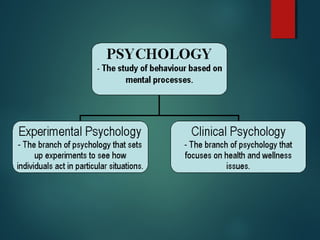
This document discusses different theories in psychology, including:
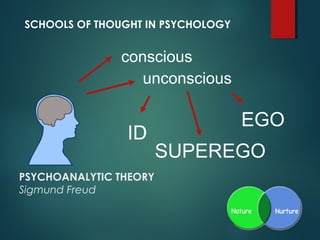
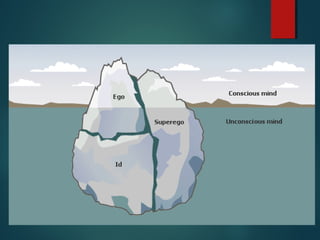
- Psychoanalytic theory proposed by Sigmund Freud which focuses on the conscious, unconscious, id, ego, and superego.
- Learning theory which suggests that most human behavior is learned through conditioning like Ivan Pavlov's classical conditioning experiments with dogs. Behaviorists like John Watson and B.F. Skinner studied observable behavior and its consequences.
- Different schools of thought around self-assessment questions like whether humans are rational or irrational and whether nature or nurture has a greater influence on behavior.