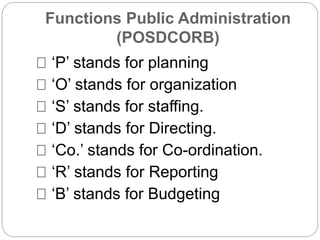
Public administration refers to the implementation of government policies and programs to serve the public. It involves the management of public programs and agencies. The document outlines several definitions of public administration provided by different scholars. It discusses the key functions of public administration such as planning, organizing, staffing, directing, coordinating, reporting and budgeting.
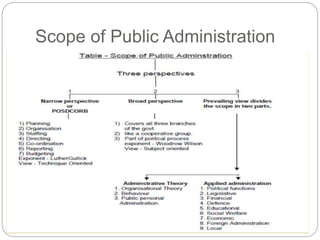
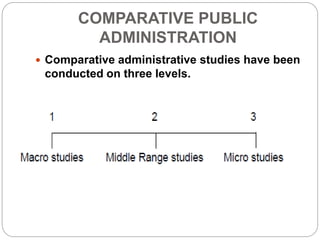
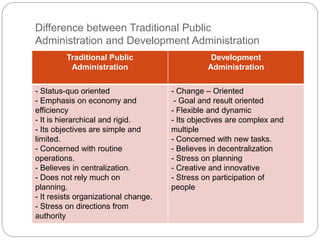
The document also examines different aspects of public administration including administrative theories, applied administration, organizational behavior, and public personnel administration. It explores the scope of public administration in maintaining government operations and facilitating development. Comparative public administration and the differences between traditional and development administration are also summarized