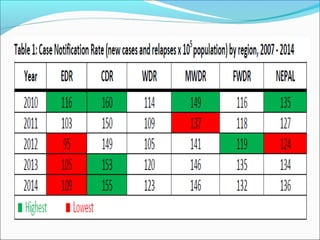
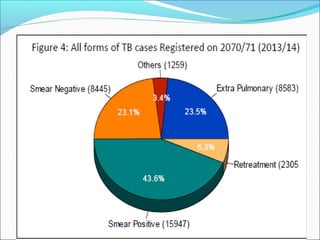
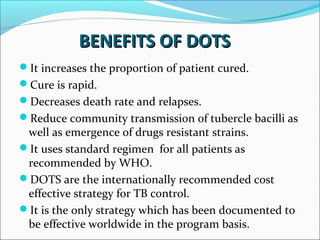
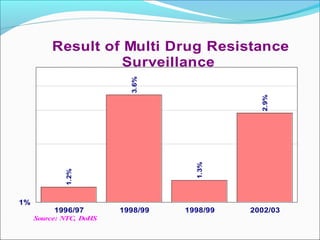
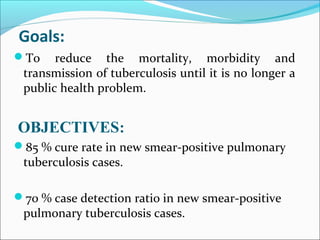
Tuberculosis is an infectious disease caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis that primarily affects the lungs. The cardinal signs of pulmonary TB include chronic cough lasting more than 2-3 weeks, chest pain, fever, night sweats, and weight loss. TB transmission occurs via airborne droplets. Nepal has a high burden of TB and implements the WHO-recommended DOTS strategy for prevention and control, which involves directly observed treatment to improve adherence and cure rates. Expansion of DOTS nationwide and addressing issues like drug-resistant TB and co-infection with HIV are national policy priorities.