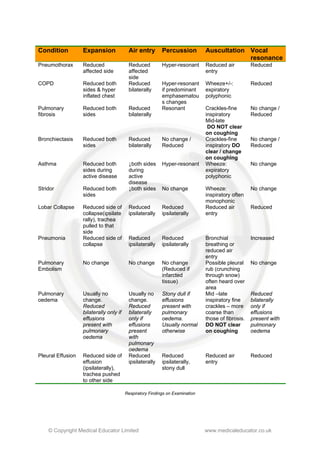
- The document provides guidance on performing a respiratory exam, including positioning the patient, inspecting the patient and areas around the bed, examining the hands, face, neck, chest, and auscultating breath sounds.
- Key steps are inspecting for signs of distress, noting peripheral clues, assessing expansion and movements of the chest, percussion findings, breath sounds, and timing of crackles.
- Performing techniques like assessing forced expiratory time can help evaluate for obstructive lung diseases like COPD.