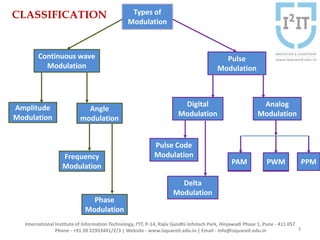
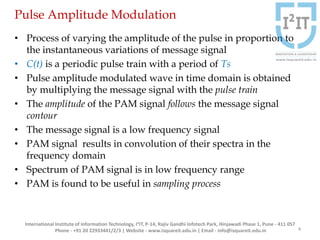
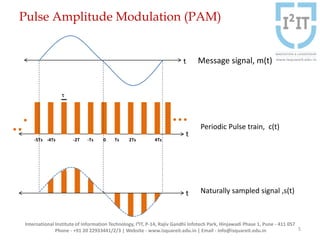
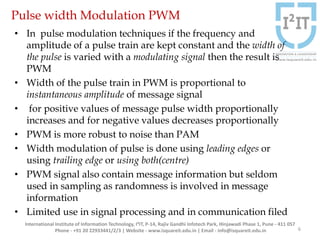
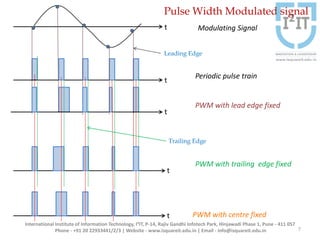
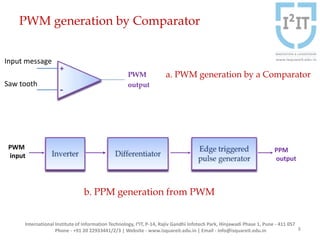
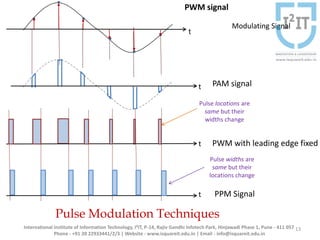
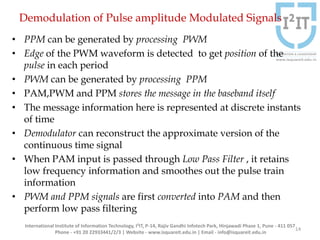
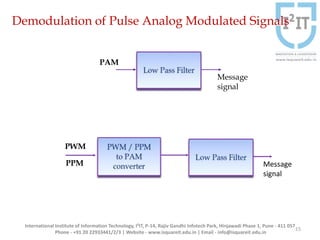
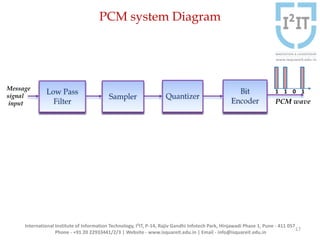
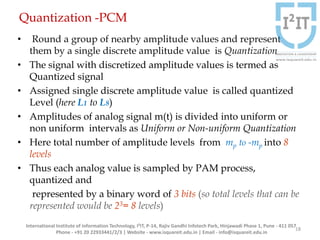
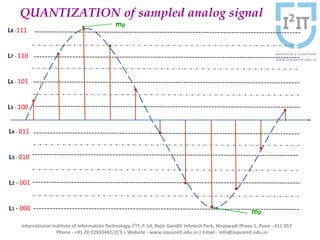
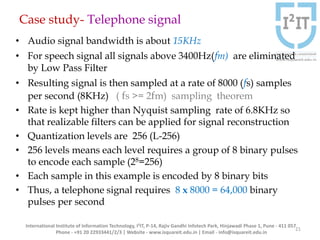
The document discusses various pulse modulation techniques, including Pulse Amplitude Modulation (PAM), Pulse Width Modulation (PWM), and Pulse Position Modulation (PPM), explaining their principles and applications. Notably, it emphasizes the importance of Pulse Code Modulation (PCM) for converting analog signals into digital format. Additionally, it covers the quantization process involved in ADC and provides case studies relevant to telephone and compact disc signals.