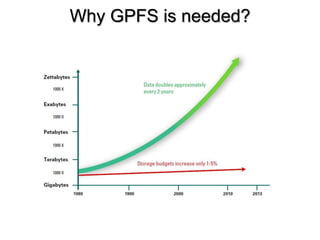
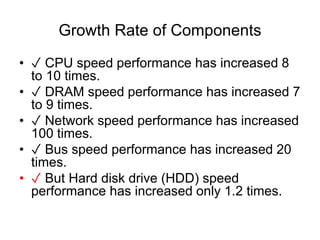
GPFS (General Parallel File System) is a high-performance clustered file system developed by IBM that can be deployed in shared disk or shared-nothing distributed parallel modes. It was created to address the growing imbalance between increasing CPU, memory, and network speeds, and the relatively slower growth of disk drive speeds. GPFS provides high scalability, availability, and advanced data management features like snapshots and replication. It is used extensively by large companies and supercomputers due to its ability to handle large volumes of data and high input/output workloads in distributed, parallel environments.


![Existing Solutions Inability
• DAS, NAS, SAN [alone]
• Many data centers have become victims of
“filer-sprawl”
• Data administration and management
(such as migration, backups, archiving)
costs to skyrocket!
• I/O performance & application workflow](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/4272d31a-c8c5-4c2b-8e77-68eb62b9d2fa-150903104546-lva1-app6891/85/IBM-GPFS-5-320.jpg)



