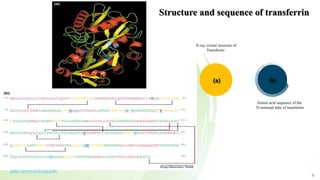
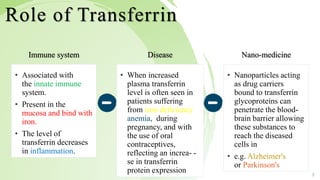
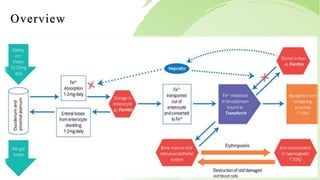
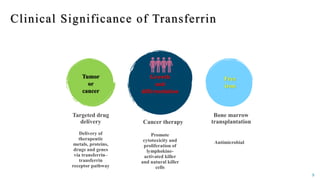
Transferrin is a 76 kDa glycoprotein encoded by the TF gene located on chromosome 3 that transports iron in the bloodstream. It is produced primarily in the liver and contains two binding sites for Fe3+ ions. The protein consists of two lobes, the N-lobe and C-lobe, each containing two subdomains made up of alpha helices and beta sheets. Four conserved amino acids play an important role in iron binding and release: two tyrosines, one aspartic acid, and one histidine. Transferrin transports iron throughout the body, and is important for processes like the immune response and cell growth and differentiation.