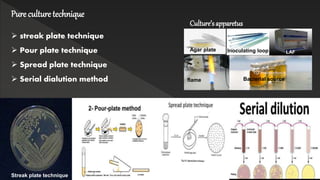
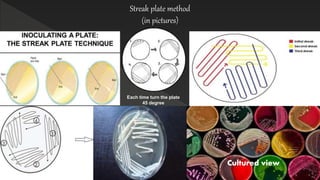
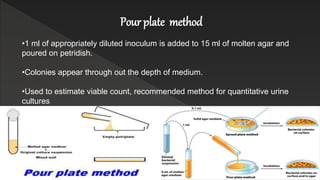
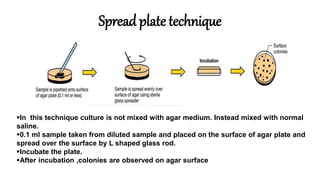
The document presents an overview of pure culture techniques used in microbiology, including methods like streak plate, pour plate, and spread plate techniques, which are essential for isolating and multiplying microbial organisms. It explains the importance of aseptic techniques to prevent contamination and the role of various culture media in obtaining pure cultures. The presentation emphasizes that not all microorganisms are harmful, highlighting the significance of understanding both beneficial and harmful microbes.