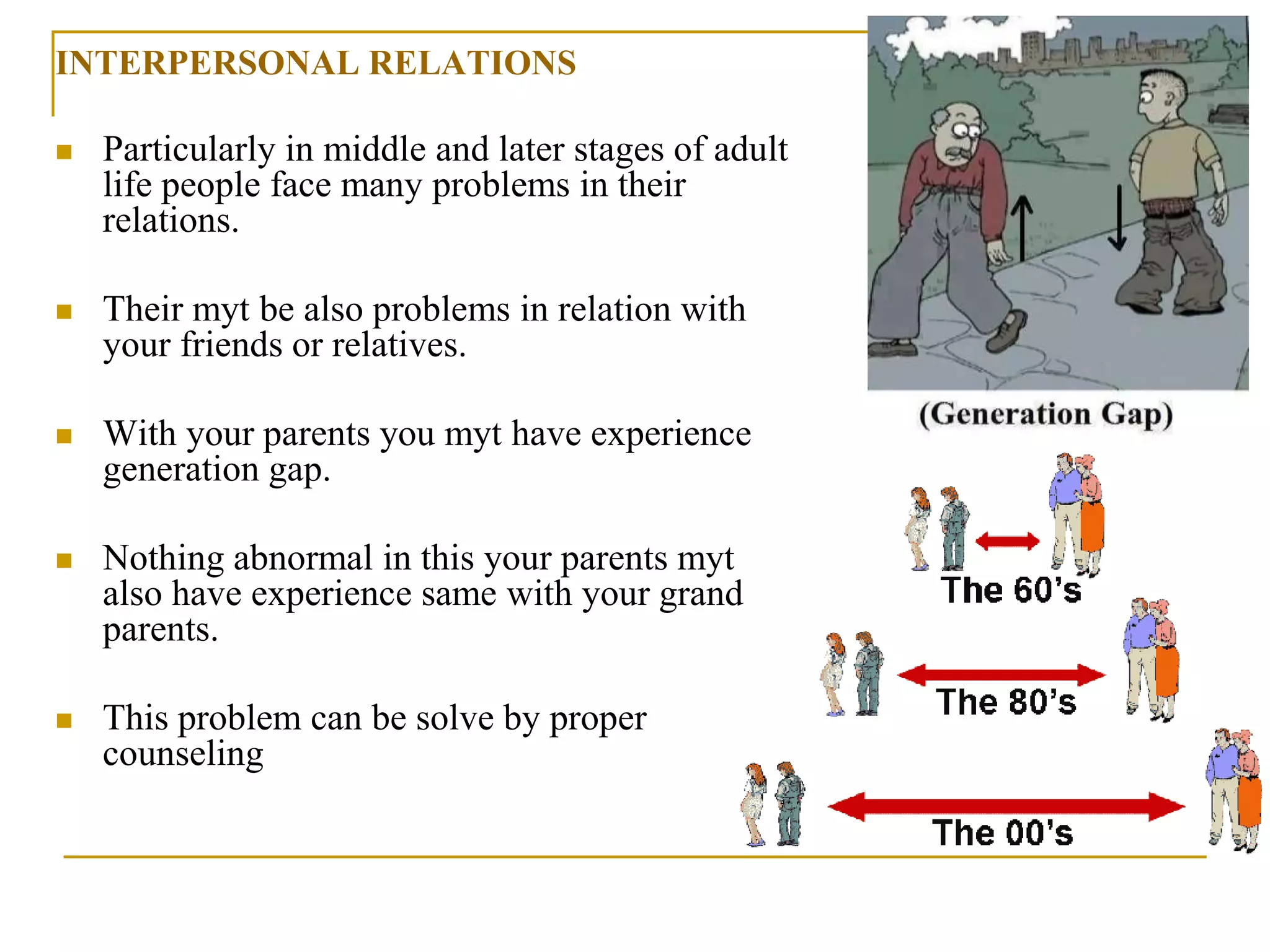
The document provides an overview of industrial psychology. It begins by defining psychology as the study of the mind and behavior. It then discusses the Hawthorne experiments conducted in the 1920s, which found that increased productivity in workers was due more to feeling noticed rather than changes in illumination. The document outlines the major subfields of psychology, including basic areas like biological psychology and applied areas like industrial psychology. Industrial psychology focuses on applying psychological principles to problems in business and industry, with the goal of improving worker satisfaction, productivity and relationships. It operates using methods like surveys, observation and clinical procedures to diagnose issues and develop intervention strategies.