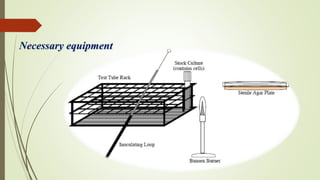
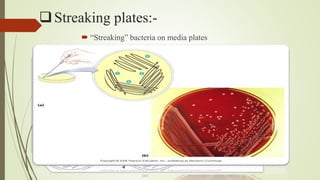
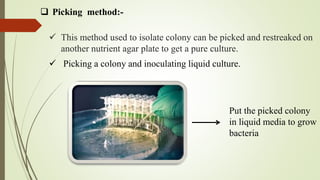
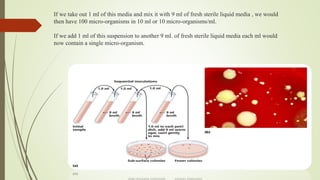
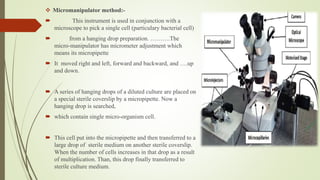
The document discusses various techniques for obtaining pure cultures of microorganisms, including streak plating, spread plating, serial dilution, and single cell isolation. Streak plating involves streaking bacteria across nutrient agar plates using a loop to separate individual colonies. Serial dilution uses successive dilutions of a mixed culture in liquid media to isolate a predominant microorganism. Single cell isolation picks a single cell from a culture using a micromanipulator or capillary pipette and allows it to multiply, producing a pure culture. These pure culture techniques are important for laboratory study of individual microbial species.