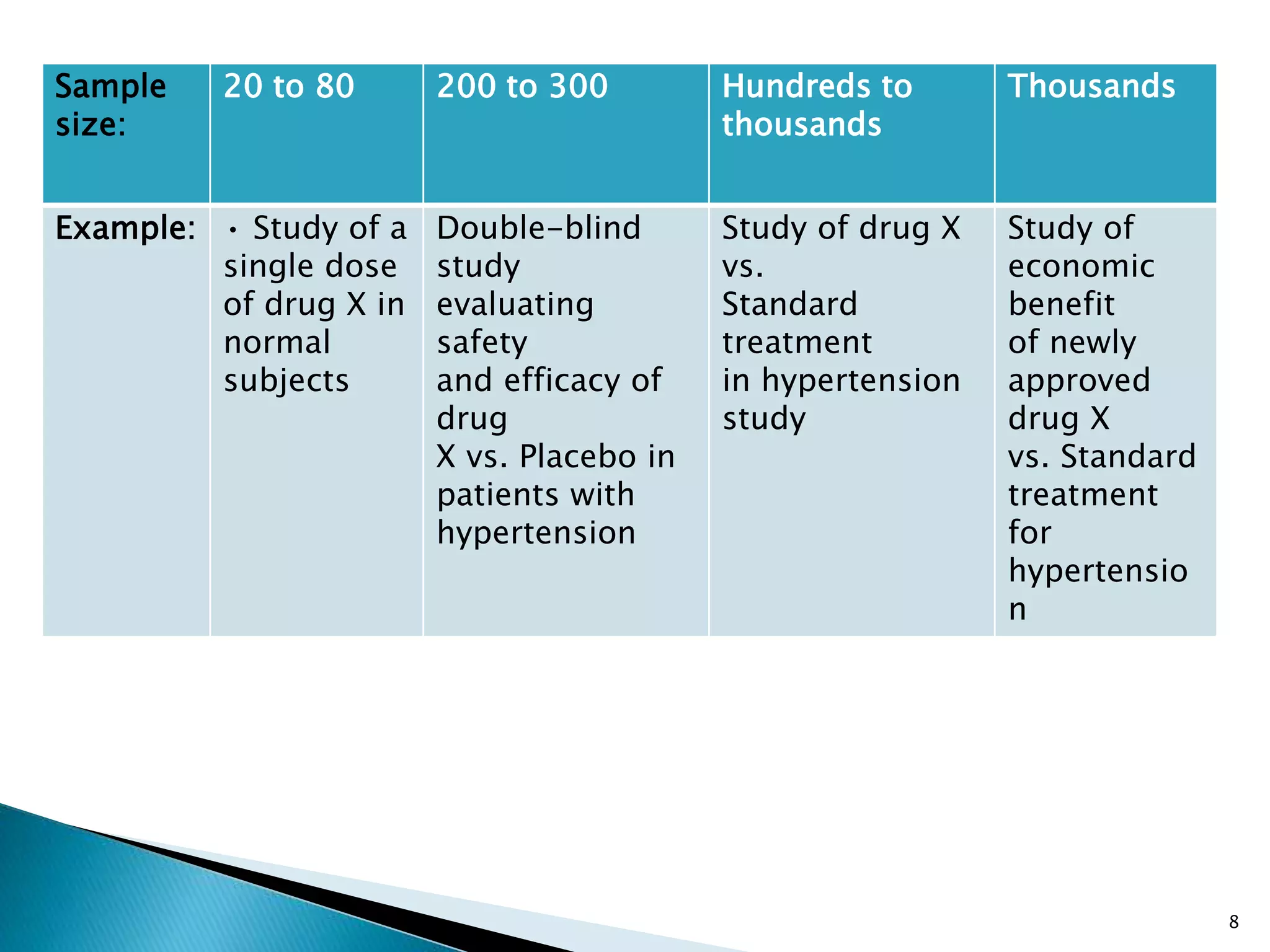
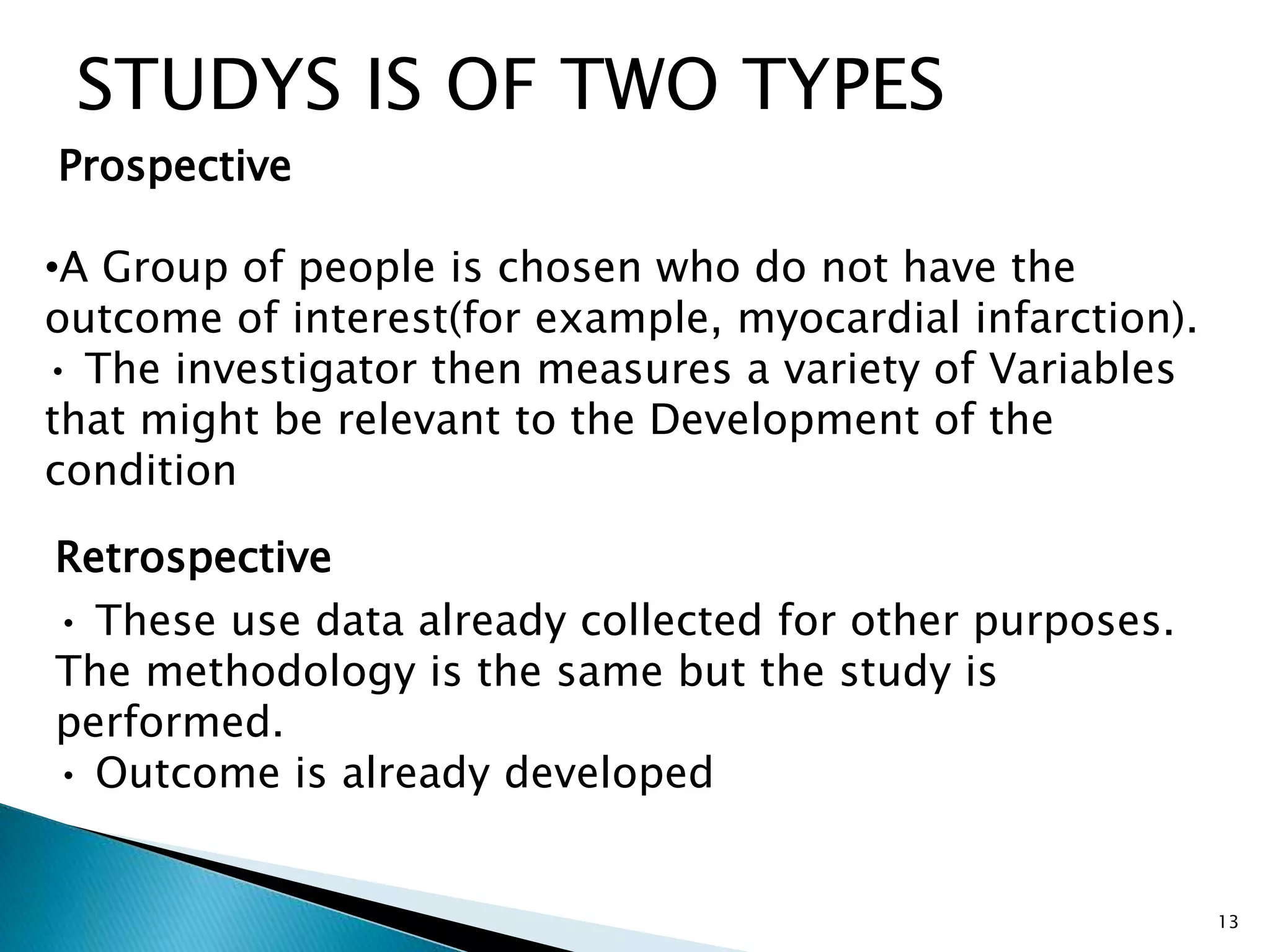
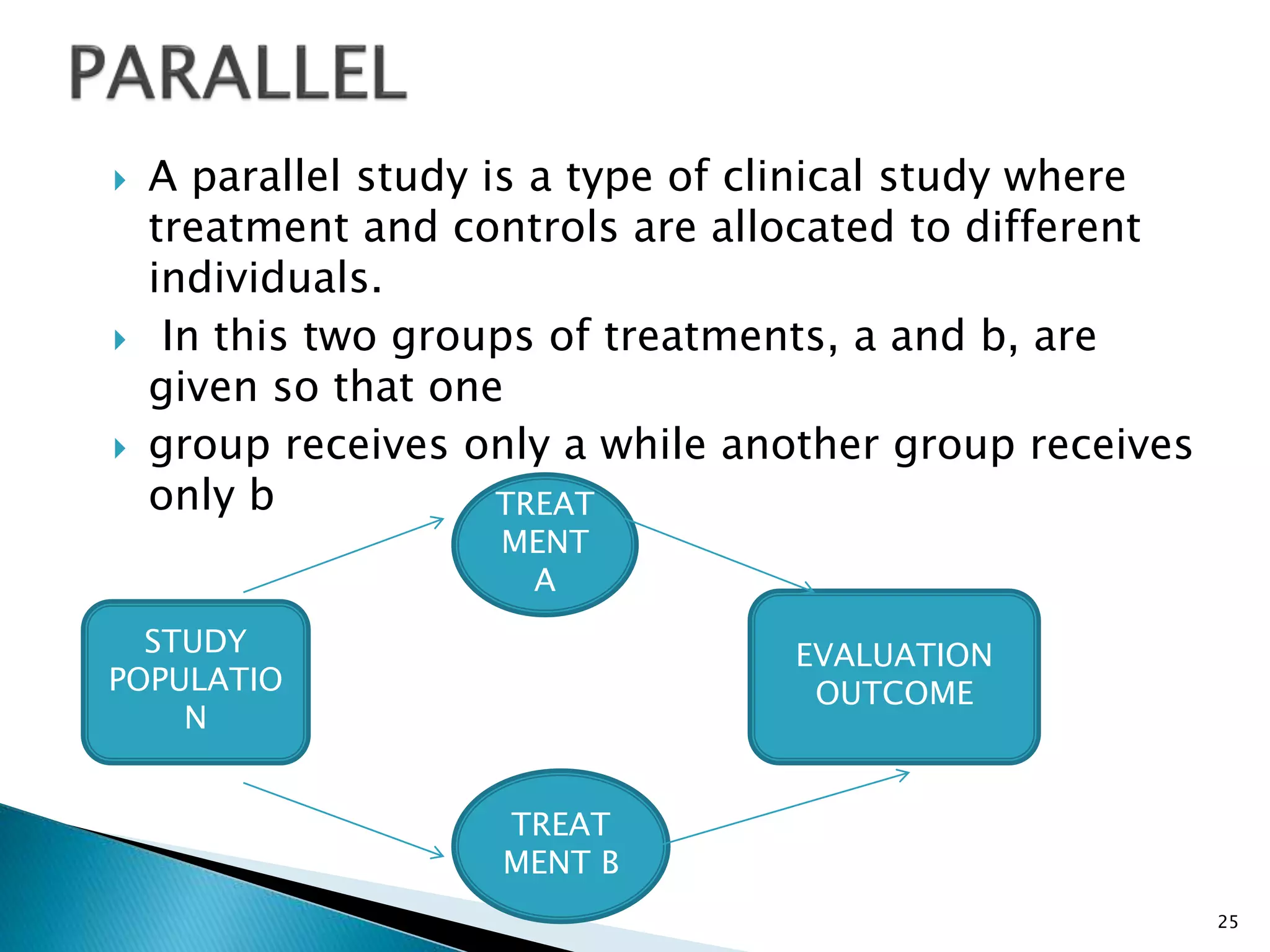
Clinical trials are conducted to test new drugs, treatments or medical devices in humans to assess their safety and efficacy. There are four main phases of clinical trials:
Phase I trials involve small groups of people to determine basic safety and dosing requirements. Phase II trials expand the testing to more people to determine efficacy and further evaluate safety. Phase III trials involve large groups of people to confirm effectiveness, monitor side effects, compare to commonly used treatments and collect information to allow safe use of the intervention. Phase IV trials occur after the intervention has been marketed to gather information on effects in various populations and any long-term side effects.