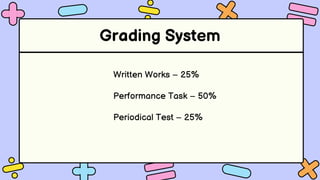
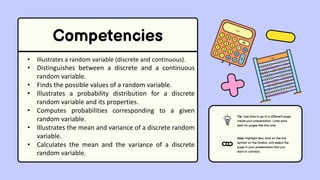
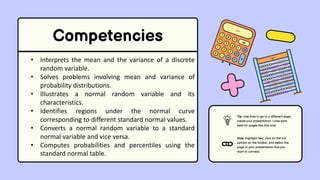
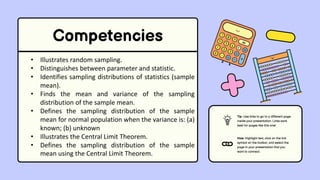
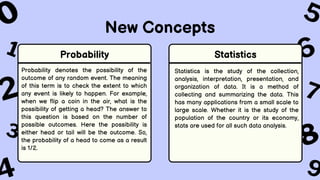
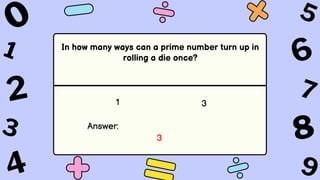
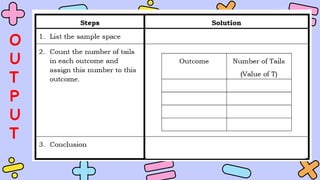
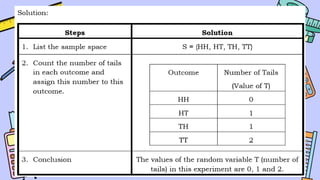
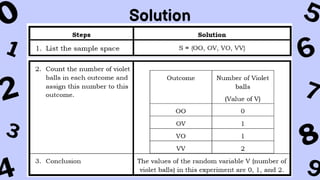
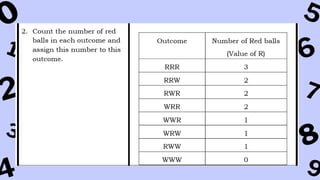
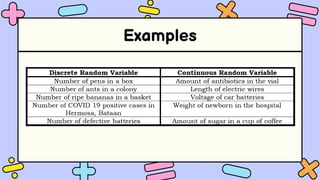
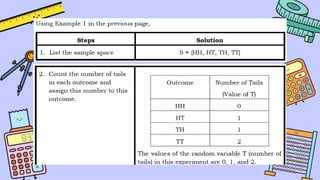
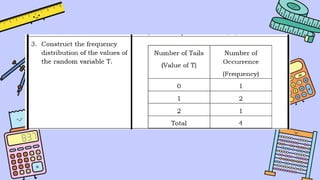
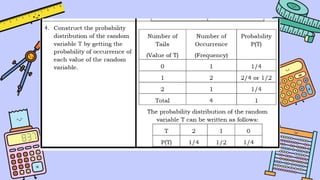
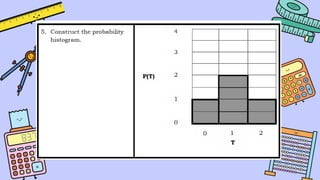
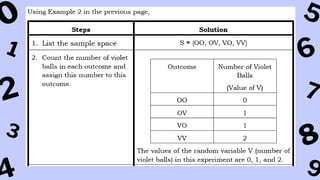
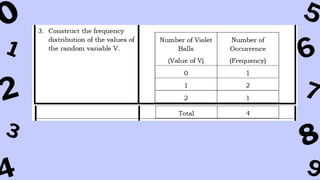
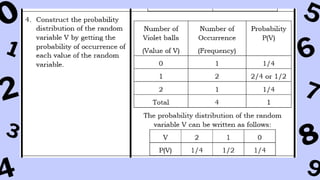
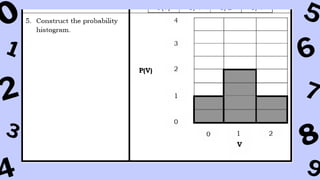
The document discusses key concepts in statistics and probability. It provides details on grading systems, competencies, definitions, and examples. The grading system includes weights for written works, performance tasks, and periodical tests. Competencies cover topics like random variables, probability distributions, sampling, and confidence intervals. Definitions explain probability as dealing with chance while statistics analyzes data. Examples illustrate concepts like sample spaces, events, and discrete vs. continuous random variables.