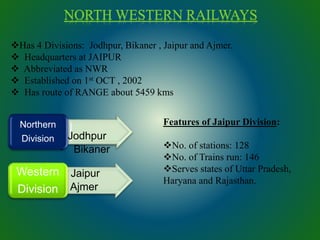
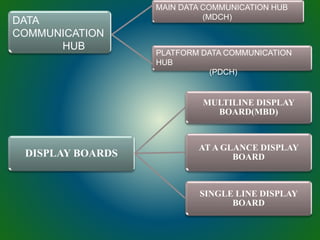
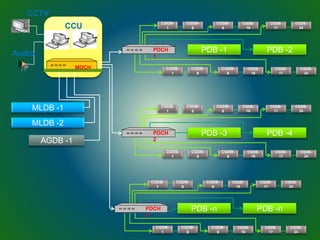
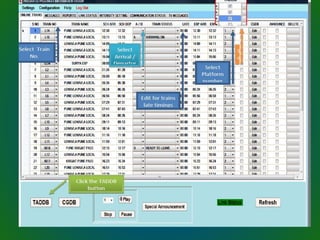
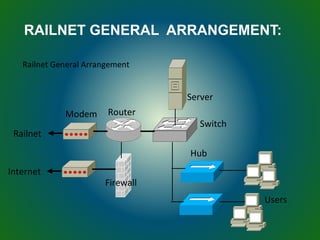
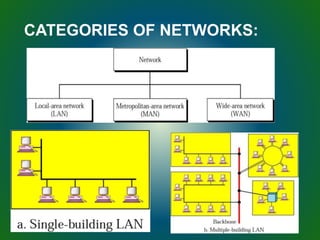
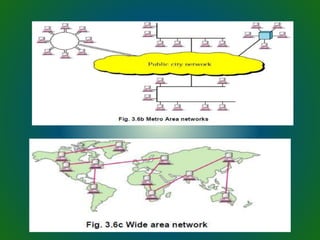
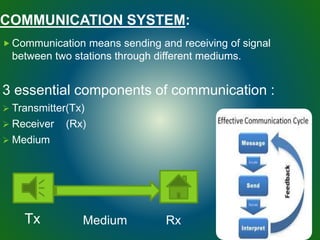
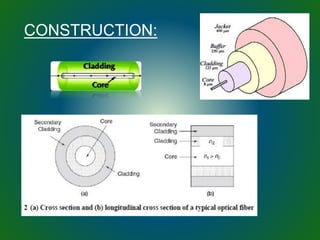
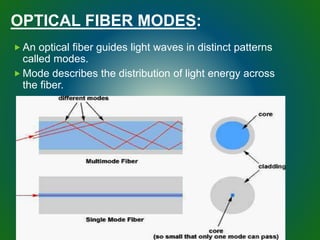
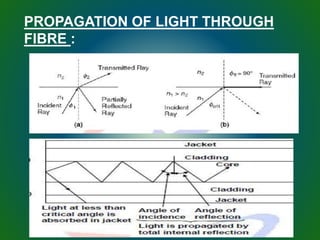
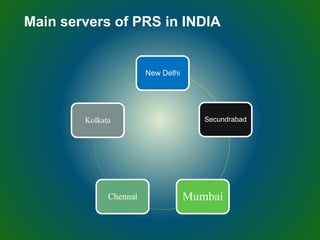
The document discusses technologies used in Indian Railways. It describes the Integrated Passenger Information System (IPIS) which provides audio and visual arrival/departure information to passengers. It also discusses Railnet, the internal communication network for Indian Railways, and various communication systems used like microwave and optical fiber. The document also summarizes the passenger reservation system, signaling systems and some interesting facts about Indian Railways.