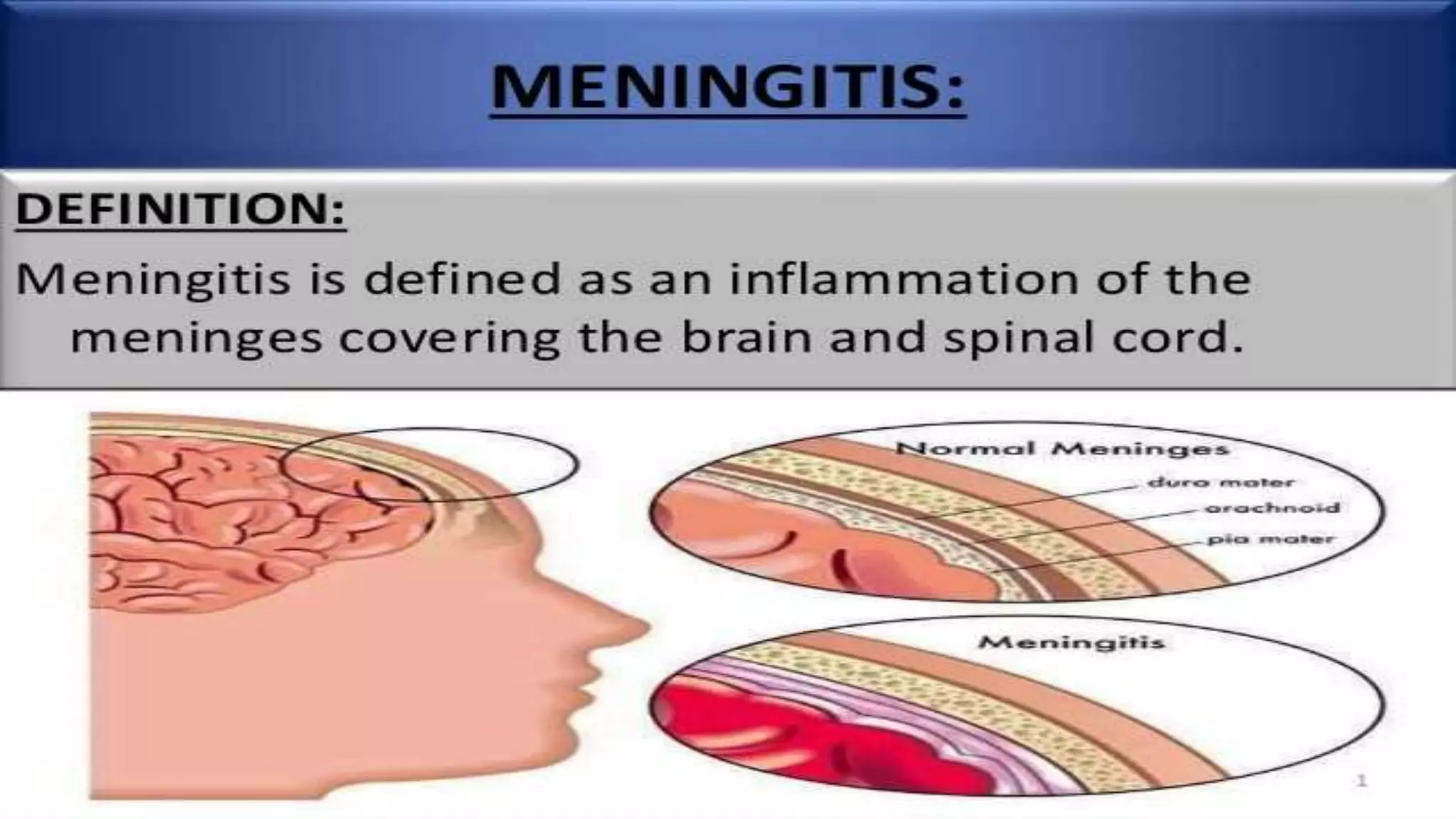
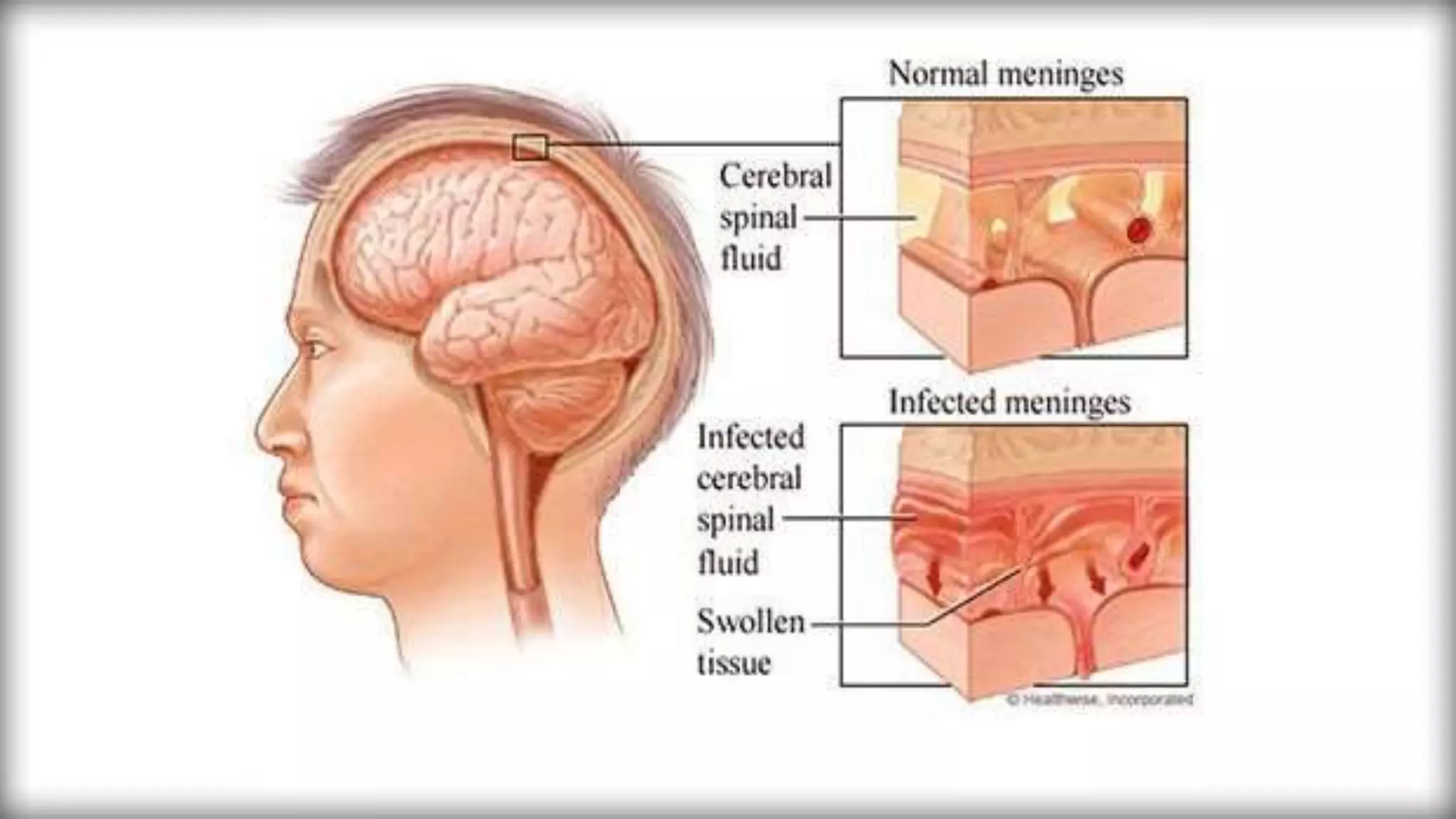
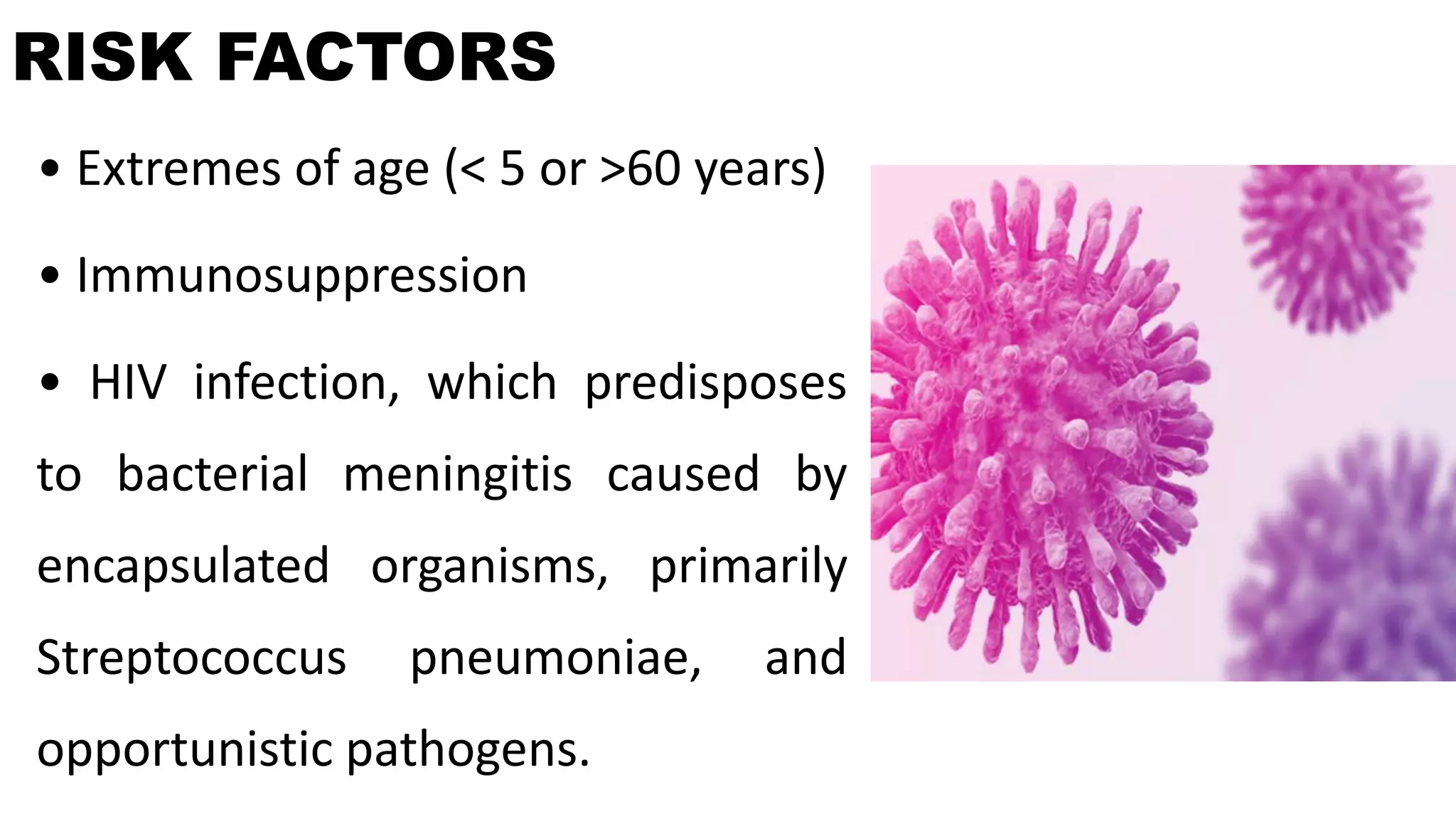
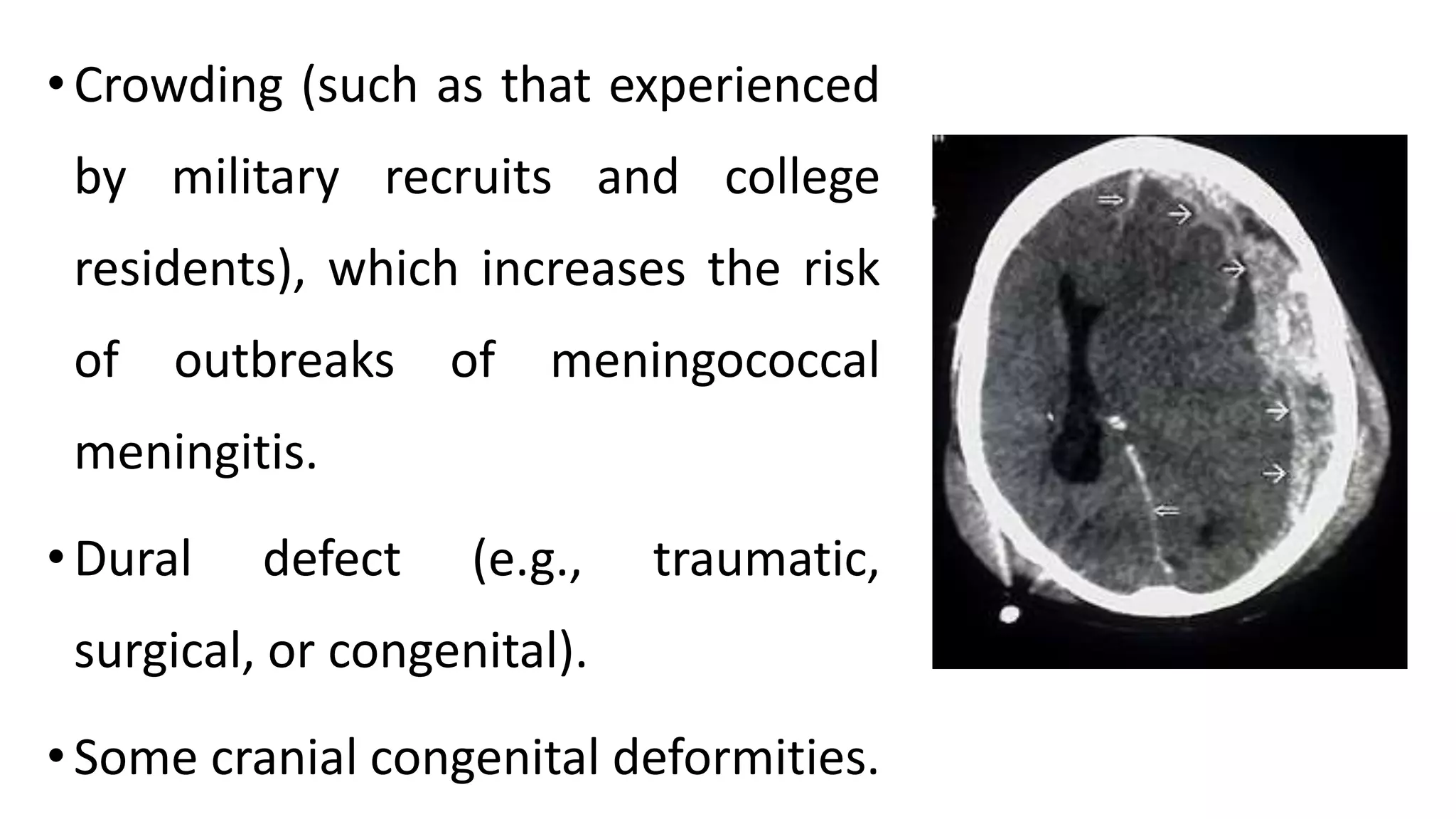
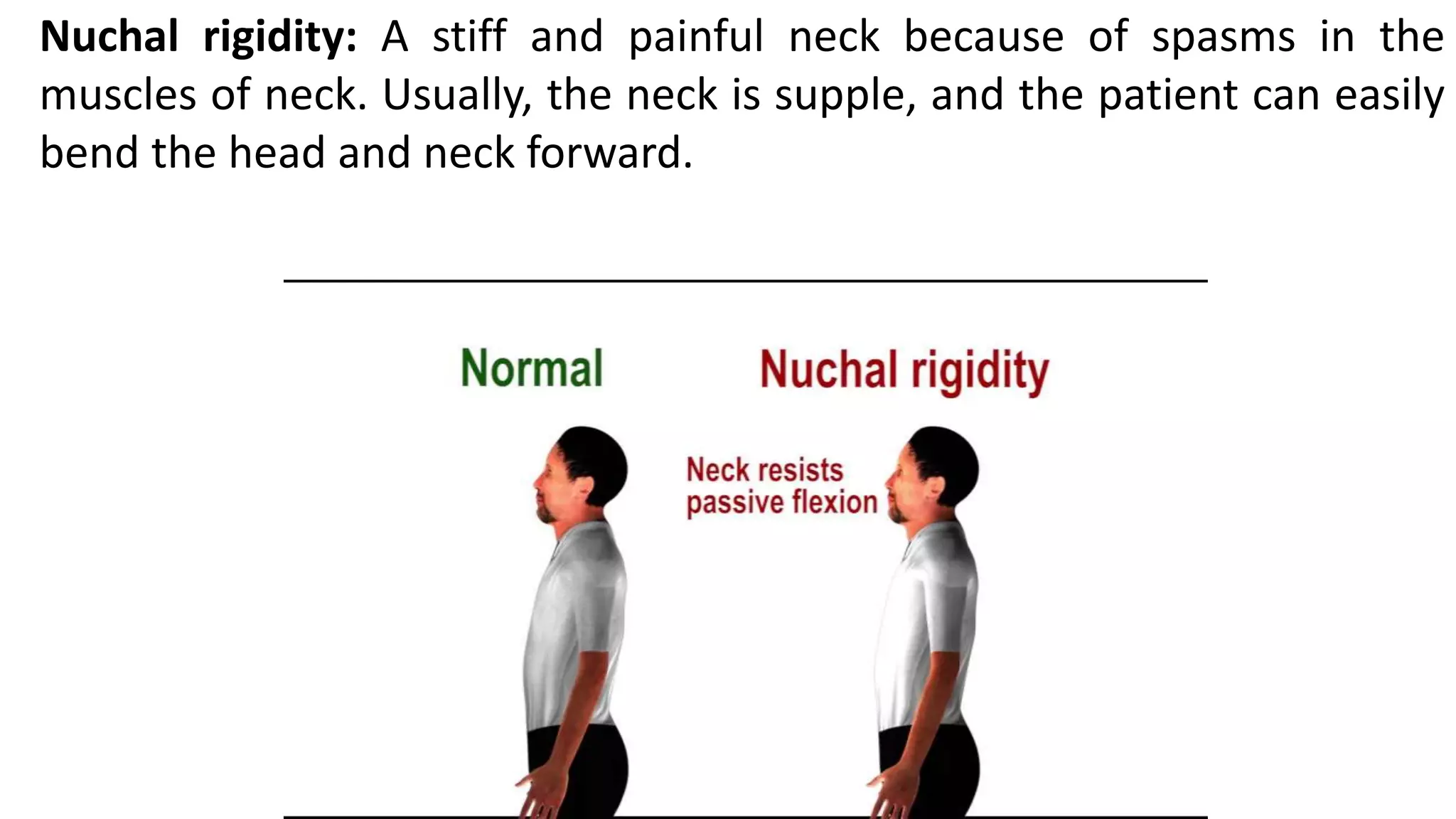
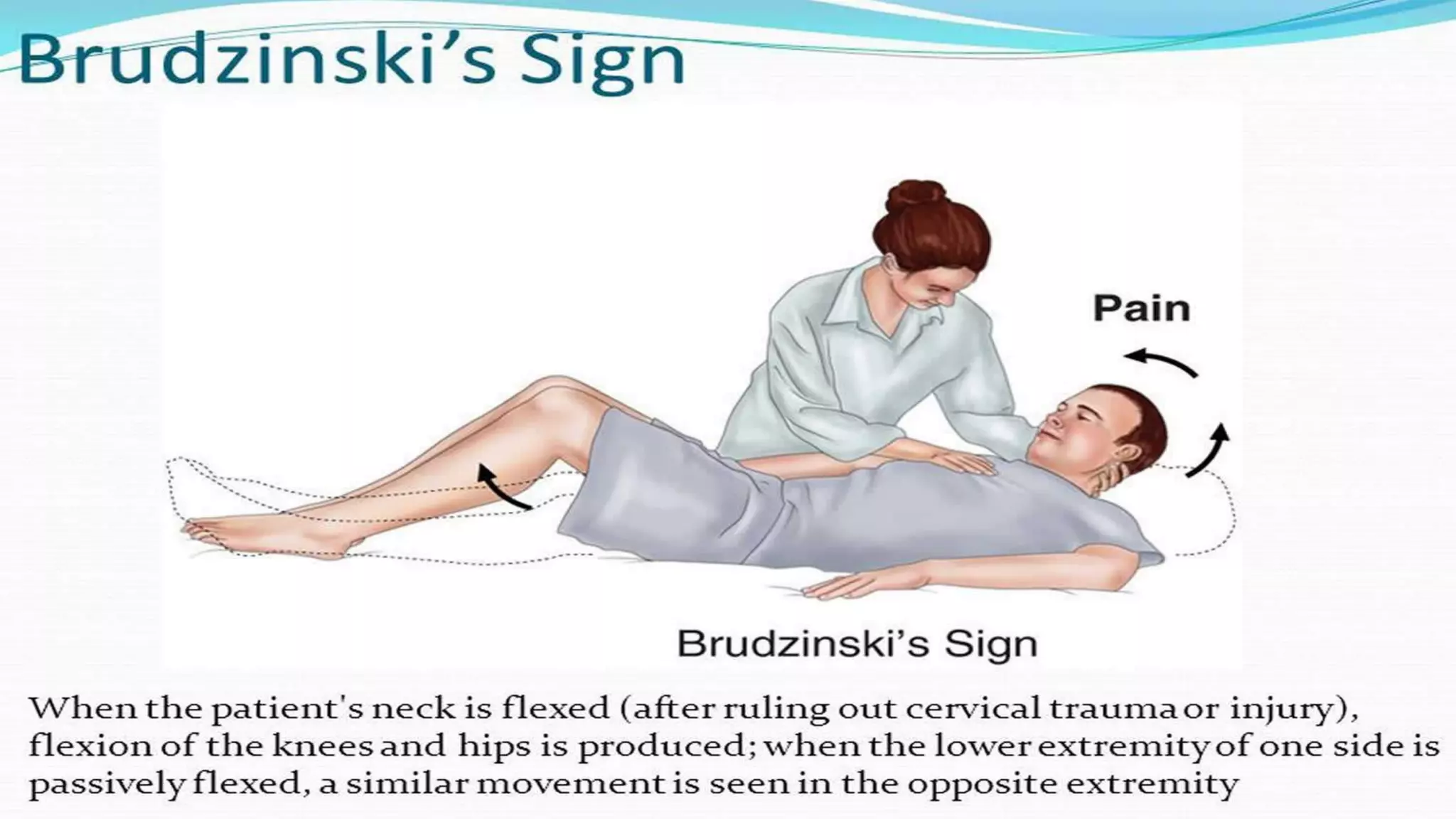
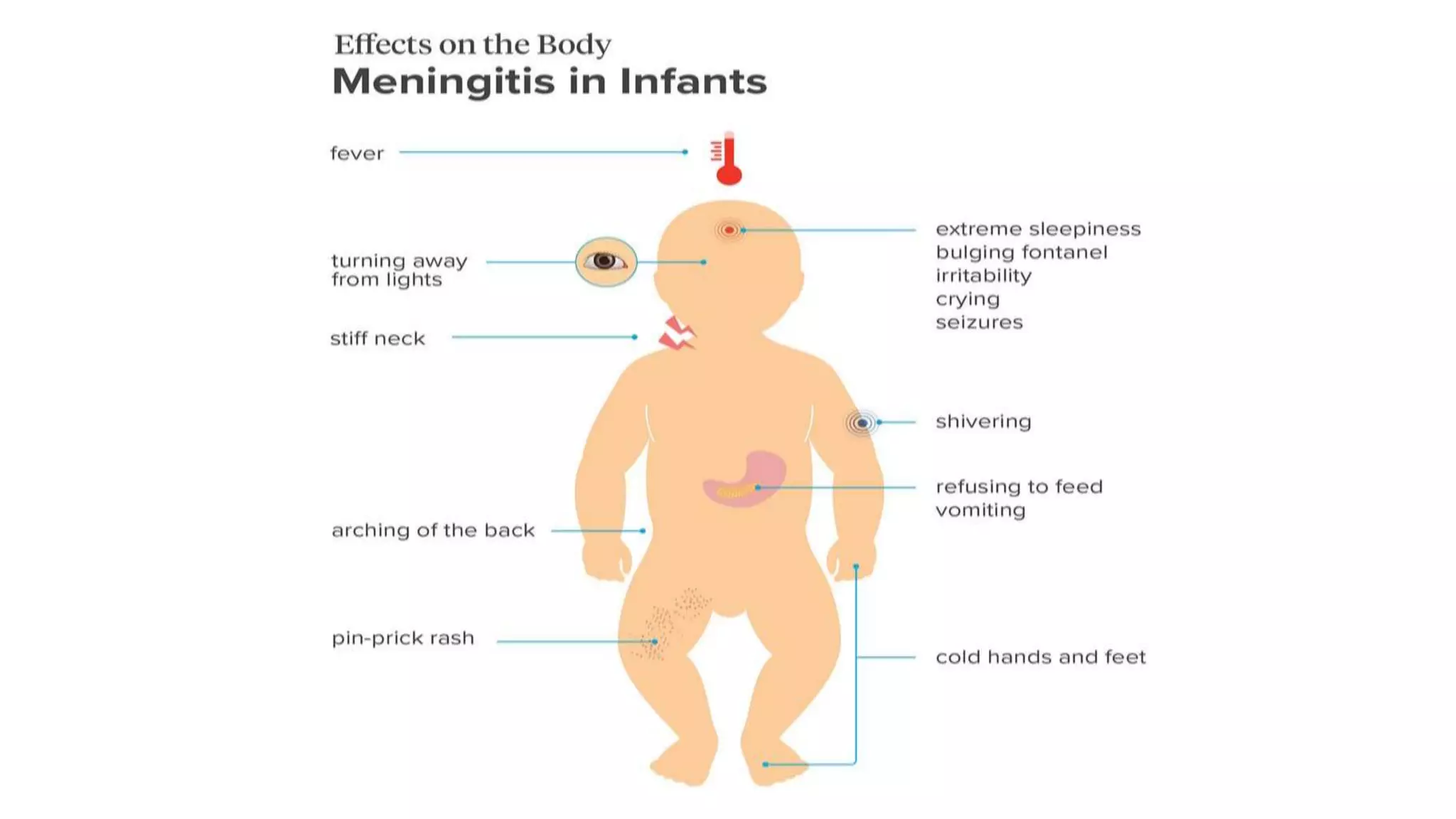
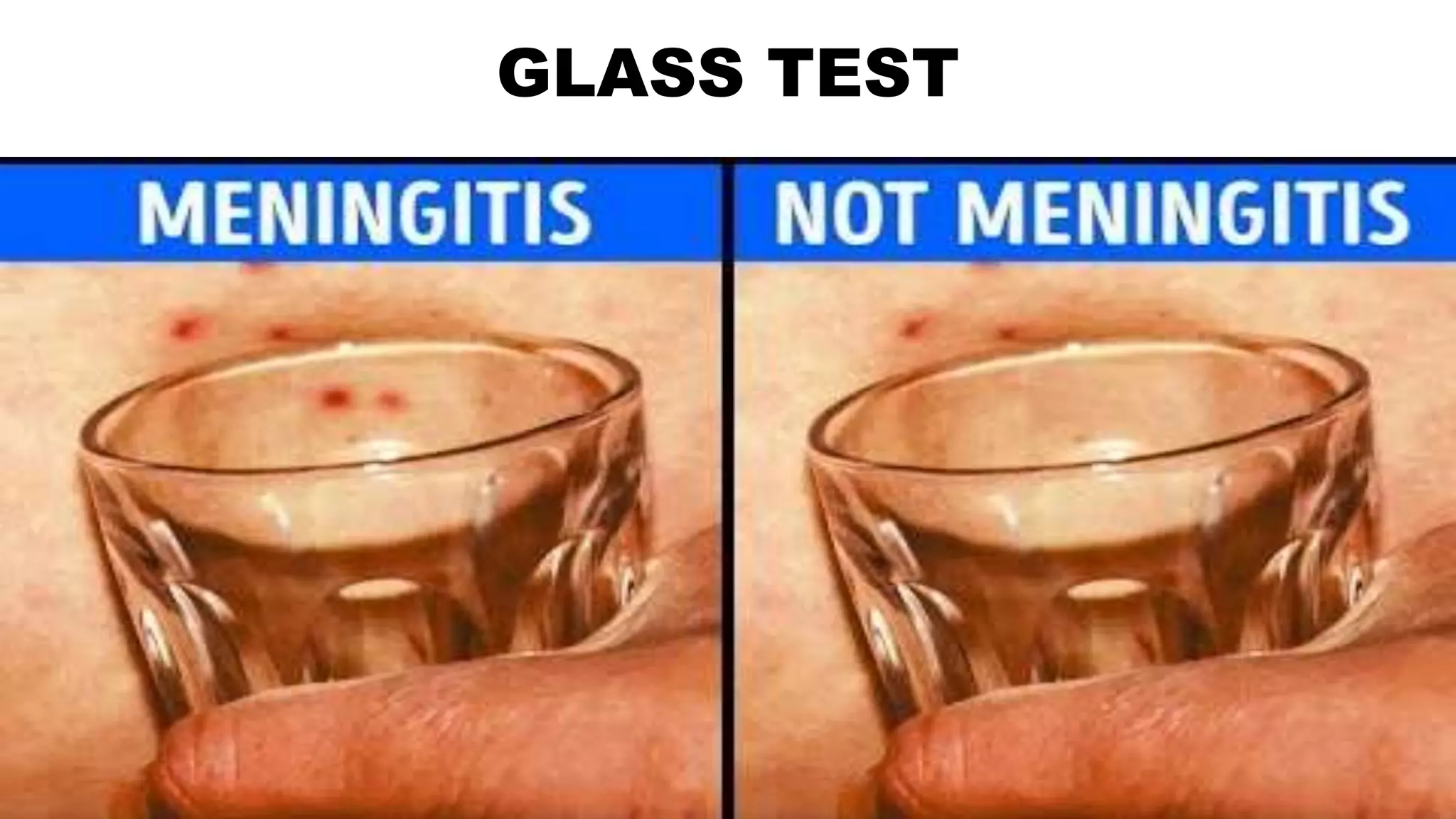
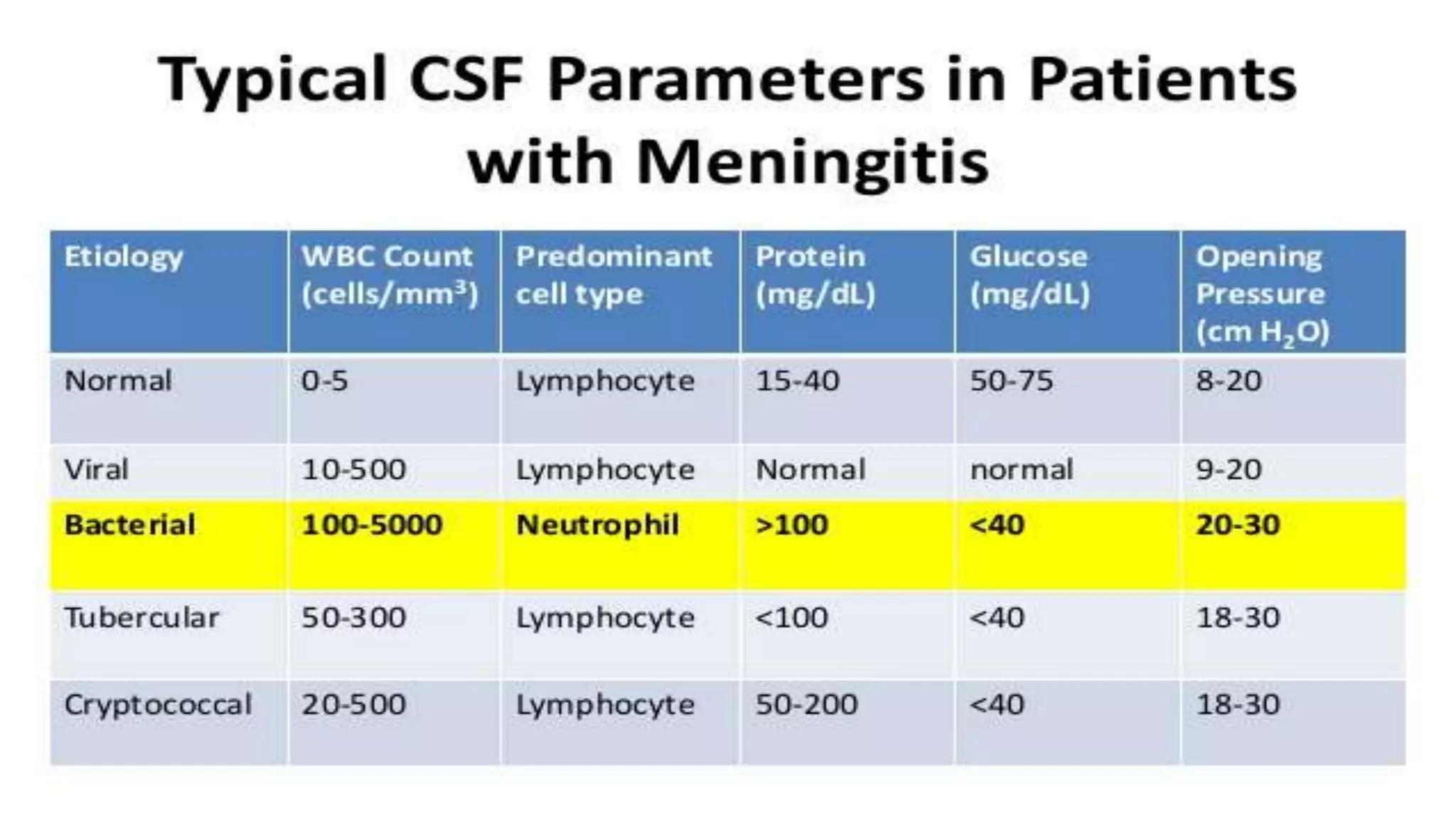
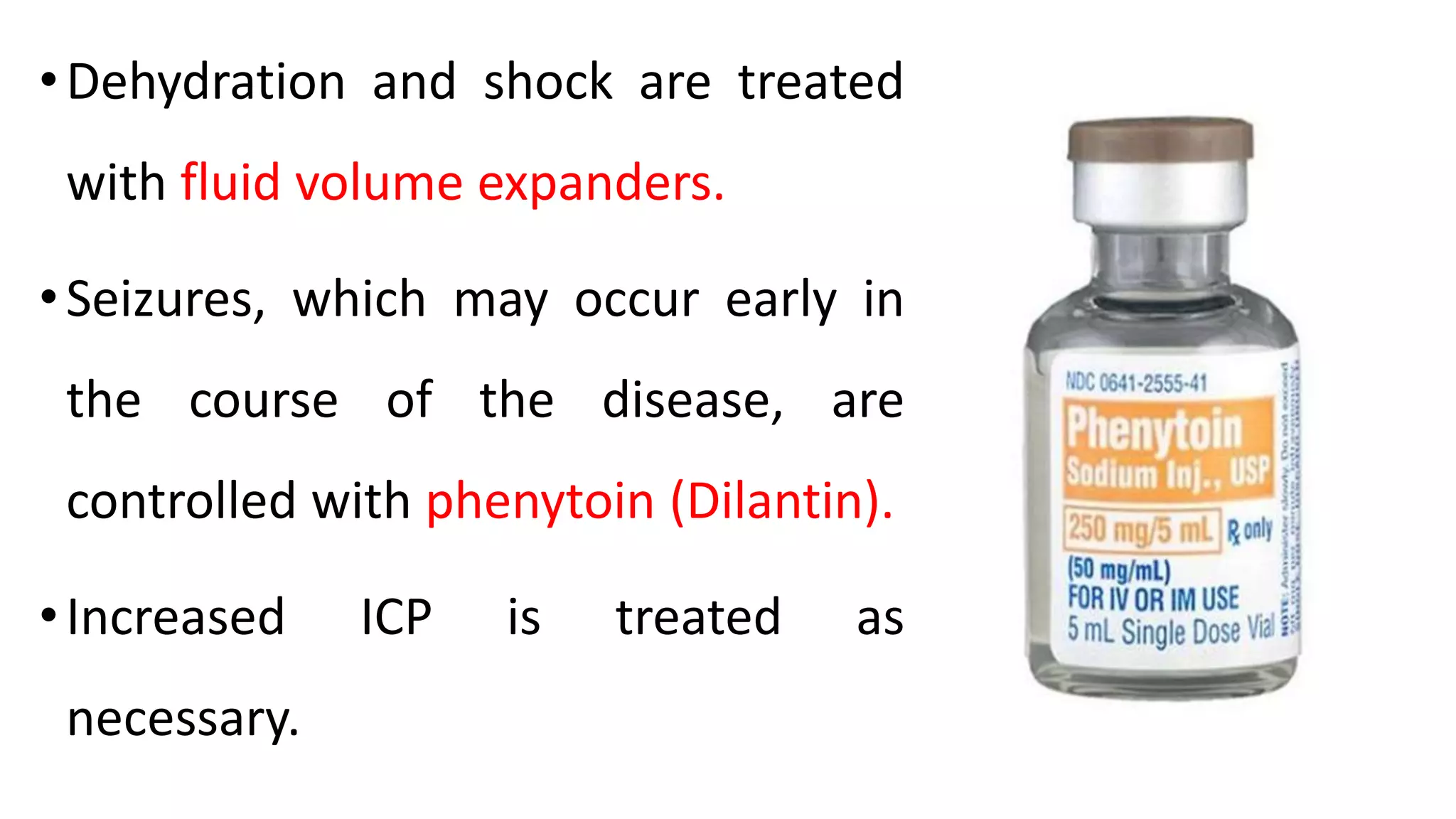
Meningitis is an inflammation of the meninges that can be caused by bacterial, viral, fungal or parasitic infections. Bacterial meningitis is the most common and can be life-threatening if not treated promptly with antibiotics. Symptoms include headache, fever, neck stiffness, nausea and altered mental status. Diagnosis involves lumbar puncture, culture and analysis of cerebrospinal fluid. Treatment focuses on identifying the causative organism and administering the appropriate antibiotics, antivirals or antifungals. Outcomes depend on early diagnosis and treatment, with sequelae including hearing loss, neurological deficits, and death.