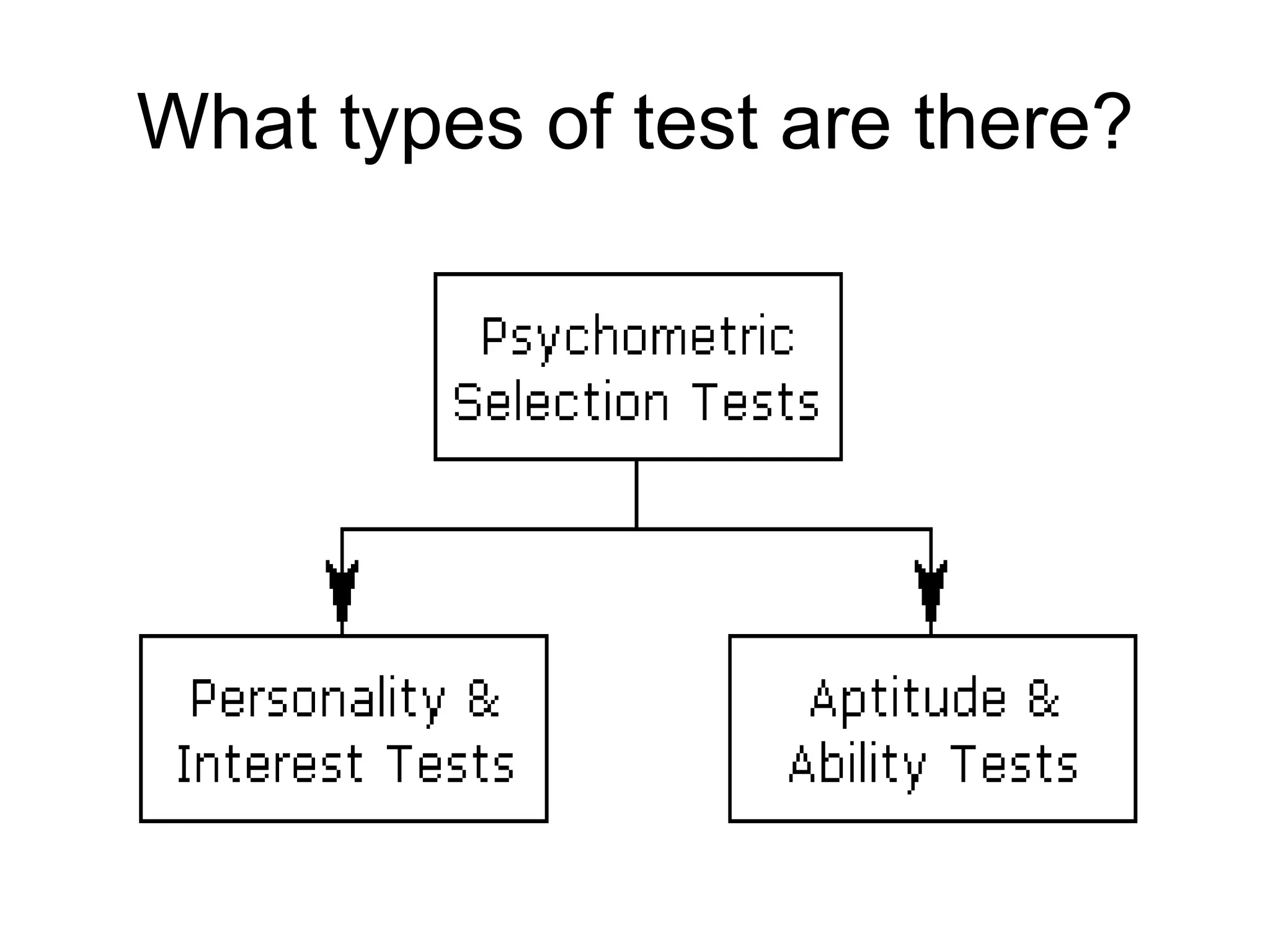
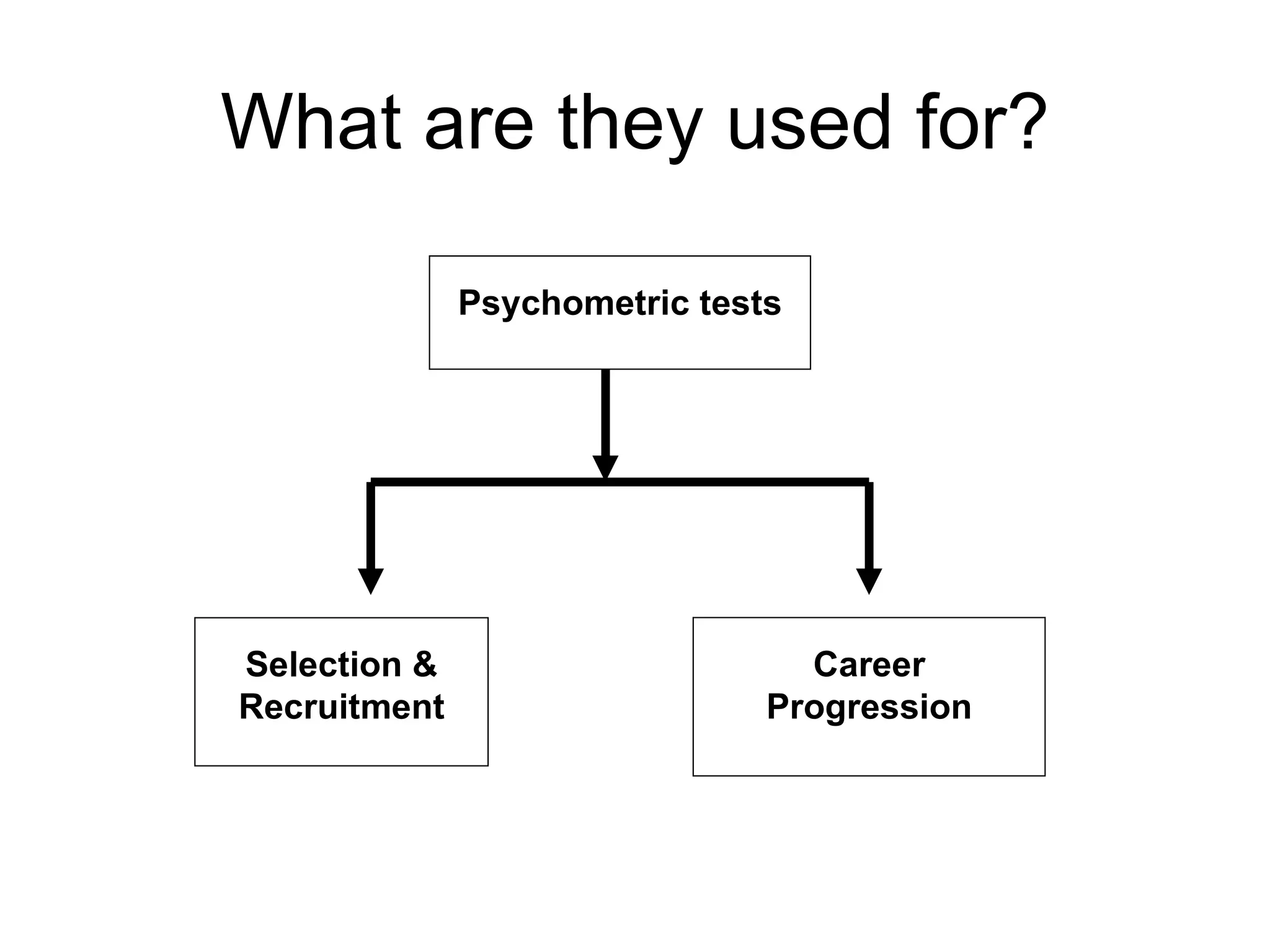
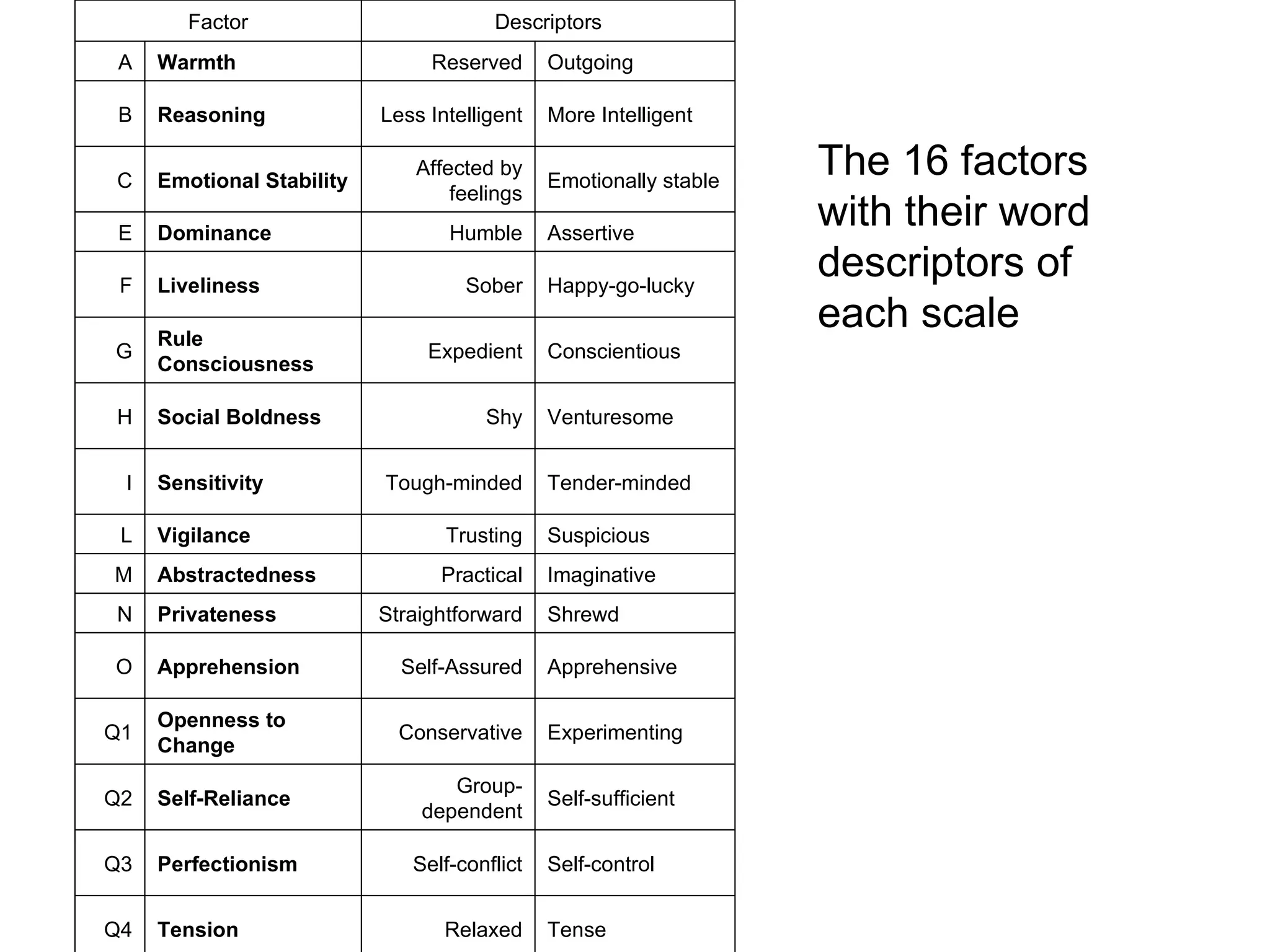
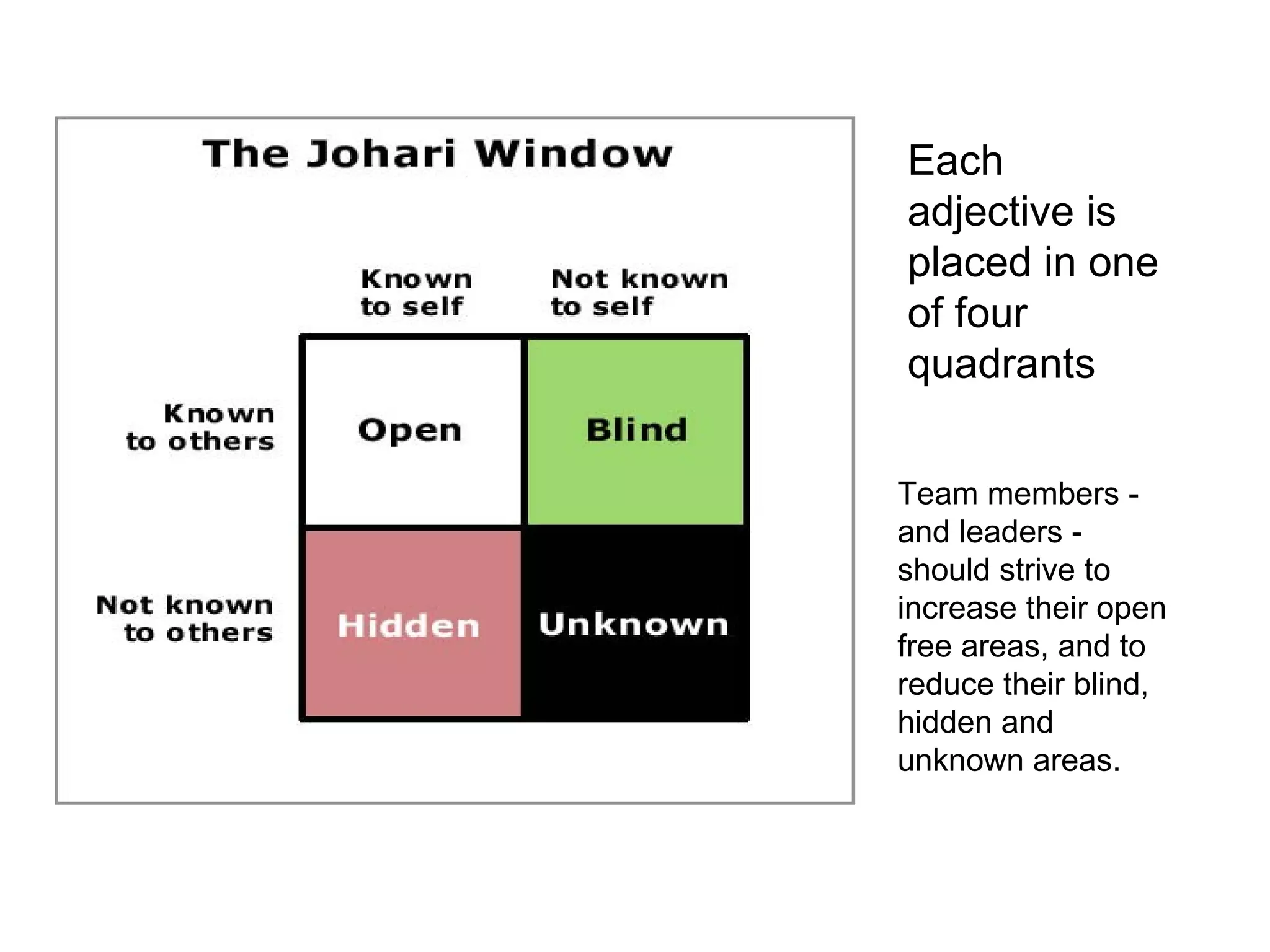
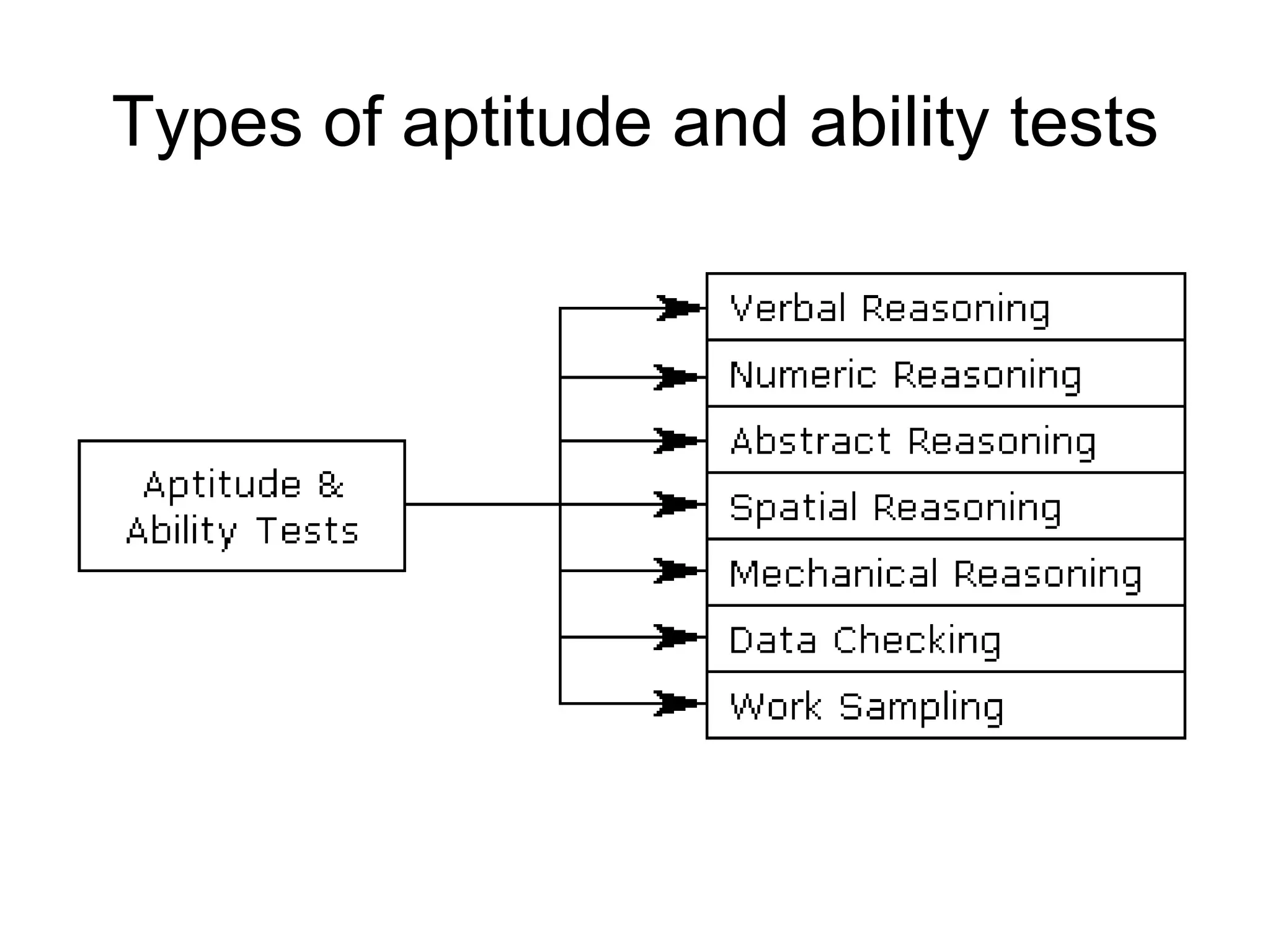
Psychometric tests are standardized assessments used to measure mental abilities, personality, and aptitude, particularly in recruitment and career progression, with widespread use among Fortune 500 companies. These tests aim to objectively predict job performance without discriminating against any group and include various types, like MBTI and DISC, for different organizational needs. Common applications of these tests include individual development, team building, and conflict resolution.