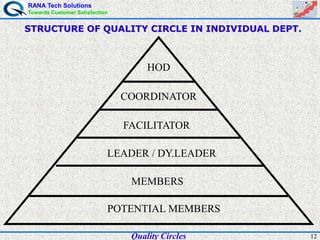
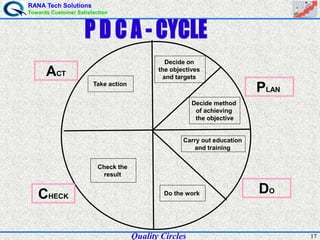
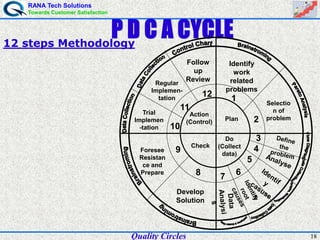
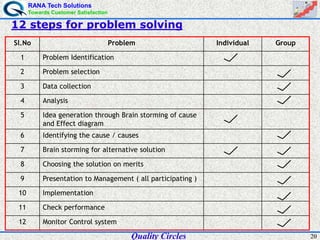
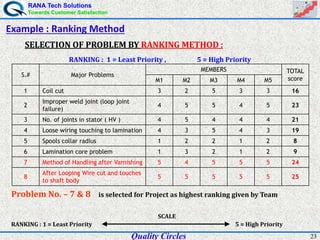
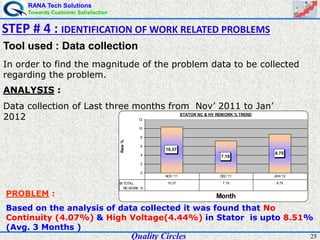
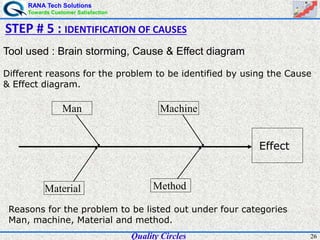
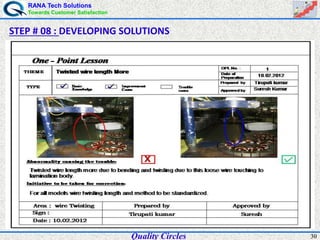
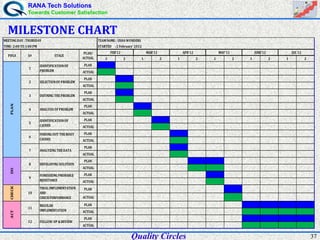
The document discusses quality circles, which are small groups of employees who voluntarily meet regularly to identify, analyze, and solve work-related problems. It provides definitions of quality from experts like Juran and Crosby. Quality circles evolved from craftsmanship to techniques like total quality management. The document also outlines the history and methodology of quality circles, beginning in Japan in the 1960s. It describes the roles of circle leaders and members and gives examples of problem-solving tools used in the 12-step methodology.