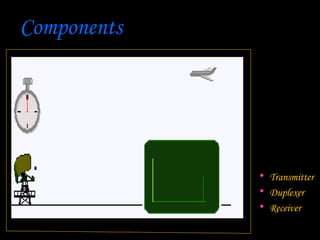
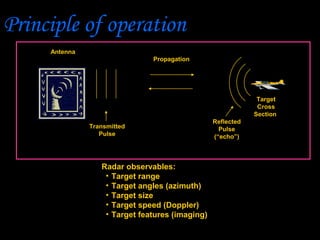
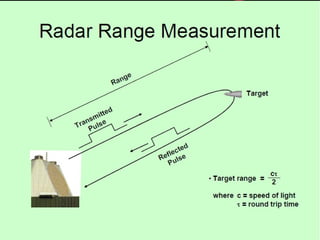
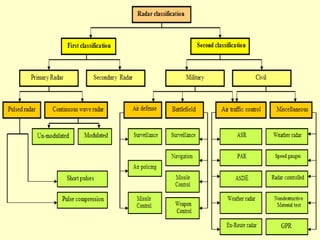
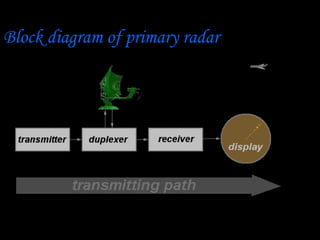
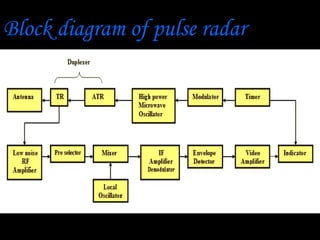
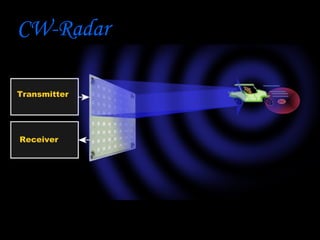
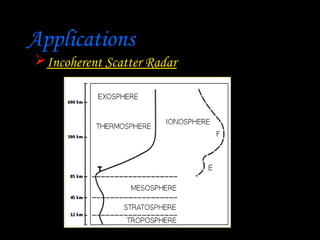
Radar, which stands for Radio Detection and Ranging, is a system that uses radio waves to detect distant objects and determine their range, angle, or velocity. It works by transmitting pulses of radio waves that reflect off objects back to the radar receiver. By measuring the time delay and Doppler shift of the reflected signals, radar can calculate properties of detected objects such as distance, direction, speed and dimensions. Radar has many applications including air traffic control, weather monitoring, and military uses such as air defense systems.