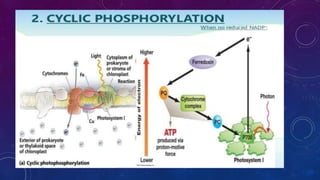
This document presents a topic on cyclic photophosphorylation. It begins with an introduction to photophosphorylation and defines cyclic photophosphorylation. There are two types of photophosphorylation: cyclic and non-cyclic. Cyclic photophosphorylation involves the same excited electron returning to the excited chlorophyll, producing one ATP molecule. The mechanism involves an electron being energized in photosystem I and passing through an electron transport system before returning to the reaction center. This releases energy to produce ATP. The steps involve an electron moving from P700 to acceptors to the cytochrome complex and back to P700, producing one ATP via chemiosmosis.