This document provides an overview of quality circles, including:
- A definition of quality circles as volunteer groups that identify and solve work-related problems to improve organizational performance.
- A brief history noting their creation in Japan in 1962 and later spread internationally.
- An explanation of the need for quality circles to improve efficiency and customer satisfaction in both public and private sectors.
- Details on the typical structure of quality circles including roles for members, leaders, facilitators, coordinators, and management oversight.
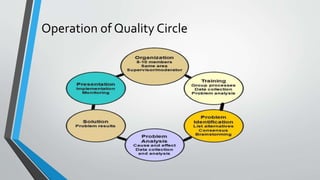
- The process quality circles follow including problem identification, analysis, solution selection, and presenting recommendations to management.
- Potential benefits like reduced errors, improved teamwork and communication, and cost reductions