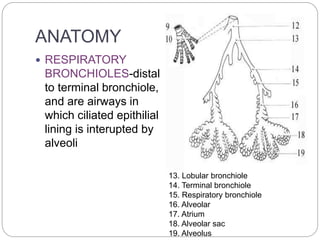
Small airways disease refers to pathologies that affect the small conducting airways less than 3mm in diameter. CT scanning is the imaging modality of choice for evaluating small airways disease. On HRCT, direct signs of small airways disease include thickened airway walls, dilated or obliterated airways, and nodules. Indirect signs include air trapping, subsegmental atelectasis, centrilobular emphysema, and centrilobular nodules. Common patterns seen on HRCT include tree-in-bud, poorly defined centrilobular nodules, decreased lung attenuation, and ground glass opacities with consolidation.