1) Pulmonary drug delivery involves administering drugs to the lungs for treating respiratory diseases and enabling systemic delivery. Drugs readily pass into the bloodstream without enhancers from the lungs.
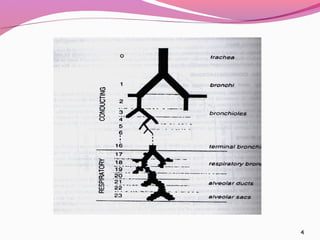
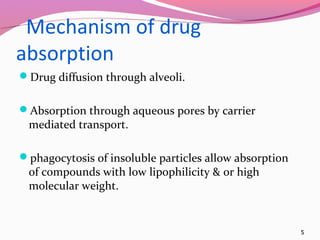
2) The pulmonary system consists of two regions - the conducting zone which branches into smaller tubes, and the respiratory zone containing alveoli where gas exchange occurs. Drugs are absorbed via diffusion, carrier-mediated transport, or phagocytosis of particles.
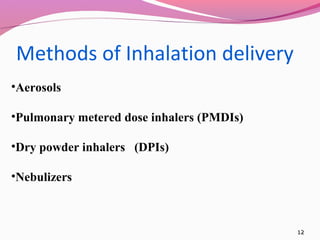
3) Common pulmonary delivery methods include metered dose inhalers, dry powder inhalers, and nebulizers. Each method has advantages like direct delivery and rapid onset but also limitations like cost and potential irritation.