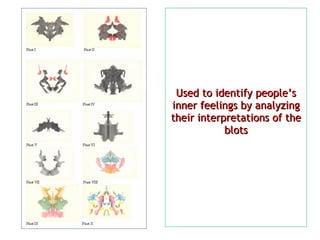
The document provides an overview of psychological tests, which are structured techniques used to assess various mental attributes such as intelligence, personality, and cognitive functioning. It describes different types of tests, including intelligence tests (e.g., Stanford-Binet and Wechsler), personality tests (like MMPI and Rorschach), and neuropsychological assessments, emphasizing their characteristics, methods, and applications in diagnosis and employment. The significance of these tests lies in their ability to compare individual differences, predict life outcomes, and aid in psychological treatment and vocational guidance.














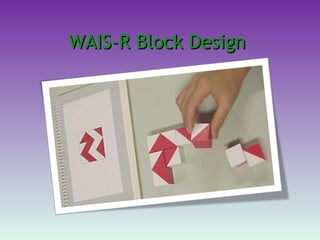

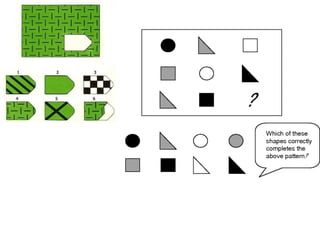
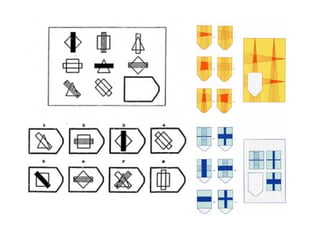



![Personality tests Minnesota Multiphasic Personality Inventory (MMPI] Rorschach Inkblot Test Thematic Apperception Test , or TAT 16PF Questionnaire Performance testing](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/psychassessment-111121232638-phpapp01/85/Psychometric-Assessment-23-320.jpg)