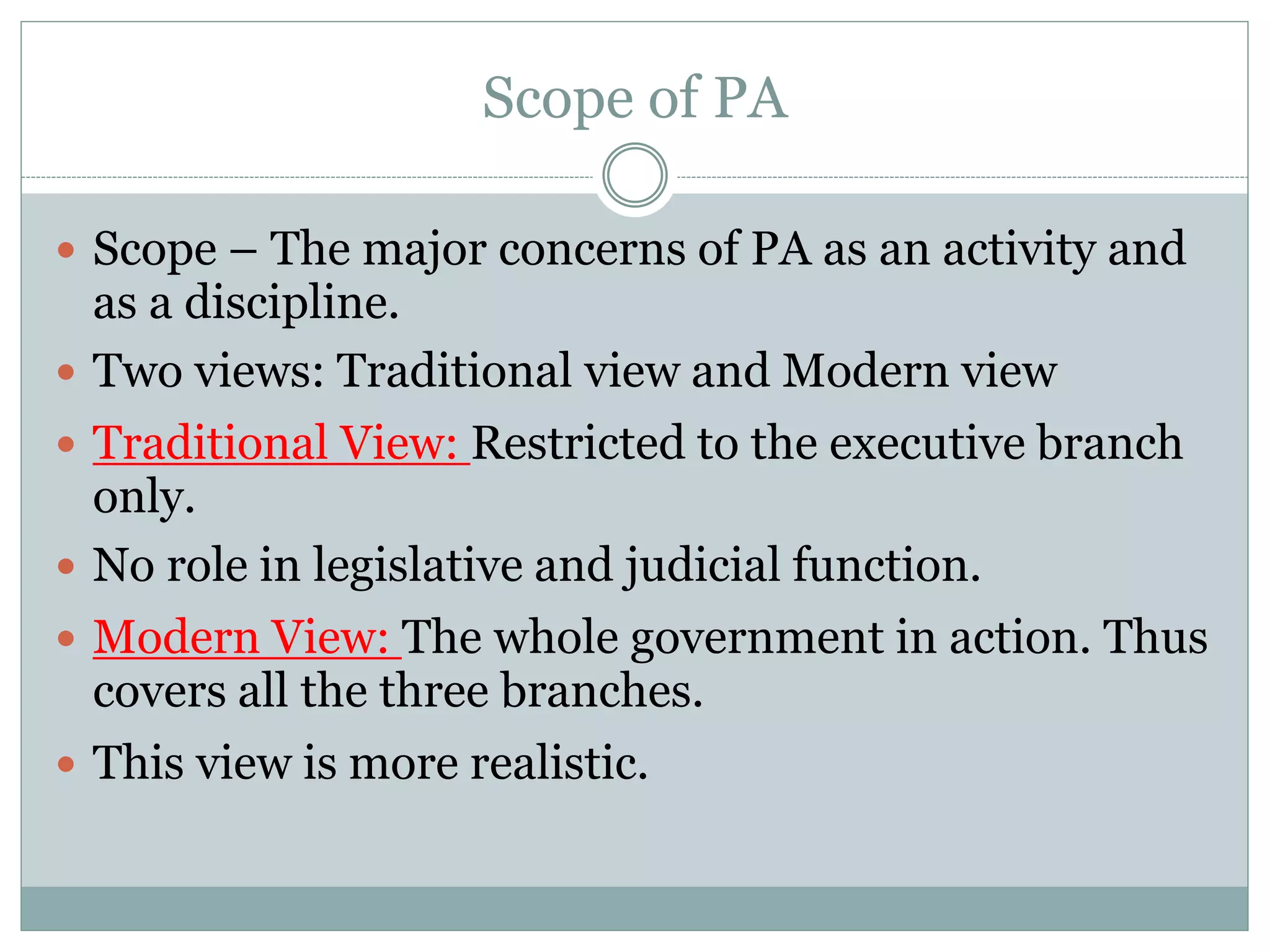
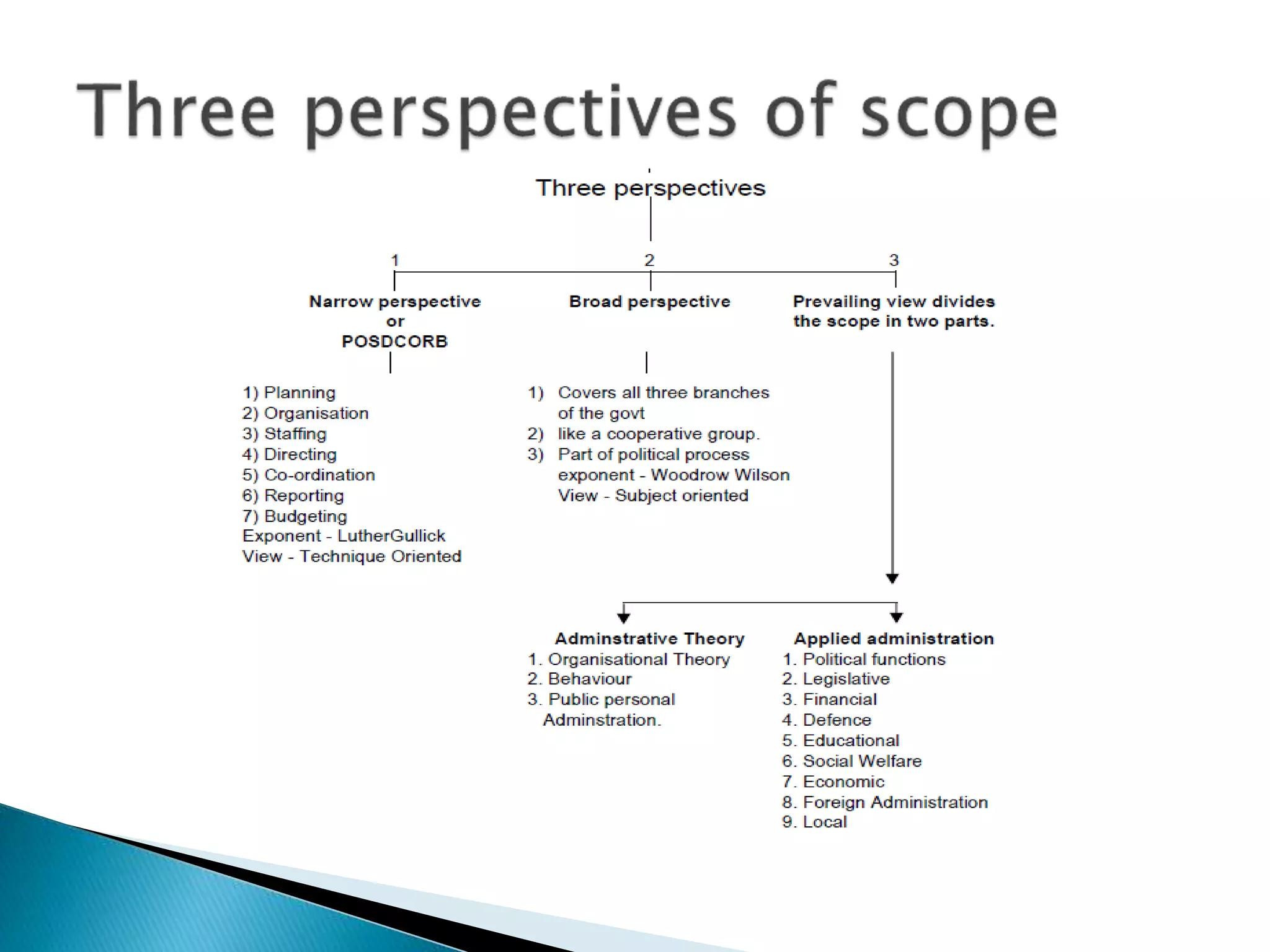
The document provides an overview of public administration, including its definition, significance, and scope, with contributions from key figures such as Woodrow Wilson and Dwight Waldo. It contrasts public administration with private administration, highlighting similarities and differences in their nature, purpose, and organizational structure. The discussion encompasses various theories, methods, and the role of public administration in implementing government policies and services.