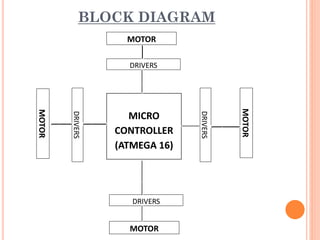
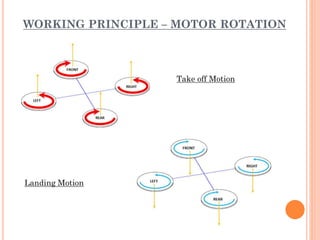
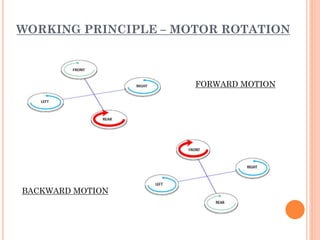
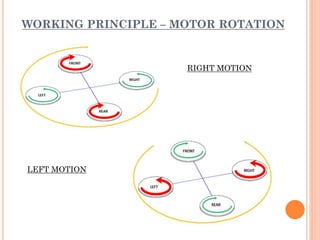
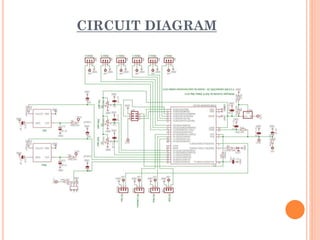
A quadcopter is a type of unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) that uses four rotors for lift and propulsion, allowing independent flight controlled by varying motor speeds. It has several advantages, such as safer flight in challenging environments and simpler design, but faces challenges related to ambitious development timelines and funding. Applications include military surveillance and commercial aerial imagery, although regulations limit commercial use in some areas.