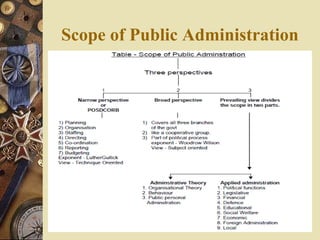
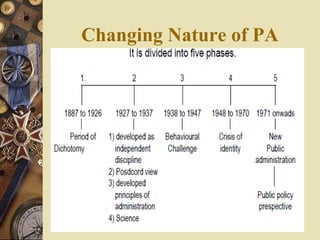
Public administration involves managing and administering public/government affairs. It has evolved over time from traditional public administration to development administration and new public administration. Traditional public administration focused on efficiency and following rules, while development administration emphasizes goals, participation, decentralization and planning for change. New public administration rejects being value-neutral and instead focuses on social equity, being client-oriented, and qualitative transformation through decentralization. The key functions of public administration include planning, organizing, staffing, directing, coordinating, reporting and budgeting.