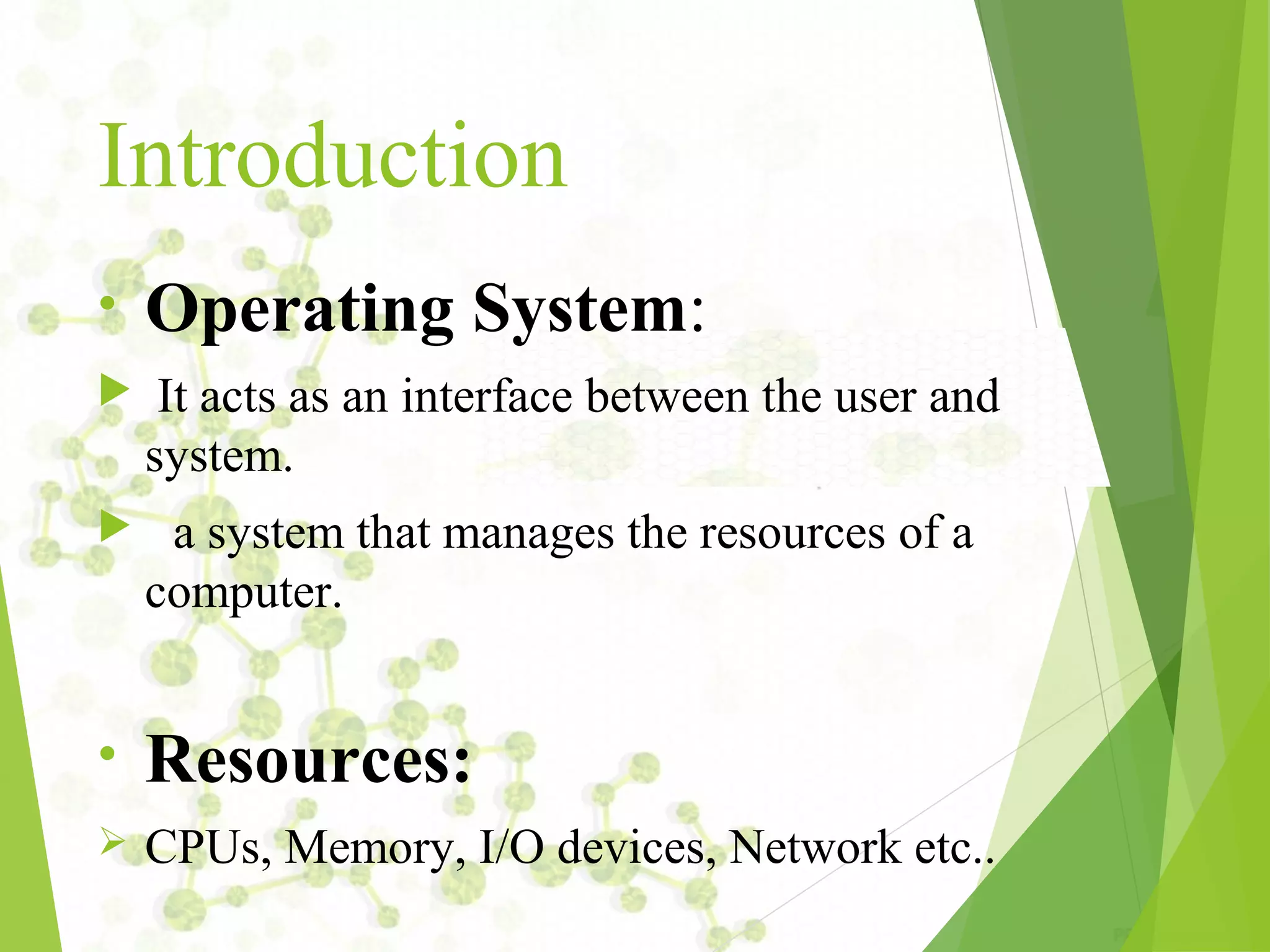
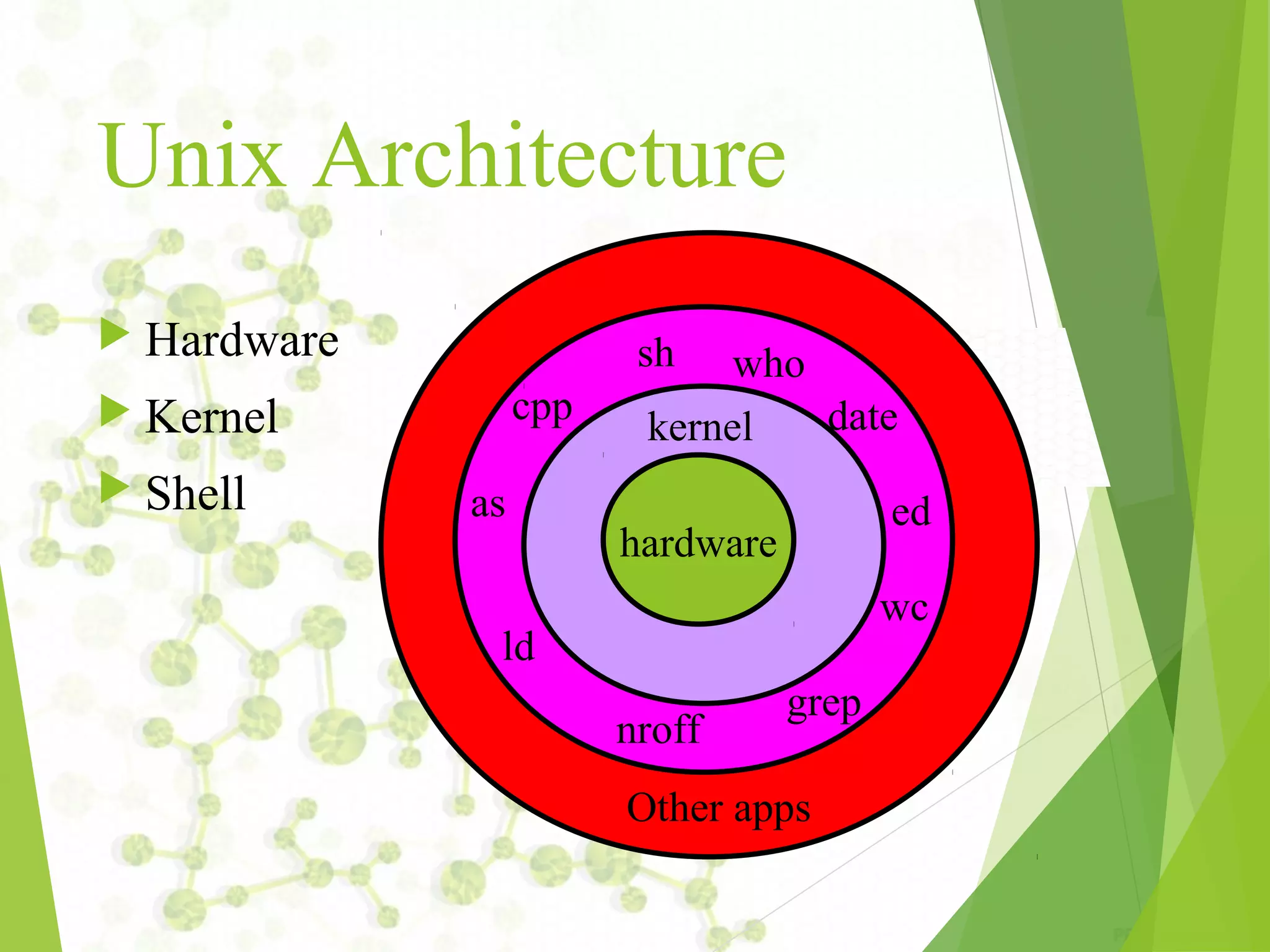
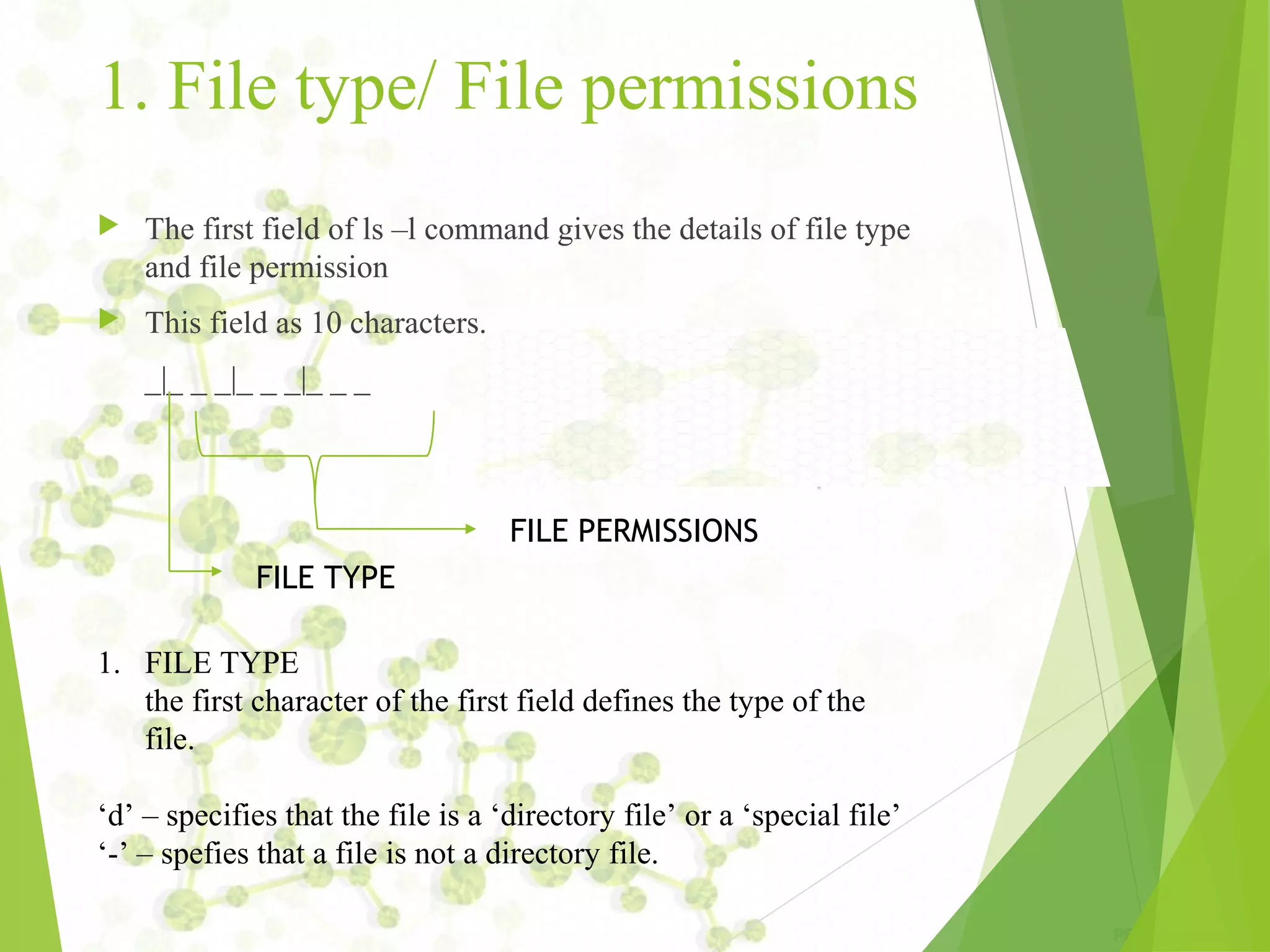
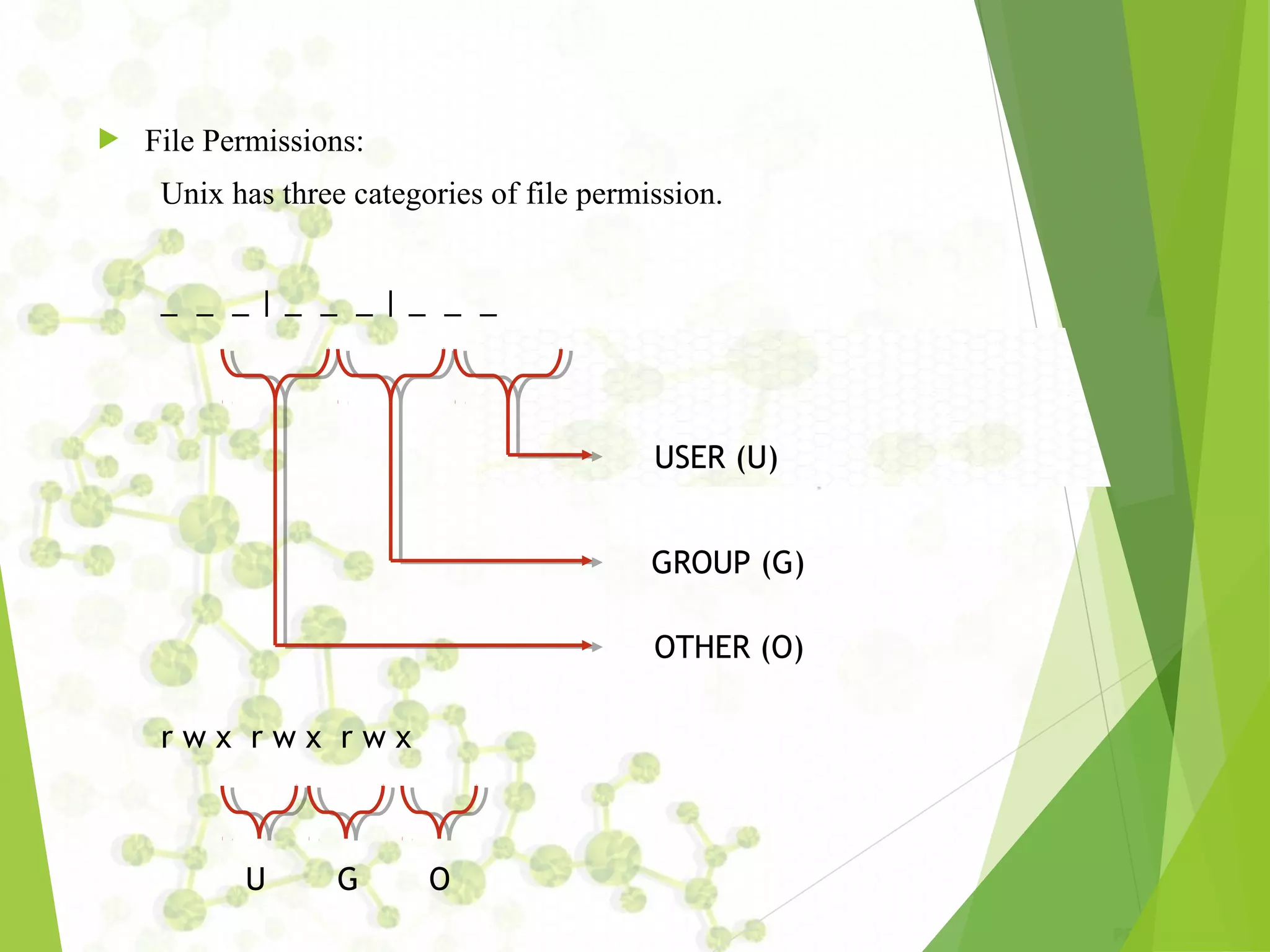
The document provides an introduction to UNIX operating systems, detailing their architecture, major components, and the role of the kernel, shell, and file management. It covers essential commands for file handling, user management, permissions, and regular expressions, along with explanations of file attributes and links. Additionally, it describes how to perform various administrative tasks within a UNIX environment.








![To change file Permission
‘chmod’ command is used to change the permissions of
the file.
USAGE: chmod [options] mode[,mode] file1 [file2 ...]
Unix allows the user to specify modes in two ways.
1. Absolute
2. Relative
1. Absolute:
in this we use a series of 3 octal numbers to specify
the permission of a file.
Ex: chmod 501 demo.txt, chmod 777 demo.txt](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unixnotes-part1-170214102205/75/QSpiders-Unix-Operating-Systems-and-Commands-13-2048.jpg)




![ln Command
This command is used to create link for a file.
USAGE: ln [option] target link_name
ex: ln file1 file2
‘-s’ option is used to provide a soft link.
USAGE: ln –s target_file Link_name
ex: ln –s file1 file3](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unixnotes-part1-170214102205/75/QSpiders-Unix-Operating-Systems-and-Commands-18-2048.jpg)





![File Handling
commands
•
•
mkdir – is used to create directories
Usage: mkdir [OPTION]
DIRECTORY...
ex: mkdir demo
ls – is used to list all the files and
subdirectories
of the current directory.
Usage: ls [OPTION]... [FILE]...
eg. ls, ls l, ls l demo](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unixnotes-part1-170214102205/75/QSpiders-Unix-Operating-Systems-and-Commands-24-2048.jpg)
![File
Handling(contd...)
• pwd - print name of current working directory
Usage: pwd
• cd change directories
Usage: cd [DIRECTORY]
eg. cd demo
Note: the Directory can be a relative or absolute path
of Directory](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unixnotes-part1-170214102205/75/QSpiders-Unix-Operating-Systems-and-Commands-25-2048.jpg)
![cp – copy files and directories
Usage: cp [OPTION]... SOURCE DEST
Examples:
1. cp file1 file2
cp a.txt b.txt
2. cp file 1 file2…. filen directory
cp file1 file2 /home/user/demo](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unixnotes-part1-170214102205/75/QSpiders-Unix-Operating-Systems-and-Commands-26-2048.jpg)
![mv – this command is used to move a file
from one directory to another
It is also used to rename a file.
Usage: mv [OPTION]... SOURCE DEST
eg. mv source.txt target_dir
mv old.txt new.txt
rm remove files or directories
Usage: rm [OPTION]... FILE... eg. rm file1.txt , rm rf
some_dir](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unixnotes-part1-170214102205/75/QSpiders-Unix-Operating-Systems-and-Commands-27-2048.jpg)
![• find – search for files in a directory
hierarchy
Usage: find [OPTION] [path]
[action]
eg. 1. find file1.txt,
2. find name file1.txt
• history – prints recently used commands
Usage: history](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unixnotes-part1-170214102205/75/QSpiders-Unix-Operating-Systems-and-Commands-28-2048.jpg)






![Metacharacters
^ (Caret)=match expression at the start of a line, as in
^A.
$ (Dollar)=match expression at the end of a line, as in
A$.
(Back Slash)=turn off the special meaning of the next
character, as in ^.
[ ] (Brackets)=match any one of the enclosed characters,
as in [aeiou]. Use Hyphen "-" for a range, as in [0-9].
[^ ]=match any one character except those enclosed in
[ ], as in [^0-9].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unixnotes-part1-170214102205/75/QSpiders-Unix-Operating-Systems-and-Commands-35-2048.jpg)


![Examples
grep '^From: ' demo.txt
grep '[a-zA-Z]'{any line with at least one
letter}
grep '[^a-zA-Z0-9]{anything not a letter or
number}
grep '[0-9]{3}-[0-9]{4}'{999-9999, like
phone numbers}
grep '^.$'{lines with exactly one character}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unixnotes-part1-170214102205/75/QSpiders-Unix-Operating-Systems-and-Commands-38-2048.jpg)
![ grep '"smug"'{'smug' within double
quotes}
grep '"*smug"*'{'smug', with or without
quotes}
grep '^.'{any line that starts with a
Period "."}
grep '^.[a-z][a-z]'{line start with "." and
2 letters}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unixnotes-part1-170214102205/75/QSpiders-Unix-Operating-Systems-and-Commands-39-2048.jpg)